List of Diseases
Diseases can have a profound impact on an individual’s life and can range from minor illnesses to life-threatening conditions. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive list of diseases, including their types, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. This list of diseases groups together the main familiese of diseases. Disease is an alteration in the functions or health of a living organism.
We speak as well of disease, referring to all the alterations in health, as of a disease, which then designates a particular entity characterized by causes, symptoms, development and specific therapeutic possibilities.
A patient is a person suffering from a disease, whether it is determined or not. When it is the subject of medical care, we speak of a patient.
Health and disease are linked to biological processes and to interactions with the social and environmental environment. Generally, disease is defined as an entity opposed to health, the negative effect of which is due to an alteration or disharmonization of a system at any level (molecular, bodily, mental, emotional, etc.) of the state. physiological or morphological considered as normal, balanced or harmonious. We can speak of faulty homeostasis.
This list of diseases groups together the main families of diseases
- List of dermatological diseases
- List of cardiovascular diseases
- List of respiratory diseases
- Cancer list
- List of eye diseases and disorders
- List of genetic or hereditary diseases (identified gene, unidentified gene)
- List of infectious diseases
- Mental illness (mood disorders, personality disorders)
- List of rare diseases
List of dermatological diseases
Signs can include itching, pain, and hyperhidrosis. Physical signs include: vitropression effect, Nikolsky’s sign, Wood’s lamp fluorescence, and Blaschko lines.
Dermatological investigations include skin biopsy.
Dermatological lesions
Atrophies: This refers to a thinning or shrinkage of the skin. Common examples of atrophies include striae, which are stretch marks, and senile purpura, which are bruises that occur in older individuals with thin skin.
Blisters or Bubbles: These are fluid-filled sacs that form on the surface of the skin. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including friction, burns, and certain medical conditions.
Dyschromia: This refers to any change in skin color. Common examples of dyschromia include hyperpigmentation, which is an increase in skin color, and hypopigmentation, which is a decrease in skin color.
Erythema (and exanthema): Erythema refers to redness of the skin, while exanthema refers to a widespread rash. These can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection, allergy, and autoimmune conditions.
Keratosis: This refers to the overgrowth of keratin, a protein found in the skin. Common examples of keratosis include actinic keratosis, which is caused by sun damage, and seborrheic keratosis, which is a benign growth that often appears as a waxy, stuck-on lesion.
Macules: These are flat, discolored spots on the skin. Examples of macules include freckles and age spots.
Nodules: These are solid, raised lesions that can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection, inflammation, and tumors.
Papules: These are small, raised bumps on the skin. Examples of papules include acne and warts.
Purpuras: These are bruises caused by bleeding under the skin. They can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma and certain medical conditions.
Pustules: These are raised bumps on the skin that are filled with pus. Examples of pustules include acne and impetigo.
Scales: These are flakes of dead skin that can be caused by a variety of factors, including dry skin and psoriasis.
Sclerosis: This refers to a hardening of the skin. Common examples of sclerosis include scleroderma, which is an autoimmune condition that causes hardening and tightening of the skin, and keloids, which are raised scars that form after injury.
Tumors: These are abnormal growths of cells that can be benign or malignant. Examples of skin tumors include basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Ulcerations: These are open sores on the skin that can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection, injury, and certain medical conditions.
Vegetations or Condylomas: These are wart-like growths on the skin that are caused by certain viruses, including human papillomavirus (HPV).
Vesicles: These are small, fluid-filled sacs that can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection and allergic reactions. Examples of vesicles include herpes simplex virus (HSV) and chickenpox.
Dermatological pathologies
Here are some the explanations and details for each of the dermatological pathologies:
Acanthosis nigricans
Is a skin condition that causes dark, thick, and velvety patches of skin, typically on the neck, armpits, and groin area. It is associated with insulin resistance, obesity, and hormonal disorders. Treatment includes managing underlying conditions, such as diabetes or obesity, as well as topical creams and laser therapy to improve the appearance of the affected areas.
Achromia
Also known as hypopigmentation, is a condition characterized by the loss of pigment in the skin, resulting in white or lighter colored patches. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, autoimmune disorders, and skin damage. Treatment options may include topical medications, phototherapy, or skin grafting.
Symptoms: Acanthosis nigricans is a skin condition characterized by dark, thick, and velvety patches of skin that usually develop on the neck, armpits, and groin. It may also cause mild itching, and in rare cases, the affected skin may become thicker and harder.
Causes: Acanthosis nigricans is often associated with insulin resistance, obesity, and hormonal imbalances. It may also be a side effect of certain medications, such as oral contraceptives or corticosteroids. Rarely, it can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as cancer or autoimmune disorders.
Treatment: Treatment for acanthosis nigricans may involve addressing the underlying medical condition, if present. Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and increased physical activity, can also be helpful in managing insulin resistance and obesity-related acanthosis nigricans. Topical medications, such as retinoids and keratolytics, can improve the appearance of affected skin.
Acne
Is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. It is most commonly associated with hormonal changes during puberty, but can also be caused by stress, certain medications, and other underlying conditions. Treatment options may include topical or oral medications, chemical peels, and light therapy. Proper skin care, such as gentle cleansing and avoiding certain cosmetics, can also help manage acne.
Symptoms: Acne is a common skin condition characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads on the face, neck, chest, and back. It may also cause inflammation, redness, and scarring.
Causes: Acne is caused by a combination of factors, including excess oil production, clogged hair follicles, and bacterial overgrowth. Hormonal changes, certain medications, and diet may also contribute to the development of acne.
Treatment: Treatment for acne may involve topical medications, such as benzoyl peroxide and retinoids, or oral medications, such as antibiotics or hormonal therapies. In severe cases, procedures such as chemical peels or laser therapy may be recommended.
Alopecia
Is a condition that causes hair loss, often in patches on the scalp, but it can also affect other areas of the body. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications. Treatment options may include topical or oral medications, corticosteroid injections, and hair transplantation surgery.
Symptoms: Alopecia is a condition that causes hair loss on the scalp or other areas of the body. It may cause bald patches or thinning hair, and in rare cases, complete hair loss.
Causes: Alopecia can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, autoimmune disorders, and hormonal imbalances. It may also be a side effect of certain medications or a complication of other medical conditions.
Treatment: Treatment for alopecia depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, topical medications, such as minoxidil, may be used to promote hair growth. Oral medications, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, may also be recommended. In some cases, hair transplant surgery may be an option.
Amyloidosis
Is a rare condition that occurs when an abnormal protein called amyloid builds up in various tissues and organs, including the skin. It can cause a variety of skin symptoms, such as itching, bruising, and a thickened or waxy appearance. Treatment options may include medications to reduce amyloid production, as well as supportive therapies to manage symptoms.
Symptoms: Amyloidosis is a rare condition that occurs when abnormal proteins, called amyloid, build up in various organs and tissues, including the skin. Skin-related symptoms may include thickened or waxy skin, purple or red patches, and easy bruising or bleeding.
Causes: Amyloidosis can be caused by genetic mutations, or it may develop as a complication of other medical conditions, such as multiple myeloma or rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment: managing underlying health conditions, chemotherapy, and stem cell transplantation.
Angiodermatitis
Is a skin condition that occurs when small blood vessels in the skin become inflamed and leak fluid into surrounding tissues. This can lead to redness, swelling, and the formation of small blisters or sores. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as allergies, infections, and exposure to irritants. Treatment options may include topical or oral medications, as well as identifying and avoiding triggers.
Symptoms: redness, swelling, and itching in the affected area, and the development of small bumps or blisters.
Causes: allergic reactions, insect bites, exposure to irritants or toxins, and autoimmune disorders.
Treatment: identifying and avoiding triggers, topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, and immunomodulators.
Stellate angioma
Also known as spider angioma or spider nevus, is a benign skin condition that causes small, red, spider-like lesions to form on the skin. They are typically found on the face, neck, and upper body, and are caused by dilated blood vessels. Treatment may not be necessary unless the lesions are causing cosmetic concerns or bleeding, in which case they can be treated with lasers or electrosurgery.
Symptoms: small, red or purple bumps on the skin that appear in a star-like pattern.
Causes: dilated blood vessels near the skin’s surface.
Treatment: typically not required as the condition is benign, but may be treated with laser therapy or electrocautery for cosmetic purposes.
Staphylococcal anthrax
Is a rare but serious bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. It can cause a variety of symptoms, including fever, chills, skin lesions, and in severe cases, sepsis. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and supportive therapies.
Symptoms: painful, raised blisters or ulcers that may be black in the center, fever, and fatigue.
Causes: infection with the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. Treatment: antibiotics such as penicillin or clindamycin, and surgical debridement of infected tissue in severe cases.
Aphthosis
Is a condition that causes recurrent, painful ulcers to form in the mouth, often on the tongue or inside the cheeks. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as stress, injury, and certain medications. Treatment options may include topical or oral medications, as well as identifying and avoiding triggers.
Symptoms: recurrent, painful sores or ulcers in the mouth or genital area. Causes: genetics, stress, trauma, infection, and autoimmune disorders. Treatment: topical or oral anti-inflammatory medications, antiviral medications, and managing underlying conditions.
Atrophy
Is a skin condition that occurs when the skin thins and loses its elasticity, leading to a sagging or wrinkled appearance. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as aging, sun damage, and certain medical conditions. Treatment options may include topical or oral medications, as well as cosmetic procedures to improve the appearance of the affected areas.
Symptoms: thinning and shrinking of the skin, leading to wrinkles, easy bruising, and decreased elasticity. Causes: aging, prolonged use of corticosteroids, sun exposure, and autoimmune disorders. Treatment: managing underlying conditions, discontinuing the use of corticosteroids, and using moisturizers and sunscreen to protect the skin.
Balanitis
Is a condition that causes inflammation and swelling of the head of the penis. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as poor hygiene, skin conditions, and certain medical conditions. Treatment options may include topical or oral medications, as well as improving hygiene and avoiding irritants. In severe cases, circumcision may be recommended.
Symptoms: inflammation, redness, swelling, and itching of the head of the penis. Causes: poor hygiene, irritation from chemicals or soaps, and infection with bacteria or fungi. Treatment: good hygiene practices, topical antifungal or antibiotic medications, and managing underlying conditions.
Behçet (disease of)
Behçet’s disease is a rare inflammatory disorder that affects the blood vessels of the body. It is characterized by recurrent oral and genital ulcers, skin lesions, and inflammation in the eyes. The exact cause of the disease is unknown, but it is thought to be related to the immune system. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Symptoms: recurrent oral and genital ulcers, skin lesions, and inflammation of the eyes and other organs. Causes: unknown, but may involve genetic and environmental factors. Treatment: managing symptoms with medications such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics, as well as avoiding triggers such as stress and certain foods.
Bowen’s disease
Bowen’s disease, also known as squamous cell carcinoma in situ, is a precancerous skin condition that appears as a red, scaly patch on the skin. It is caused by sun exposure and may develop into a type of skin cancer known as squamous cell carcinoma. Treatment options include surgery, cryotherapy, or topical chemotherapy.
Symptoms: recurrent oral and genital ulcers, skin lesions, and inflammation of the eyes and other organs.
Causes: unknown, but may involve genetic and environmental factors.
Treatment: managing symptoms with medications such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics, as well as avoiding triggers such as stress and certain foods.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, affecting the cells that produce new skin cells. It typically appears as a small, raised, pink or pearly bump on the skin and may have a central depression. The primary cause of basal cell carcinoma is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, or topical chemotherapy.
Symptoms: a pearly or waxy bump, a flat, flesh-colored or brown scar-like lesion, a bleeding or scabbing sore that heals and recurs, and a pink growth with a slightly elevated border and a crusted indentation in the center.
Causes: overexposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds, exposure to radiation, and certain genetic conditions.
Treatment: surgical removal, cryotherapy, radiation therapy, and topical medications.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that affects the cells that make up the outer layer of the skin. It usually appears as a red, scaly patch or raised bump on the skin and can be caused by long-term sun exposure, exposure to toxic substances, or a weakened immune system. Treatment options depend on the size, location, and stage of the cancer and may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Symptoms: a firm, red nodule, a flat lesion with a scaly or crusted surface, and a new sore or raised area on an old scar or ulcer. Causes: overexposure to UV radiation, exposure to radiation, and long-term exposure to certain chemicals. Treatment: surgical removal, radiation therapy, topical medications, and in some cases, chemotherapy.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus. It can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, mouth, throat, and genitals. Symptoms of candidiasis on the skin include red, itchy patches or bumps that may have a white, cheesy discharge. Treatment options include antifungal medications and topical creams.
Symptoms: red, itchy, and painful rashes with surrounding redness, white patches in the mouth or throat, and itching and burning sensations in the genital area. Causes: overgrowth of the Candida fungus due to factors such as weakened immune system, antibiotics, pregnancy, diabetes, and certain medications. Treatment: antifungal medications such as topical creams, oral medications, and in severe cases, intravenous medications.
Soft chancroid
Soft chancroid, also known as chancroid, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi. It usually appears as a painful, open sore on the genitals or around the anus and can be accompanied by swollen lymph nodes in the groin. Treatment options include antibiotics and wound care.
Symptoms: painful, red, and swollen sores or ulcers in the genital area, with pus or blood-filled bumps. Causes: infection with the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi through sexual contact. Treatment: antibiotics such as azithromycin or ceftriaxone, and good hygiene practices.
Symptoms: painful, red, and swollen sores or ulcers in the genital area, with pus or blood-filled bumps. Causes: infection with the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi through sexual contact. Treatment: antibiotics such as azithromycin or ceftriaxone, and good hygiene practices.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that typically affects the face, causing redness, flushing, and acne-like pimples. It may also cause dryness, burning, stinging, and visible blood vessels. The cause of rosacea is not fully understood, but it may involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. There is no cure for rosacea, but it can be managed with treatments such as topical or oral antibiotics, azelaic acid, and laser therapy.
Symptoms:
- Facial redness
- Swollen, red bumps
- Eye problems like dryness, irritation, and redness
- Enlarged nose
Causes:
- The exact cause is unknown, but some factors that can trigger or worsen it are:
Genetics - Environmental factors like sun exposure, hot and cold weather, stress, and spicy foods
- Abnormal immune system response to bacteria
Treatment:
- Topical creams and gels like azelaic acid, metronidazole, and ivermectin
- Oral antibiotics like tetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline
- Laser therapy to reduce redness and enlarged blood vessels
- Avoiding triggers like sun exposure and certain foods
Darier’s disease
Darier’s disease, also known as keratosis follicularis, is a rare genetic disorder that affects the skin and nails. It is caused by a mutation in a specific gene that results in abnormal keratinization, leading to scaly papules and plaques that are greasy, malodorous, and prone to bacterial and fungal infections. Darier’s disease can also cause nail abnormalities, such as ridging, pitting, and thickening. Treatment options include topical and systemic retinoids, antibiotics, and phototherapy.
Symptoms: thick, scaly, crusty bumps or patches on the skin, foul-smelling skin, nail changes, warty growths on the scalp, forehead, and upper arms. Causes: genetic mutations that affect calcium regulation within cells, resulting in abnormal keratinization and differentiation of cells in the skin. Treatment: Topical or oral retinoids, topical or oral antibiotics, acitretin, and photodynamic therapy.
Degos (disease)
Degos disease, also known as malignant atrophic papulosis, is a rare and potentially life-threatening skin disorder that primarily affects the small blood vessels in the skin, brain, and gastrointestinal tract. It is characterized by the appearance of small, raised, red or purple papules on the skin that develop into depressed, atrophic scars with a white center. In addition to skin lesions, Degos disease can cause neurological and gastrointestinal symptoms, such as headache, confusion, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. The cause of Degos disease is unknown, and there is no cure or specific treatment. Treatment is focused on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Symptoms: red or purple papules, typically with white centers, which develop into plaques with a central depression, skin ulcerations, and abdominal pain. Causes: unknown, but possibly autoimmune or thrombotic. Treatment: There is no known cure or effective treatment. Some treatments have been tried, including immunosuppressive agents, anticoagulants, and antiplatelet drugs, but none have been shown to be consistently effective.
Chronic actinic dermatitis
Chronic actinic dermatitis (CAD) is a rare and chronic skin condition that develops in response to long-term exposure to sunlight. It is characterized by red, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin that are typically located on sun-exposed areas such as the face, neck, arms, and hands. CAD can cause significant discomfort and impaired quality of life. The exact cause of CAD is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Treatment options include topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and phototherapy. Sun protection is also essential to prevent the progression of the disease.
Symptoms: severe itching, redness, and thickening of the skin on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, neck, and hands, which may become crusted and scaly. Causes: a reaction to sunlight or other sources of ultraviolet radiation in people with a genetic predisposition to photosensitivity. Treatment: Topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, topical tacrolimus, and oral immunosuppressive agents.
Fixed pigmented erythema
Is a skin condition characterized by reddish-brown patches or spots that remain unchanged over time. It usually affects the face, neck, and trunk. It can occur due to a variety of causes, such as exposure to sunlight, certain medications, and genetic factors.
Symptoms: reddish-brown patches on the skin that do not change size or color with time, often found on the face or neck. Causes: unknown, but possibly a reaction to medications or chemicals, sun exposure, or genetics. Treatment: Topical or oral corticosteroids, topical tacrolimus, and topical retinoids.
Erythema multiforme
Is a type of hypersensitivity reaction of the skin and mucous membranes that can be triggered by infections, medications, or other factors. It usually presents as red, raised, and sometimes blistering lesions on the skin that can be painful or itchy. The lesions typically have a characteristic target-like appearance, with a red outer ring and a paler center.
Symptoms:
Red, raised skin lesions, often with a target-like appearance, on the hands, feet, face, and trunk, accompanied by fever and flu-like symptoms.
Causes:
most commonly caused by a reaction to medications, but can also be triggered by infections or autoimmune diseases.
Treatment:
Discontinuing the causative agent if drug-induced, supportive care, and symptomatic treatment such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, and pain relievers. Severe cases may require hospitalization and intravenous immunoglobulin therapy.
Erythroderma
Is a rare skin condition characterized by widespread redness and scaling of the skin. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including underlying skin diseases, medications, and infections. The condition can be accompanied by itching, pain, and fever. Erythroderma is a medical emergency that requires prompt evaluation and treatment.
Symptoms:
Erythroderma is a rare skin disorder characterized by redness and scaling of the entire skin surface. The skin may also be thickened, itchy, and painful. In severe cases, there may be blistering, oozing, or crusting.
Causes:
Erythroderma can be caused by a variety of factors including allergic reactions, drug reactions, infections, or pre-existing skin conditions such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Treatment:
Treatment for erythroderma depends on the underlying cause. In many cases, hospitalization may be required to manage severe symptoms. Treatment options may include topical or oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or antibiotics if an infection is present.
Erythrasma
Is a bacterial skin infection caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum. It usually affects moist areas of the skin, such as the groin, armpits, and between the toes. The infection can cause red, scaly patches on the skin that may be itchy or painful. Treatment typically involves the use of topical or oral antibiotics.
Symptoms:
Erythrasma is a bacterial infection of the skin that typically affects moist areas of the body such as the groin, armpits, and toes. It is characterized by red, scaly patches that may itch or burn.
Causes:
Erythrasma is caused by the bacteria Corynebacterium minutissimum. Factors that increase the risk of developing erythrasma include warm and humid environments, obesity, diabetes, and poor hygiene.
Treatment:
Erythrasma can be treated with topical or oral antibiotics. In addition, keeping the affected area clean and dry can help prevent recurrence.
Pressure sore
Also known as a bed sore or pressure ulcer, a pressure sore is a type of skin injury that occurs due to prolonged pressure on the skin. It usually develops on bony areas such as the hips, back, elbows, and heels. It is commonly seen in individuals who are bedridden or have difficulty moving, and can range from a mild redness to a deep, open wound.
Symptoms:
A pressure sore, also known as a bedsore or decubitus ulcer, is a skin injury that occurs when prolonged pressure on the skin compresses underlying tissues. The skin may appear red, swollen, or tender and may eventually develop an open sore or blister.
Causes:
Pressure sores can develop in people who are bedridden or confined to a wheelchair for extended periods of time. Factors that increase the risk of developing pressure sores include immobility, malnutrition, and incontinence.
Treatment:
Treatment for pressure sores depends on the severity of the injury. Mild cases may be treated with topical ointments or dressings. More severe cases may require debridement (removal of dead tissue) or surgical intervention.
Fiessinger-Leroy-Reiter (syndrome)
This is a rare autoimmune disorder that can affect the skin, joints, and eyes. It is characterized by a triad of symptoms that include arthritis, urethritis, and conjunctivitis. Skin involvement in the form of red, scaly patches and painful nodules can also occur.
Folliculitis: This is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become infected with bacteria, fungi, or viruses. It can appear as small, red bumps that are often itchy or painful, and may contain pus. Folliculitis can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows, including the scalp, face, neck, chest, back, and legs.
Symptoms:
Fiessinger-Leroy-Reiter syndrome is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects multiple systems of the body. Symptoms may include joint pain, eye inflammation, skin rashes, and genital ulcers.
Causes:
The exact cause of Fiessinger-Leroy-Reiter syndrome is unknown, but it is thought to be triggered by an infection in people who are genetically predisposed to the condition.
Treatment:
Treatment for Fiessinger-Leroy-Reiter syndrome may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to manage symptoms and prevent joint damage. Antibiotics may also be prescribed if there is evidence of an underlying infection.
Boil
A boil, also known as a furuncle, is a painful, pus-filled lump that develops on the skin. It usually starts as a red, tender bump and gradually becomes larger and more painful as it fills with pus. Boils can occur anywhere on the body, but are most commonly seen on the face, neck, armpits, buttocks, and thighs.
Symptoms:
A boil, also known as a furuncle, is a painful, pus-filled bump that forms beneath the skin. Boils can occur anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, armpits, and buttocks.
Causes:
Boils are caused by a bacterial infection of a hair follicle. Factors that increase the risk of developing boils include poor hygiene, compromised immune system, and skin injuries.
Treatment:
Treatment for boils may include warm compresses to encourage drainage, topical or oral antibiotics to treat the infection, and in some cases, surgical drainage of the abscess. It is important to keep the affected area clean and avoid picking at the boil to prevent further infection. In some cases, recurrent boils may require further medical evaluation to rule out underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or immune system disorders.
Scabies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by a tiny mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. It is characterized by intense itching and a rash that often appears as small, red bumps or blisters. Scabies is usually spread through close physical contact with an infected person, and can affect people of all ages.
Symptoms:
Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by a mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. Symptoms include intense itching, especially at night, and a rash with small red bumps and blisters. The rash may appear on the skin between fingers, wrists, elbows, armpits, waistline, genitals, and buttocks.
Causes:
Scabies is caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows into the skin to lay eggs. It is highly contagious and can be transmitted through close personal contact, such as sexual contact or prolonged skin-to-skin contact.
Treatment:
Treatment for scabies usually involves the use of prescription-strength creams or lotions that kill the mites and eggs. Antihistamines or topical steroids can help relieve itching. All clothing, bedding, and towels should be washed in hot water to kill any mites or eggs.
Gangrene
This is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a part of the body loses its blood supply and begins to die. It most commonly affects the fingers, toes, and limbs, and can be caused by a number of factors including injury, infection, and poor circulation. Symptoms of gangrene may include severe pain, swelling, and discoloration of the affected area.
Symptoms: Gangrene is a serious condition that occurs when a body tissue dies due to a lack of blood supply. Symptoms include pain, swelling, redness, blisters, and the skin may turn black, blue, or green.
Causes: Gangrene can be caused by a variety of factors, including diabetes, peripheral arterial disease, atherosclerosis, and injury to the skin.
Treatment: Treatment for gangrene typically involves removing the affected tissue and treating the underlying cause. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to amputate the affected limb or tissue. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to treat any underlying infections.
Granuloma annulare
This is a chronic inflammatory condition that results in the formation of firm, round bumps or lesions on the skin, typically on the hands and feet. The exact cause of granuloma annulare is unknown, but it may be related to a genetic predisposition or an immune system response to an infection or injury.
Symptoms:
Granuloma annulare is a chronic skin condition characterized by small, firm, raised bumps on the skin that form rings. The bumps may be skin-colored or reddish-purple and usually appear on the hands, feet, elbows, or knees. The rash is usually asymptomatic, but itching or burning sensations may occur.
Causes:
The exact cause of granuloma annulare is unknown, but it may be related to an immune system dysfunction. It can be associated with thyroid disease, diabetes, and HIV.
Treatment:
Treatment for granuloma annulare may involve topical or oral corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, or cryotherapy (freezing the affected area with liquid nitrogen). In some cases, the rash may resolve on its own without treatment.
Herpes
Herpes is a viral infection that causes painful blisters or sores on the skin, usually around the mouth or genitals. The herpes virus can be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, and there is no cure for the infection, although antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Symptoms:
Herpes is a common viral infection that causes painful blisters or sores on the mouth, lips, or genitals. The blisters may break open, leaving tender ulcers that can take several weeks to heal. Flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache, and swollen lymph nodes, may also occur.
Causes:
Herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and is spread through direct contact with an infected person’s skin or bodily fluids, such as saliva or genital secretions.
Treatment:
Treatment for herpes includes antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir, which can reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Pain relievers and topical creams or ointments may also be used to relieve discomfort and speed up healing.
Ichthyosis
This is a group of genetic disorders that affect the skin’s ability to shed dead cells, leading to the buildup of thick, scaly patches of skin. There are many types of ichthyosis, each with varying degrees of severity and onset, and treatment may involve moisturizing creams, topical or oral medications, or light therapy.
Symptoms: Ichthyosis is a group of genetic skin disorders that result in dry, scaly, and thickened skin. Symptoms vary depending on the type of ichthyosis, but may include scales that are white, gray, or brown in color, itchy and dry skin, and cracks or splits in the skin.
Causes: Ichthyosis is caused by genetic mutations that affect the production of proteins that are essential for skin development and maintenance. It can be inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner.
Treatment: Treatment for ichthyosis typically involves managing the symptoms, including keeping the skin moisturized with emollients, using topical retinoids to reduce scaling, and taking oral retinoids or other medications to improve skin texture and reduce itching. In severe cases, phototherapy or other advanced treatments may be necessary.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial infection that causes red, itchy sores or blisters on the skin, typically around the mouth and nose. The infection is highly contagious and can spread easily through close contact, so it is important to keep the affected area clean and avoid scratching the sores.
Symptoms: Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that commonly affects young children. Symptoms include red, oozing sores that eventually burst and leave a yellow-brown crust. The sores may be itchy, and lymph nodes in the affected area may become swollen.
Causes: Impetigo is caused by a bacterial infection, usually Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. It can be spread through close contact, such as touching the infected skin, sharing personal items like towels, or from contact with infected clothing or bedding.
Treatment: Treatment for impetigo typically involves antibiotic creams or oral antibiotics. The sores should be kept clean and covered with gauze or a dressing to prevent spreading. All clothing and bedding should be washed in hot water and dried on high heat to kill any bacteria.
Intertrigo
Intertrigo is a skin condition that occurs when skin folds rub against each other, leading to irritation, inflammation, and infection. The condition is common in overweight individuals and those with diabetes or other medical conditions that affect the skin’s ability to heal, and treatment may involve keeping the affected area dry, using topical or oral medications, or surgery in severe cases.
Symptoms: Intertrigo is a common skin condition that occurs in areas where the skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. Symptoms include redness, itching, burning, and sometimes, painful cracks or blisters.
Causes: Intertrigo is caused by a combination of factors, including moisture, heat, and friction. It can be exacerbated by obesity, diabetes, poor hygiene, and certain medications.
Treatment: Treatment for intertrigo involves keeping the affected area clean and dry. Over-the-counter creams or ointments containing zinc oxide or hydrocortisone may help relieve symptoms. Severe cases may require prescription-strength topical or oral medications.
Actinic keratosis
A precancerous skin condition that results from long-term exposure to sunlight. It appears as rough, scaly patches on the skin, usually on sun-exposed areas such as the face, scalp, and arms. It is most commonly seen in fair-skinned individuals over the age of 40.
Symptoms: Actinic keratosis is a skin condition that results from prolonged sun exposure. Symptoms include rough, scaly patches of skin that may be pink, red, or brown. The patches may be itchy or tender and may bleed if scratched or rubbed.
Causes: Actinic keratosis is caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. It is most common in fair-skinned individuals and those who live in sunny areas.
Treatment: Treatment for actinic keratosis may involve cryotherapy (freezing the affected area with liquid nitrogen), topical chemotherapy, or photodynamic therapy (using a special light to activate a medication that destroys abnormal cells). In some cases, surgical removal may be necessary.
Keratosis pilaris
A common benign skin condition that causes small, rough bumps on the skin. It usually appears on the upper arms, thighs, and buttocks, and may also occur on the face. It is caused by the buildup of keratin, a protein that protects the skin from infections and other harmful substances.
Symptoms: Keratosis pilaris is a common skin condition that causes small, rough bumps on the skin, usually on the arms, thighs, cheeks, or buttocks. The bumps may be white, red, or brown and may be surrounded by dry, flaky skin.
Causes: Keratosis pilaris is caused by an overproduction of keratin, a protein that protects the skin. It is often associated with dry skin and eczema.
Treatment: Treatment for keratosis pilaris involves moisturizing the affected area regularly and using exfoliating creams or scrubs to remove dead skin cells. In some cases, topical retinoids or corticosteroids may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and improve the appearance of the skin.
Leishmaniasis
A parasitic infection caused by the Leishmania parasite that is transmitted by the bite of infected sandflies. It can cause a range of skin lesions, including nodules, ulcers, and papules, which may be painful and itchy. The lesions can last for months or even years if left untreated.
Symptoms: Leishmaniasis is a parasitic infection that is transmitted by the bite of infected sandflies. Symptoms vary depending on the type of leishmaniasis, but may include skin sores, fever, and enlarged spleen and liver.
Causes: Leishmaniasis is caused by parasites of the Leishmania species, which are transmitted by the bite of infected sandflies. The disease is most common in tropical and subtropical regions, especially in areas with poor living conditions and inadequate sanitation.
Treatment: Treatment for leishmaniasis depends on the type and severity of the infection. Mild cases may not require treatment, as the body’s immune system can often clear the infection. In more severe cases, medication may be necessary to kill the parasites, including antimonial drugs, pentamidine, and amphotericin B. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove affected tissue. Prevention involves avoiding sandfly bites by using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding outdoor activities at dusk and dawn when sandflies are most active.
Meadow
A type of rash that appears on the skin after exposure to sunlight. It is characterized by red, itchy, and sometimes painful bumps or blisters. It is caused by an abnormal reaction of the immune system to sunlight and is most commonly seen in individuals with fair skin.
Symptoms: Erythema Multiforme or “Meadow” is a skin condition that results in a rash, which can appear as red, raised bumps or as large, flat, target-like lesions. The rash may be itchy or painful and can occur on the arms, legs, hands, feet, and face.
Causes: The cause of Erythema Multiforme is often unknown, but it is thought to be triggered by infections, medications, or other factors that can cause an immune response. Herpes simplex virus is a common trigger for this condition.
Treatment: Treatment for Erythema Multiforme involves identifying and treating the underlying cause, if possible. Medications like antihistamines, corticosteroids, or immune-suppressing drugs may be prescribed to relieve symptoms and reduce inflammation.
Leukokeratosis
A condition characterized by white, thickened patches on the skin or mucous membranes, such as the inside of the mouth. It is often caused by chronic irritation or inflammation, and may be associated with tobacco use or other factors. It is usually benign, but in some cases may develop into cancer.
Symptoms: Leukokeratosis is a skin condition that results in white patches on the skin, which may appear scaly, rough, or thickened. The patches may occur anywhere on the body, but are most commonly found on the mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals, and anus.
Causes: The cause of leukokeratosis is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to chronic irritation, infection, or other factors that can cause changes in the skin cells.
Treatment: Treatment for leukokeratosis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In mild cases, no treatment may be necessary, but regular monitoring may be recommended. In more severe cases, medications or other treatments may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, improve skin texture, or remove the affected tissue.
Lichen planus
Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the skin, mucous membranes, nails, and hair. It appears as itchy, flat-topped, polygonal, purple or reddish-brown papules or plaques on the skin. In the mouth, it can cause white, lacy patches or sores. The exact cause of lichen planus is unknown, but it is thought to be an autoimmune disorder. Treatment may include topical or oral corticosteroids, antihistamines, or immunosuppressive drugs.
Symptoms: Lichen Planus is a chronic inflammatory condition that can affect the skin, mucous membranes, and nails. It results in flat-topped, itchy, purple or reddish bumps or patches on the skin, which may have fine white streaks or lines. The rash may occur anywhere on the body, but is most common on the wrists, ankles, and lower back.
Causes: The cause of Lichen Planus is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to an autoimmune reaction, infections, or other factors that can cause an immune response.
Treatment: Treatment for Lichen Planus depends on the location and severity of the condition. Topical corticosteroids or immunomodulating agents may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. For severe cases, systemic medications like corticosteroids, antihistamines, or immune-suppressing drugs may be necessary.
Scleroatrophic lichen
Scleroatrophic lichen is a rare subtype of lichen planus that affects the skin, typically in the genital area. It appears as white, flat-topped papules or plaques with central atrophy and scarring. It can cause itching, pain, and difficulty with sexual activity. The exact cause is unknown, but it is thought to be an autoimmune disorder. Treatment may include topical or oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, or other medications.
Symptoms: Scleroatrophic Lichen is a rare skin condition that results in white, scaly patches on the skin, which may appear thickened and hardened. The patches may occur anywhere on the body, but are most common on the lower legs and feet.
Causes: The cause of Scleroatrophic Lichen is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to chronic inflammation or an autoimmune reaction.
Treatment: Treatment for Scleroatrophic Lichen involves managing symptoms and preventing complications, like infections or ulcerations. Topical corticosteroids, immunomodulating agents, or other medications may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. In severe cases, surgery or other advanced treatments may be necessary.
Livedo
Livedo is a skin condition that appears as a mottled, bluish-purple discoloration on the skin. It can occur in various patterns and may be related to a number of underlying medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, vasculitis, or clotting disorders. Treatment depends on the underlying cause.
Symptoms:
Livedo is a skin condition characterized by a mottled, net-like discoloration of the skin. It may appear as red or purple patches on the skin, which are caused by changes in the blood vessels. Livedo can occur anywhere on the body, but is most common on the legs, arms, and trunk.
Causes:
Livedo is often associated with underlying medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders, clotting disorders, or infections. In some cases, it may be a side effect of certain medications.
Treatment:
Treatment for livedo depends on the underlying cause. Medications may be prescribed to manage the underlying condition, such as anticoagulants for clotting disorders or immunosuppressants for autoimmune disorders. In some cases, cosmetic treatments may be used to improve the appearance of the skin.
Lupus erythematosus
Lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, and other organs. It appears as a red, scaly rash on the face, scalp, or other areas of the body. Other symptoms may include joint pain, fatigue, fever, and kidney problems. Treatment may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, or other medications.
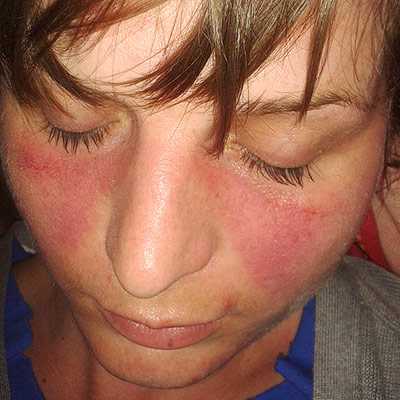
Young woman with the distinctive butterfly rash that many individuals with lupus experience. Doktorinternet, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Symptoms:
Lupus Erythematosus is an autoimmune disorder that can affect the skin, joints, and organs. It may cause a range of symptoms, including a butterfly-shaped rash on the face, joint pain, fatigue, fever, and kidney problems.
Causes:
The cause of Lupus Erythematosus is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Treatment:
Treatment for Lupus Erythematosus depends on the severity of the condition and the organs affected. Medications like corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and antimalarials may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms. Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding sun exposure and quitting smoking, may also be recommended.
Lyell syndrome
Lyell syndrome, also known as toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), is a rare and potentially life-threatening skin reaction that is often triggered by a medication. It causes the top layer of skin to peel off, leaving large, painful areas of raw skin. It can also affect the eyes, mouth, and other mucous membranes. Treatment typically involves hospitalization and supportive care, such as pain management, fluid replacement, and wound care.
Symptoms:
Lyell Syndrome, also known as toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), is a rare but serious skin condition characterized by widespread skin blistering and shedding. The condition may cause flu-like symptoms, fever, and severe pain.
Causes:
Lyell Syndrome is often triggered by an adverse reaction to medications, such as antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and NSAIDs. It may also be caused by infections, malignancies, or autoimmune disorders.
Treatment:
Treatment for Lyell Syndrome involves immediate hospitalization and discontinuation of the offending medication. Supportive care, such as fluid replacement, wound care, and pain management, may be necessary. In severe cases, skin grafting or other surgical interventions may be required.
Plantar Perforator
Plantar perforator is a type of venous insufficiency that affects the veins in the foot. It occurs when the valves in the veins of the foot become damaged or fail to function correctly, causing blood to pool in the veins. This can lead to the development of varicose veins, ulcers, and other complications.
Symptoms:
Plantar Perforator is a skin condition characterized by small, painful nodules on the soles of the feet. The nodules may be red or brown and may cause discomfort while walking.
Causes:
The cause of Plantar Perforator is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to chronic pressure or trauma to the feet.
Treatment:
Treatment for Plantar Perforator may involve padding or orthotic devices to relieve pressure on the affected area. Steroid injections or surgical removal of the nodules may also be considered in some cases.
Occupational Disease
Occupational diseases are illnesses or health conditions that are caused by exposure to hazardous substances or conditions in the workplace. These conditions can include respiratory diseases, skin diseases, cancers, and other health problems.
Symptoms: Occupational diseases are conditions that result from exposure to hazards in the workplace. They may cause a range of symptoms, depending on the specific disease and the extent of exposure. Examples of occupational diseases include lung diseases, skin disorders, and cancer.
Causes: Occupational diseases are caused by exposure to hazardous substances or conditions in the workplace. These may include chemicals, dusts, radiation, and infectious agents.
Treatment: Treatment for occupational diseases depends on the specific condition and the extent of damage. It may involve supportive care, such as oxygen therapy or pain management, or may require more intensive interventions, such as surgery or chemotherapy. Prevention of further exposure to the hazardous substance, and it is crucial in managing occupational diseases.
Mastocytosis
Mastocytosis is a rare disorder characterized by the accumulation of mast cells in various organs and tissues of the body. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including skin rashes, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis.
Symptoms: Mastocytosis is a rare condition characterized by an abnormal accumulation of mast cells in the skin or other organs. Symptoms may include skin lesions, itching, flushing, abdominal pain, and difficulty breathing.
Causes: Mastocytosis is caused by a genetic mutation that results in the overproduction of mast cells. The condition may be inherited or may occur spontaneously.
Treatment: Treatment for mastocytosis depends on the severity and location of the disease. Medications, such as antihistamines, mast cell stabilizers, and corticosteroids, may be prescribed to manage symptoms. In severe cases, chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be necessary. Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding triggers and wearing protective clothing, may also be recommended.
Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells in the skin called melanocytes. It is the most dangerous form of skin cancer because it can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. The main risk factors for melanoma include excessive sun exposure, a history of sunburns, and a family history of the disease.
Symptoms: Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that usually appears as a new or changing mole on the skin. Symptoms may include asymmetrical mole, border irregularity, color variation, diameter greater than 6mm, or evolving size or shape.
Causes: Melanoma is caused by the uncontrolled growth of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin. Risk factors for melanoma include excessive sun exposure, fair skin, family history of melanoma, and certain genetic mutations.
Treatment: Treatment for melanoma depends on the stage and location of the cancer. Surgery is the primary treatment, and may involve removal of the tumor and nearby lymph nodes. Other treatments may include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy.
Miliary
Miliary is a type of skin rash that is characterized by small, red bumps that resemble millet seeds. It can be caused by a variety of conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications.
Symptoms: Miliary refers to the appearance of small, pinhead-sized bumps on the skin. These bumps may be red or flesh-colored and may be itchy or painful.
Causes: Miliary may be caused by a variety of conditions, including fungal infections, bacterial infections, or viral infections. It may also be a symptom of an underlying systemic condition, such as sarcoidosis or tuberculosis.
Treatment: Treatment for miliary depends on the underlying cause. Antifungal, antibacterial, or antiviral medications may be prescribed to treat infections. In some cases, treatment of the underlying condition may be necessary.
Mucinosis
Mucinosis is a rare disorder that affects the skin and is characterized by the accumulation of a substance called mucin in the skin tissues. This can lead to the development of lesions, thickening of the skin, and other skin abnormalities. There are several types of mucinosis, including primary cutaneous mucinosis, scleromyxedema, and lichen myxedematosus.
Symptoms: Mucinosis is a condition in which the skin becomes thickened and leathery, and may have a waxy or greasy appearance. The affected skin may be itchy or painful.
Causes: Mucinosis may be caused by a variety of conditions, including systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, and lymphoma. It may also occur as a result of exposure to certain medications or chemicals.
Treatment: Treatment for mucinosis depends on the underlying cause. Medications, such as corticosteroids, may be prescribed to manage symptoms. In some cases, treatment of the underlying condition may be necessary.
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection that affects the skin. It is caused by a poxvirus and is characterized by the development of small, raised, pearl-like bumps on the skin. These bumps may be itchy or tender and can occur anywhere on the body.
Symptoms: Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that usually appears as small, raised bumps on the skin. These bumps may be flesh-colored, pink, or white and may have a central indentation.
Causes: Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus and is highly contagious. It is most commonly spread through skin-to-skin contact or by sharing towels or other personal items.
Treatment: Treatment for molluscum contagiosum may involve physical removal of the bumps, such as through cryotherapy or curettage. Topical medications, such as imiquimod, may also be prescribed. In some cases, the condition may resolve on its own without treatment.
Myases
Myiasis is a parasitic infection that occurs when fly larvae infest the skin or other tissues of the body. The larvae feed on the tissues and can cause a range of symptoms, including itching, pain, and swelling.
Symptoms: Myiasis is a condition in which fly larvae infest the skin or other tissues of the body. Symptoms may include itching, pain, or the sensation of movement under the skin.
Causes: Myiasis is caused by the infestation of fly larvae in the body. It may occur in people who live in areas where fly infestations are common or in those who have open wounds or other skin conditions that attract flies.
Treatment: Treatment for myiasis involves physical removal of the fly larvae. This may be done using forceps or other instruments, or by covering the affected area with petroleum jelly to suffocate the larvae. Antibiotics or other medications may also be prescribed to prevent infection.
Lipoid necrobiosis
Lipoid necrobiosis is a rare skin condition that is characterized by the development of yellow or brown patches on the skin. These patches may be itchy or painful and can occur anywhere on the body. The condition is caused by a breakdown of the fatty tissue in the skin.
Symptoms: Lipoid necrobiosis is a rare skin condition that usually appears as small, yellowish-brown patches on the skin. These patches may be flat or slightly raised and may have a shiny or waxy appearance. The affected skin may also be itchy or painful.
Causes: The exact cause of lipoid necrobiosis is not known, but it may be associated with conditions such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis. It may also occur as a result of exposure to certain chemicals or medications.
Treatment: Treatment for lipoid necrobiosis may involve managing underlying conditions, such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis. Topical or oral medications, such as corticosteroids, may be prescribed to manage symptoms. In some cases, physical removal of the affected skin may be necessary.
Angioedema
Angioedema is a type of swelling that occurs under the skin. It is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the tissues and can be a result of an allergic reaction, medication, or a medical condition. The swelling can occur anywhere on the body but is most common in the face, lips, and throat.
Symptoms: Angioedema is characterized by swelling of the deeper layers of the skin and tissues, usually in the face, lips, tongue, throat, or genital region. The swelling may be accompanied by itching or a burning sensation and can last for several hours or days.
Causes: Angioedema can be caused by an allergic reaction to certain foods, medications, or insect bites. It can also be a side effect of certain medications or occur as a result of an underlying medical condition, such as hereditary angioedema or autoimmune disorders.
Treatment: Treatment for angioedema depends on the underlying cause and may involve antihistamines, corticosteroids, or epinephrine injections in severe cases. Avoiding triggers, such as certain foods or medications, may also help prevent angioedema from occurring.
Panniculitis
Panniculitis is a condition that affects the layer of fat beneath the skin. It is characterized by the development of nodules or lumps in the fat layer, which can be painful or tender. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, medications, and autoimmune disorders.
Symptoms: Panniculitis is characterized by painful, tender nodules or bumps that form under the skin, usually on the legs or arms. The affected area may also be red, swollen, or warm to the touch.
Causes: Panniculitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and reactions to medications or chemicals. It may also occur as a result of an underlying medical condition, such as lupus or pancreatitis.
Treatment: Treatment for panniculitis depends on the underlying cause and may involve antibiotics, corticosteroids, or other medications to manage symptoms. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove affected tissue.
Papillonite
Papillonite, also known as papular urticaria, is a type of skin rash that is caused by an allergic reaction to insect bites. It is characterized by the development of small, red bumps on the skin that may be itchy or painful. The rash can occur anywhere on the body and is most common in children.
Symptoms: Papillonite is a skin rash that is characterized by small, itchy bumps that may be red or flesh-colored. The bumps may be clustered together in patches and can occur anywhere on the body.
Causes: The exact cause of papillonite is not known, but it is thought to be associated with an allergic reaction to certain substances, such as plants, cosmetics, or medications.
Treatment: Treatment for papillonite may involve topical or oral antihistamines or corticosteroids to manage itching and inflammation. Avoiding exposure to the triggering substance is also important to prevent further outbreaks.
Achromiant parakeratosis
Achromiant parakeratosis is a rare skin condition that is characterized by the development of white, scaly patches on the skin. The condition is caused by a buildup of keratin in the skin and can occur anywhere on the body. The patches may be itchy or tender and can become inflamed.
Symptoms: Achromiant parakeratosis is characterized by the presence of scaly, white or grayish patches on the skin. The affected skin may also be thickened and may itch or burn.
Causes: The exact cause of achromiant parakeratosis is not known, but it is thought to be a genetic condition that is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
Treatment: There is no cure for achromiant parakeratosis, and treatment is focused on managing symptoms. Topical creams and ointments may be prescribed to soften and reduce the thickness of the affected skin. Light therapy may also be used to manage symptoms.
Guttate parapsoriasis
Guttate parapsoriasis is a type of skin condition that is characterized by the development of small, scaly patches on the skin. The patches are typically oval or round in shape and may be pink or red in color. The condition is often associated with stress or infections and can occur anywhere on the body.
Symptoms:
Guttate parapsoriasis is characterized by small, red, scaly patches that may appear on the trunk, arms, or legs. The patches may be itchy and can last for several months.
Causes:
The exact cause of guttate parapsoriasis is not known, but it is thought to be associated with an abnormal immune response. It may also be triggered by infections or medications.
Treatment:
Treatment for guttate parapsoriasis may involve topical corticosteroids or phototherapy to manage symptoms. In severe cases, oral medications may be prescribed.
Body pediculosis
Body pediculosis is an infestation of the skin by lice. The lice feed on the blood of the host and can cause itching, redness, and irritation. The condition is most common in areas where clothing is tight-fitting, such as the waistband or cuffs of clothing.
Symptoms: Body pediculosis, also known as body lice, is characterized by intense itching and the presence of small, red bumps on the skin. The bumps may be clustered together and may be more common in areas where clothing is tight-fitting.
Causes: Body pediculosis is caused by the presence of body lice, which are spread through close contact with an infected person or contaminated clothing or bedding.
Treatment: Treatment for body pediculosis involves washing all clothing and bedding in hot water and using topical or oral medications to kill the lice. In severe cases, the affected person may need to be hospitalized.
Scalp pediculosis
Scalp pediculosis is an infestation of the scalp by lice. The lice feed on the blood of the host and can cause itching, redness, and irritation. The condition is most common in children and can be spread through close contact with an infested person.
Symptoms: Scalp pediculosis, also known as head lice, is characterized by intense itching and the presence of small, white or brown lice eggs (nits) on the hair shafts. The scalp may also be red and irritated.
Causes: Scalp pediculosis is caused by the presence of head lice, which are spread through close contact with an infected person or contaminated clothing or bedding.
Treatment: Treatment for scalp pediculosis involves using a special shampoo or lotion to kill the lice and combing out the nits with a fine-tooth comb. It may also be necessary to wash all clothing and bedding in hot water and vacuum the home to remove any remaining lice or eggs.
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is a type of hair loss that occurs when the immune system attacks the hair follicles. The condition is characterized by the development of round, bald patches on the scalp or other parts of the body. The condition can occur at any age and can be triggered by stress or other factors.
Symptoms: Alopecia areata is characterized by patchy hair loss on the scalp or other parts of the body. The affected skin may be smooth or have a slightly raised or bumpy appearance.
Causes: The exact cause of alopecia areata is not known, but it is thought to be an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the hair follicles.
Treatment: Treatment for alopecia areata may involve corticosteroid injections, topical medications, or light therapy to promote hair regrowth. In some cases, hair transplantation may be necessary.
Note: Please note that while dermatological pathologies can have distinct features and characteristics, a definitive diagnosis requires a medical examination by a licensed healthcare provider.
Bullous pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is characterized by the development of large, fluid-filled blisters on the skin. The condition is caused by the immune system attacking the skin, and can be triggered by certain medications or infections. The blisters can be painful or itchy, and may leave scars when they heal.
Symptoms: Bullous pemphigoid is characterized by large, fluid-filled blisters that develop on the skin, usually on the arms, legs, or trunk. The blisters may be itchy and painful, and they can break open and form crusts.
Causes: Bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the skin, specifically the proteins that hold the skin layers together.
Treatment: Treatment for bullous pemphigoid may involve topical or oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressive medications to control the immune response. In severe cases, intravenous immunoglobulin therapy or plasmapheresis may be necessary.
Pemphigus
Pemphigus is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is characterized by the development of blisters on the skin and inside the mouth. The condition is caused by the immune system attacking the skin, and can be triggered by certain medications or infections. The blisters can be painful and may lead to scarring.
Symptoms: Pemphigus is characterized by the development of fluid-filled blisters on the skin and mucous membranes, including the mouth, throat, and genitals. The blisters are fragile and can break open easily, leaving painful sores.
Causes: Pemphigus is also an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the proteins that hold skin cells together.
Treatment: Treatment for pemphigus may involve corticosteroids or immunosuppressive medications to control the immune response. In severe cases, intravenous immunoglobulin therapy or plasmapheresis may be necessary.
Perionyxis
Perionyxis, also known as paronychia, is a bacterial or fungal infection of the skin around the nails. The condition is characterized by redness, swelling, and pain around the nail bed. In severe cases, the infection can cause pus to form around the nail.
Symptoms: Perionyxis, also known as paronychia, is characterized by redness, swelling, and tenderness around the nail bed. The affected area may also be warm to the touch and may contain pus.
Causes: Perionyxis can be caused by a bacterial or fungal infection or by trauma to the nail bed, such as from biting the nails or a hangnail.
Treatment: Treatment for perionyxis may involve warm compresses to reduce inflammation, and in some cases, oral or topical antibiotics or antifungal medications may be necessary.
Perleche
Perleche, also known as angular cheilitis, is a condition that affects the corners of the mouth. It is characterized by redness, cracking, and irritation around the corners of the mouth. The condition is often caused by a fungal or bacterial infection, and can be worsened by dry skin, nutritional deficiencies, or certain medical conditions.
Symptoms: Perleche, also known as angular cheilitis, is characterized by dry, cracked skin at the corners of the mouth. The affected area may be red, swollen, and painful, and may also be prone to bacterial or fungal infections.
Causes: Perleche can be caused by a variety of factors, including dry or chapped lips, nutritional deficiencies, fungal infections, and poorly fitting dentures.
Treatment: Treatment for perleche may involve keeping the affected area clean and dry, using a moisturizing lip balm, and in some cases, topical or oral antifungal medications or corticosteroids. Addressing any underlying nutritional deficiencies or dental issues may also be necessary.
Photodermatosis
Photodermatosis is a group of skin conditions that are caused by an abnormal reaction to sunlight. The conditions are characterized by the development of rashes, blisters, or bumps on the skin after exposure to sunlight. The conditions can be triggered by certain medications or medical conditions, and can be managed through sun protection and avoidance.
Symptoms: Photodermatosis refers to a group of skin conditions that are triggered by exposure to sunlight. Symptoms can include redness, itching, swelling, and the development of blisters or hives on the skin.
Causes: Photodermatosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including medications, chemicals in cosmetics or other skin care products, and certain medical conditions.
Treatment: Treatment for photodermatosis may involve avoiding exposure to sunlight, using sunscreen with a high SPF, and wearing protective clothing. In some cases, topical or oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressive medications may be necessary to control the immune response.
Gibert’s rosé pityriasis
Gibert’s rosé pityriasis, also known as pityriasis rosea, is a common skin condition that is characterized by the development of a single, large, scaly patch on the skin, followed by multiple smaller patches that are pink or red in color. The condition is thought to be caused by a viral infection and is often self-limiting, resolving on its own within a few weeks.
Symptoms: Gibert’s rosé pityriasis is characterized by the development of small, scaly patches on the skin, usually on the chest, back, or arms. The patches may be pink or red in color, and may be accompanied by itching or burning.
Causes: The exact cause of Gibert’s rosé pityriasis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to a viral or bacterial infection.
Treatment: Treatment for Gibert’s rosé pityriasis may involve topical corticosteroids or antihistamines to control itching and inflammation, and in some cases, phototherapy may be beneficial.
Tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor is a fungal skin infection that is characterized by the development of discolored patches on the skin. The patches can be white, pink, or brown in color and may be itchy or scaly. The condition is caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin and can be treated with antifungal medications.
Symptoms: Tinea versicolor is characterized by the development of small, scaly patches on the skin, usually on the chest, back, or arms. The patches may be lighter or darker than the surrounding skin and may be accompanied by itching.
Causes: Tinea versicolor is caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin, which can be triggered by a variety of factors, including heat, humidity, and hormonal changes.
Treatment: Treatment for tinea versicolor may involve topical or oral antifungal medications to control the growth of yeast on the skin.
Poikiloderma
Poikiloderma is a skin condition that is characterized by a combination of hyperpigmentation, hypopigmentation, and atrophy of the skin. The condition can be caused by sun damage, aging, or certain medical conditions. The affected skin may appear thin, wrinkled, and fragile.
Symptoms: Poikiloderma is characterized by the development of mottled, discolored patches on the skin, usually on the face, neck, or chest. The affected skin may be red or brown in color and may be accompanied by itching or burning.
Causes: Poikiloderma can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to sunlight, certain medications, and certain medical conditions.
Treatment: Treatment for poikiloderma may involve avoiding exposure to sunlight, using sunscreen with a high SPF, and wearing protective clothing. In some cases, topical or oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressive medications may be necessary to control the immune response.
Porphyrias
Porphyrias are a group of rare genetic disorders that affect the production of heme, a component of hemoglobin. The disorders can cause a variety of symptoms, including skin sensitivity to sunlight, blisters, and skin thickening. Treatment for porphyrias depends on the type and severity of the disorder.
Symptoms: Porphyrias are a group of rare genetic disorders that affect the production of heme, a component of red blood cells. Symptoms can include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, muscle weakness, and sensitivity to sunlight.
Causes: Porphyrias are caused by genetic mutations that affect the production of heme.
Treatment: Treatment for porphyrias may involve medications to control symptoms and prevent complications, such as pain medications, blood transfusions, or heme infusions.
Prurigo
Prurigo is a skin condition that is characterized by the development of itchy, raised bumps on the skin. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergies, insect bites, and certain medical conditions. Treatment for prurigo depends on the underlying cause of the condition.
Symptoms: Prurigo is characterized by the development of itchy, scaly patches on the skin. The affected skin may be red or brown in color and may be accompanied by small bumps or blisters.
Causes: The exact cause of prurigo is unknown, but it is thought to be related to a variety of factors, including allergies, insect bites, and stress.
Treatment: Treatment for prurigo may involve topical or oral antihistamines, topical or oral corticosteroids, or other medications to control itching and inflammation.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the skin, scalp, and nails. The condition is characterized by the development of red, scaly patches on the skin, which can be itchy and painful. The cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Treatment for psoriasis includes topical creams and ointments, phototherapy, and systemic medications.
Symptoms: Psoriasis is characterized by the development of red, scaly patches on the skin. The affected skin may be itchy or painful, and the patches may be accompanied by small bumps or blisters.
Causes: The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an immune system malfunction.
Treatment: Treatment for psoriasis may involve topical or oral medications to control inflammation and itching, light therapy, or in some cases, systemic medications.
Purpura
Purpura is a skin condition that is characterized by the development of red or purple spots on the skin, which are caused by bleeding under the skin. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including blood disorders, infections, and medications. Treatment for purpura depends on the underlying cause of the condition.
Symptoms: Purpura is characterized by the development of small, purple or red spots on the skin or mucous membranes. The spots may be accompanied by bleeding or bruising.
Causes: Purpura can be caused by a variety of factors, including autoimmune disorders, infections, or certain medications.
Treatment: Treatment for purpura may depend on the underlying cause and may involve medications to control bleeding, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, or other treatments to address the underlying condition.
Rosacea
Rosacea is a common skin condition that is characterized by redness, flushing, and small bumps on the skin, particularly on the face. The condition can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, alcohol, and certain medications. Treatment for rosacea includes topical creams and ointments, oral medications, and laser therapy.
Symptoms: Rosacea is characterized by redness, flushing, and small bumps or pimples on the face. It may also cause burning, stinging, or itching sensations and can cause the nose to become swollen and bumpy.
Causes: The exact cause of rosacea is unknown, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as sun exposure and certain triggers like alcohol and spicy foods.
Treatment: Treatment for rosacea may involve topical or oral medications to reduce inflammation and control symptoms, as well as avoiding triggers and protecting the skin from sun exposure.
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the skin, lungs, and other organs. The condition is characterized by the development of small nodules, called granulomas, in the affected tissues. The cause of sarcoidosis is not fully understood, but is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Treatment for sarcoidosis depends on the severity and location of the granulomas.
Symptoms: Sarcoidosis is a condition that causes the growth of tiny clusters of inflammatory cells in various parts of the body. Symptoms can include coughing, shortness of breath, fatigue, fever, and skin lesions.
Causes: The exact cause of sarcoidosis is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an abnormal immune response to an environmental trigger, such as an infection or exposure to certain chemicals.
Treatment: Treatment for sarcoidosis may depend on the severity and location of the symptoms and may involve medications to reduce inflammation and control the immune response.
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is a bacterial infection that is characterized by a bright red rash on the skin, which typically spreads from the chest to the limbs. The condition can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as a sore throat and fever. Scarlet fever is caused by the same bacteria that cause strep throat and is treated with antibiotics.
Symptoms: Scarlet fever is a bacterial infection that can cause a sore throat, fever, and a rash that feels like sandpaper. The rash typically appears on the chest and abdomen and may spread to other areas of the body.
Causes: Scarlet fever is caused by group A streptococcus bacteria.
Treatment: Treatment for scarlet fever may involve antibiotics to kill the bacteria and control the symptoms.
Sycosis
Sycosis, also known as barber’s itch, is a bacterial infection of the hair follicles in the beard and mustache area. The condition is characterized by the development of small, red, and inflamed bumps, which can be itchy and painful. Treatment for sycosis includes topical or oral antibiotics.
Symptoms: Sycosis, also known as barber’s itch, is a type of skin infection that affects hair follicles. Symptoms can include redness, itching, and small bumps or pustules around hair follicles, particularly in the beard area.
Causes: Sycosis is typically caused by a bacterial infection, often from shaving or other skin trauma.
Treatment: Treatment for sycosis may involve topical or oral antibiotics to kill the bacteria and reduce inflammation. In severe cases, corticosteroids may also be used to reduce inflammation.
Mouth-hand-foot syndrome
Mouth-hand-foot syndrome is a viral infection that is characterized by the development of small blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth. The condition is caused by several different types of viruses, including the coxsackievirus and enterovirus. Treatment for mouth-hand-foot syndrome includes over-the-counter pain relief and antiviral medications.
Symptoms: Mouth-hand-foot syndrome is a viral infection that primarily affects young children and is characterized by a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth. Symptoms can include fever, sore throat, and painful blisters or ulcers on the tongue, gums, and inside of the cheeks.
Causes: Mouth-hand-foot syndrome is caused by a viral infection, typically Coxsackie virus or enterovirus.
Treatment: Treatment for mouth-hand-foot syndrome typically involves managing the symptoms, such as using pain relief medications for fever and discomfort, and keeping the skin clean and dry.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a rare but serious skin condition that is usually caused by a reaction to medication or infection. The condition is characterized by the development of painful blisters and a widespread rash, which can be accompanied by fever and other symptoms. Treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome typically involves hospitalization, supportive care, and management of the underlying cause of the condition.
Symptoms: Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a rare but serious skin reaction that can cause a widespread rash, blisters, and peeling skin. It can also affect the eyes and mucous membranes, leading to vision loss, scarring, and respiratory problems.
Causes: Stevens-Johnson syndrome is typically caused by an adverse reaction to certain medications, such as antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Treatment: Treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome typically involves stopping the offending medication and providing supportive care, such as pain relief, wound care, and intravenous fluids. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection that is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. The condition is characterized by the development of a painless sore, called a chancre, on the genitals, anus, or mouth. If left untreated, syphilis can cause a variety of complications, including skin rashes, fever, and neurological problems. Treatment for syphilis involves antibiotics.
Symptoms: Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause a wide range of symptoms, including sores, rash, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. If left untreated, it can progress to more serious symptoms, including damage to the brain, heart, and other organs.
Causes: Syphilis is caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, which is typically spread through sexual contact.
Treatment: Treatment for syphilis typically involves antibiotics, such as penicillin or doxycycline, to kill the bacteria and prevent further damage.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a fungal infection of the skin that is characterized by the development of a circular rash on the skin, which may be red and scaly. The condition is caused by several different types of fungi and can be treated with antifungal medications.
Symptoms: Ringworm is a fungal infection that can cause a circular rash with raised edges and a clear center. It can occur on any part of the body and can cause itching, redness, and scaling of the skin.
Causes: Ringworm is caused by a type of fungi called dermatophytes, which can be spread through contact with infected people, animals, or objects.
Treatment: Treatment for ringworm typically involves topical or oral antifungal medications to kill the fungi and prevent further spread of the infection. Keeping the skin clean and dry can also help prevent the spread of ringworm.
Bullous drug eruption
Bullous drug eruption is a type of drug reaction that is characterized by the development of blisters on the skin. The condition can be caused by a variety of medications and can be life-threatening in some cases. Treatment for bullous drug eruption involves discontinuing the offending medication and providing supportive care.
Symptoms: The symptoms of bullous drug eruption include the development of large blisters, often on the arms, legs, and torso. These blisters can be painful and may itch or burn. They can also ooze or crust over.
Causes: Bullous drug eruption is caused by an allergic reaction to a medication. Certain drugs such as penicillin, sulfonamides, and diuretics are more commonly associated with this type of reaction.
Treatment: The treatment of bullous drug eruption involves discontinuing the medication causing the reaction and providing supportive care such as wound care and pain management. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
Trombidiosis
Trombidiosis, also known as harvest mite infestation or chigger bites, is a skin condition that is caused by the bite of a type of mite. The condition is characterized by the development of small, itchy red bumps on the skin, which can be treated with over-the-counter antihistamines and topical creams.
Trombidiosis: Symptoms: Trombidiosis is a skin condition caused by bites from chiggers, which are tiny mites. The symptoms include intense itching, redness, and the development of small bumps or blisters on the skin.
Causes: Trombidiosis is caused by bites from chiggers, which are found in grassy or wooded areas.
Treatment: The treatment of trombidiosis involves relieving the symptoms of itching and preventing infection of the bite sites. Over-the-counter anti-itch creams or lotions and antihistamines may be used to relieve itching. If the bite sites become infected, topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that can affect the skin, as well as the lungs and other organs. The condition is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is transmitted through the air. Tuberculosis can cause a variety of symptoms, including a skin rash, fever, and weight loss. Treatment for tuberculosis involves a combination of antibiotics.
Symptoms: Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that can affect the lungs, as well as other parts of the body. Symptoms of tuberculosis can include coughing, chest pain, fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
Causes: Tuberculosis is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is spread from person to person through the air when someone with active tuberculosis coughs or sneezes.
Treatment: The treatment of tuberculosis involves a combination of antibiotics taken over a period of several months. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary. It is important to complete the full course of treatment to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of tuberculosis.
Tungiasis
Tungiasis, also known as sand flea infestation, is a parasitic skin condition that is caused by the female sand flea burrowing into the skin and laying eggs. The condition is characterized by the development of small, itchy bumps on the skin, which can become painful and infected. Treatment for tungiasis involves removing the flea and its eggs from the skin and treating any resulting infections.
Symptoms: Tungiasis is a skin condition caused by the infestation of the feet with the female sand flea. The symptoms include intense itching, redness, swelling, and the development of small blisters or bumps.
Causes: Tungiasis is caused by the female sand flea, which burrows into the skin of the feet to lay its eggs. It is commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions.
Treatment: The treatment of tungiasis involves removing the sand flea from the skin using a sterile needle or scalpel. The affected area may also be treated with topical antiseptics to prevent infection. In severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat secondary infections.
Urticaria
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a skin condition that is characterized by the development of itchy, raised bumps on the skin. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergies, infections, and stress. Treatment for urticaria includes avoiding triggers, taking antihistamines, and in severe cases, taking corticosteroids.
Symptoms: Raised, itchy, and often red or pink bumps or welts on the skin that range in size from a few millimeters to several inches, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, and difficulty breathing or swallowing in severe cases.
Causes: Allergic reactions, insect bites or stings, certain medications, exposure to heat or cold, viral infections, and autoimmune disorders.
Treatment: Avoidance of triggers, antihistamines, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressive drugs in severe cases.
Varicella
Varicella, also known as chickenpox, is a viral infection that is characterized by the development of a rash and fluid-filled blisters on the skin. The condition is highly contagious and is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. Treatment for varicella includes rest, over-the-counter pain relief, and antiviral medications.
Symptoms: Itchy red blisters that eventually burst and crust over, fever, fatigue, and headache.
Causes: Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) that spreads through the air by coughing or sneezing, or by contact with fluid from the blisters of an infected person.
Treatment: Rest, cool baths with added oatmeal, and antihistamines to relieve itching, acyclovir or valacyclovir in severe cases.
Necrotizing vasculitis
Necrotizing vasculitis is a rare but serious skin condition that is caused by inflammation of the blood vessels. The condition can cause skin ulcers, gangrene, and other complications, and can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections and autoimmune disorders. Treatment for necrotizing vasculitis includes corticosteroids and immunosuppressant medications.
Symptoms: Fever, fatigue, weight loss, muscle and joint pain, skin ulcers or rashes, and in severe cases, tissue death (necrosis) and organ damage.
Causes: Autoimmune disorders, infections, certain medications, and cancer.
Treatment: Corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs to reduce inflammation, and treatment of underlying conditions.
Wart
A wart is a small growth on the skin that is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Warts can appear on any part of the body, but are most common on the hands, feet, and face. The condition is usually not serious, but can be unsightly and may cause discomfort. Treatment for warts includes topical medications, cryotherapy, and in some cases, surgical removal.
Symptoms: Raised, flesh-colored or grayish bumps on the skin, typically on the hands or feet, and sometimes with tiny black dots on the surface.
Causes: Human papillomavirus (HPV) that spreads through skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated surfaces.
Treatment: Over-the-counter medications containing salicylic acid or freezing (cryotherapy), surgical removal, laser treatment, and immunotherapy.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a skin condition characterized by the loss of pigment in patches on the skin. The cause of vitiligo is not fully understood, but it is thought to be an autoimmune disorder. The condition can occur at any age and affects people of all skin colors. Treatment for vitiligo may include topical medications, light therapy, or in severe cases, depigmentation.
Symptoms: White patches of skin on various parts of the body, particularly on sun-exposed areas, mucous membranes, and areas around body openings.
Causes: Destruction of melanocytes (cells that produce pigment) due to autoimmune disorders, genetic factors, and exposure to chemicals or radiation.
Treatment: Topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and phototherapy.
Vulvovaginitis
Vulvovaginitis is an inflammation of the vulva and vagina that can cause itching, burning, and discharge. The condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, allergies, and irritants. Treatment for vulvovaginitis depends on the cause, but may include antibiotics, antifungal medications, or topical steroids.
Symptoms: Vaginal itching, burning, or pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, and pain during sexual intercourse or urination.
Causes: Infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, hormonal changes, and irritants such as soaps, douches, or perfumes.
Treatment: Antibiotics, antifungal medications, topical steroids, and avoiding irritants.
Xanthoma
Xanthomas are yellowish, waxy deposits of cholesterol that can appear on the skin. The condition is usually caused by high levels of cholesterol or triglycerides in the blood, and can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes or liver disease. Treatment for xanthomas may involve managing the underlying condition and, in some cases, surgical removal.
Symptoms: Yellowish, firm, raised bumps or nodules on the skin, typically around the eyes, joints, hands, feet, or buttocks.
Causes: Accumulation of fats or cholesterol in cells due to genetic disorders, diabetes, high cholesterol, or other underlying medical conditions.
Treatment: Treatment of underlying conditions, surgical removal, laser therapy, and lipid-lowering drugs.
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Xeroderma pigmentosum is a rare genetic disorder that affects the skin and eyes. The condition causes extreme sensitivity to sunlight and an increased risk of skin cancer. Treatment for xeroderma pigmentosum involves avoiding exposure to sunlight and regular skin cancer screenings.
Symptoms: Dry, scaly, and itchy skin, freckle-like pigmentation, and skin cancers at an early age due to sun exposure.
Causes: Genetic mutations that impair the ability to repair DNA damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or other sources.
Treatment: Sun protection measures such as wearing protective clothing and avoiding sun exposure, regular skin cancer screening, and surgical removal of skin cancers.
Shingles
Shingles is a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which also causes chickenpox. The condition is characterized by a painful rash that usually appears on one side of the body. Treatment for shingles includes antiviral medications and pain relief. A vaccine is also available to help prevent shingles.
Symptoms: Painful and itchy rash or blisters on one side of the body or face, usually following a nerve pathway, and flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, and fatigue.
Causes: Reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) that causes chickenpox in people who have previously had the disease, due to weakened immune systems, stress, or aging.
Treatment: Antiviral medications, pain relievers, antihistamines, and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and prevent complications. Vaccination is also available to prevent shingles.
A Comprehensive List of Dermatological Diseases and Their Descriptions
List of cardiovascular diseases (heart diseases)
Heart disorders
- Hypertension – elevated blood pressure above “normal.” Long term high blood pressure is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease, stroke, heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, vision loss, and chronic kidney disease. Lowering blood pressure is key for preventing these diseases.
- Types of hypertension
- Essential hypertension – Hypertension with no known cause, which is about 90–95% of people with hypertension. Often thought to be due to lifestyle. Management is through medications and blood pressure that does not respond is a red flag that it may be secondary hypertension. Due to the widespread nature of hypertension, cardiologists will end up managing or recommending treatments for essential hypertension.
- Secondary hypertension – Most causes of secondary hypertension are from kidney and endocrine disorders. Cardiovascular causes of hypertension include coarctation of aorta, atherosclerosis, and aortic stenosis.
- Complications of hypertension
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy – Increased pressure results in hypertrophy of the myocardium, particularly left ventricular hypertrophy. Pulmonary hypertension — which is separate from “hypertension” described above — can result in right ventricular hypertrophy.
- Hypertensive crisis – Generally considered to be a systolic blood pressure over 180. If there is no organ dysfunction it is called a hypertensive urgency, but if there is (e.g., confusion, breathlessness) then it is called hypertensive emergency.
- Pre-eclampsia (PreE) / Eclampsia – PreE is a disease of pregnancy that results in hypertension and proteinuria. PreE has negative consequences for both the mother and fetus/baby. Progression to eclampsia involves seizures. Currently, the only definitive treatment is delivery of the fetus.
- Hemorrhagic stroke – Infarction of the brain due to internal bleeding from Charcot–Bouchard aneurysms.
- Hypertensive encephalopathy, hypertensive nephropathy, hypertensive retinopathy – Damage to organs from chronic hypertension.
- Types of hypertension
- Cardiac arrhythmias – conditions in which the heartbeat is irregular, too fast, or too slow. Many types of arrhythmia have no symptoms. When symptoms are present these may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. More seriously there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, or chest pain. While most types of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in cardiac arrest.
- Atrial fibrillation (afib or AF) – Fibrillation of the atria is fairly common and more common with increased age and overall disease of the heart. If the ventricular rate exceeds 100 then the afib is further classified as “afib with RVR” meaning rapid ventricular response.
- Atrial flutter (AFL) – A re-entrant tachycardia greater than 240 beats per minute and produces a characteristic saw-tooth pattern on ECG. It often degenerates to atrial fibrillation.
- Heart block – A decrease in the ability of the conduction system to transmit action pulses in the orderly manner. Blockage of the signal at different areas results in different types of heart block (e.g., first-degree AV block, left bundle branch block).
- Long QT syndrome – Lengthening of the QT interval can result in arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Specifically, it can lead to torsades de pointes than can then lead to ventricular fibrillation. It can be an inherited disorder or be acquired. Certain medications are associated with lengthening of the QT interval — drug-induced QT prolongation — and an EKG may be warranted before starting the medication to ensure a normal QT interval, but this practice is debated.
- Premature atrial contractions (PACs or APCs) – Normal beats originate in the SA node and extra beats originating from the atria are called PACs. They can be found in normal hearts and be asymptomatic; symptomatic PACs can be treated with beta blockers. PACs, like PVCs, can pair up with normal beats in a pattern called bigeminy.
- Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) – Normal beats are conducted through the AV node to the ventricles resulting in a narrow QRS complex. With PVCs, the extra beat originates within the ventricles and results in a wide QRS complex. Like PACs, they can be found in healthy hearts but are more likely to be found in bigeminy than PACs.
- Sick sinus syndrome, Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome (BTS) – Disease of the SA node that results in irregular changes in heart rate and in the case of BTS the arrhythmia alternates between bradycardia and tachycardia.
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) – A collection of tachycardia rhythms that originate before the ventricles and include the SA node, atria, and AV node. It is a broad, encomparsing term that includes other rhythms in this list (e.g., afib with RVR) and others.
- Torsades de pointes – A polymorphic arrhythmia that can be syptomatic and tends to resolve to a normal sinus rhythm. However, there is a concern
- Ventricular fibrillation (vfib) – Fibrillation of the ventricles is a life-threatening arrhythmia and should be treated by defibrillation and is a medical emergency. Vfib results from uncoordinated contraction of the ventricles and defibrillation acts as a ‘reset’ to synchronize contraction (i.e., a normal rhythm).
- Ventricular tachycardia (vtach) – Tachycardia that originates from within the ventricles. Typically, “vtach” implies monomorphology but it can be an umbrella term for both monomorphic and polymorphic (i.e., torsade de pointes). To classify a ventricular rhythm as vtach, at least 3 beats in a row must originate from the ventricles and have a rate over 100. If it lasts longer than 30 seconds, it can additionally be labelled as a sustained vtach.
- Coronary circulation disorders
- Atherosclerosis – Atherosclerosis is the condition in which an artery wall thickens as the result of a build-up of fatty materials (e.g., cholesterol) and white blood cells (“foam cells”). Atherosclerosis of a coronary artery leads to coronary artery disease (CAD). Atherosclerosis is a broad term referring to loss of elasticity of arteries and more specific terms exist — arteriosclerosis and arteriolosclerosis — to narrow which arteries are diseased and can easily be confused due to similar spelling. Overall, atherosclerosis tends to affect the arteries of highest pressure: aorta, coronary, renal, femoral, cerebral, and carotid.
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)– Coronary artery disease is a general term for any reduction in coronary circulation. One such cause is atherosclerosis. CAD can lead to ischemia (angina pectoris) or infarction (myocardial infarction). Treatment of CAD includes angioplasty, stenting, and coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
- Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) – ACS is a medical emergency and is a broad term encompassing many acute myocardial infarction symptoms. As a syndrome, it consists of a constellation of symptoms and can have many causes. The top three causes of ACS are ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI, 30%), non ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI, 25%), or unstable angina (38%). The first two are myocardial infarctions which are more commonly known as “heart attacks.”
- Angina pectoris – Angina pectoris literally means “chest pain” that refers to pain caused by ischemia of the heart. The main cause of angina is coronary artery disease, but can result from other non-atherosclerotic causes such as anemia and heart failure. Stable angina results if the angina resolves with rest or nitroglycerin, but can progress to unstable angina which is a form of acute coronary syndrome.
- Myocardial infarction (a.k.a. heart attack) – A myocardial infarction is the death of a part of the heart which is typically caused by a blockage of the coronary circulation but can be caused by other insufficiency such as cardiogenic shock.
- Restenosis – Recurrence of stenosis after being treated (e.g., stenting).
- Cardiac arrest – cessation of normal systemic circulation due to failure in proper contraction of the heart. There are several conditions that can cause cardiac arrest. Treatment of cardiac arrest includes cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), defibrillation, and advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), and treatment of the underlying cause of arrest.
- Asystole (“flatline”) – Asystole refers to the absence of electrical activity of the heart and is sometimes referred to as a “flatline” because the electrocardiogram shows a solid line due to the absence of electrical activity. This flatline is commonly used in television and movies to signal death. There are numerous causes of asystole that may be reversible if determined quickly enough, however, survival is very unlikely (~2% if not in a hospital). In contrast, asystole is desired and induced during cardiopulmonary bypass through a cardioplegia solution containing very high amounts of potassium. One additional example is the use of high potassium in lethal injection that results in asystole, cardiac arrest, and then death.
- Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) – Pulseless electrical activity is when the electrocardiogram shows a rhythm that should produce a pulse but it does not. PEA is commonly caused by the 6 H’s and 6 T’s (see PEA article) and results in decreased cardiac output and insufficient oxygen delivery to the body.
- Pulseless ventricular tachycardia – Pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT) Is one classification of VT such that no pulse is felt because of an ineffective cardiac output which causes cardiac arrest, which also results in insufficient oxygen delivery to the body.
- Sudden cardiac death (SCD) – concept of natural death rather than a specific medical condition. There are several causes of sudden cardiac death and it is distinct from cardiac arrest. The leading cause of SCD in young athletes is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy but can also result from commotio cordis that is often sustained during athletic activity.
- Ventricular fibrillation – Ventricular fibrillation is fibrillation of the ventricles of the heart. Rhythmic contraction is necessary for efficient movement of blood, and fibrillation disrupts this rhythm sufficiently to cause cardiac arrest.
- Disorders of the myocardium
- Cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy is a deterioration of the myocardium. Several classifications have been used to categorize cardiomyopathies with the most common being primary vs. secondary, and dilated vs. restrictive vs. hypertrophic (presented below).
- Ischemic cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy causing ischemia of the heart due to coronary artery disease.
- Nonischemic cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy caused by something other than ischemia.
- Amyloid cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy caused by amyloidosis.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) – Cardiomyopathy caused by hypertrophy of the heart and is the leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young adults.
- Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM) (Idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis (IHSS)) :
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) – Cardiomyopathy caused by dilation of the heart, typically caused by “drugs and bugs.” It is the most common form of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy and the dilitation of the heart results in larger chamber volumes & thinner myocardial walls, both of which decrease the ability to pump. Specific kinds of dilated cardiomyopathy are listed below, and other causes include Chagas disease, chemotherapeutic agents (e.g., doxorubicin), tuberculosis, and pregnancy.
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy – A type of dilated cardiomyopathy caused by chronic abuse of alcohol and results from direct toxicity of ethanol on the myocardium.
- Tachycardia induced cardiomyopathy – A type of dilated cardiomyopathy caused by chronic tachycardia. A common arrhythmia that can lead to this form of cardiomyopathy is the common atrial fibrillation.
- Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (Transient apical ballooning, stress-induced cardiomyopathy) – A type of dilated cardiomyopathy caused by a sudden temporary weakening of the myocardium, which can include emotional stress (i.e. broken-heart syndrome). It presents as sudden heart failure with ECG changes similarly found in myocardial infarction and typically is found in post-menopausal women.
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy) – Cardiomyopathy caused by a genetic mutation of the desmosomes that connect myocytes.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) – Cardiomyopathy caused by excessive rigidity of the heart that prevents effective contraction and pumping. In comparison to DCM, RCM is often secondarily caused by other diseases such as amyloidosis, scleroderma, hemachromatosis (iron overload) and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. As such, the treatment for RCM is to treat the disease causing the RCM.
- Heart failure – Heart failure is failure of the heart to produce sufficient blood flow to meet metabolic demands of the body, or to do so at higher filling pressures. The hallmark signs of heart failure include shortness of breath (especially on exertion, at night, or while lying down) and leg swelling. Chest pain is rarely a feature of heart failure, which would point a diagnosis more toward angina pectoris or myocardial infarction. Perhaps confusingly, heart failure can be caused by coronary artery disease (CAD) and myocardial infarction (MI) that result in a deficiency in pumping that then leads to heart failure. Treatment of heart failure, like most secondary disorders, depends upon treatment of the primary cause which includes CAD & MI but also valvular problems like aortic stenosis and hypertension.
- Cor pulmonale – Untreated cor pulmonale can cause right heart failure from chronic pulmonary hypertrophy.
- Ventricular hypertrophy – Hypertrophy of the ventricle. Thickening of the myocardium (i.e., hypertrophy) can be physiological (a normal response) or pathological. An example of physiological hypertrophy is the result of significant athletic training (athletic heart syndrome).
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) – Hypertrophy of the left ventricle is more common than in the right and typically due to increased afterload on the heart such as from hypertension and aortic stenosis, but also from long standing mitral valve regurgitation. It can be diagnosed by echocardiography or ECG.
- Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) – Hypertrophy of the right ventricle and, it too, can be physiological from athletic training. Other causes include pulmonary hypertension and COPD as well as several congenital heart defects like ventricular septal defect, Tetralogy of Fallot and hypoplastic left heart syndrome.
- Heart cancer – Cancer of the heart is very rare and those cancers tend to be benign.
- Myxoma – Most common tumor of the heart. It is a benign tumor most commonly found in the left atrium and can be associated with Carney syndrome.
- Myocardial rupture and ventricular aneurysm – Rupture is a gross structural failure of the heart. Commonly a result of myocardial infarction that weakens the wall sufficiently to result in frank rupture and is typically seen 7–10 days after infarction. If not significant enough, the wall can develop into a ventricular aneurysm.
- Myocarditis – Infection and inflammation of the myocardium is myocarditis. Most causes are infectious (parvovirus B19, Lyme disease, Chagas disease), toxic (ethanol, anthracyclines, clozapine), or immunologic (systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, and some of the vasculitides (see below)). Definitive diagnosis requires a biopsy.
- Uhl anomaly – A congenital heart defect in which the right ventricular myocardium is too thin or absent. It is a very rare disorder.
- Cardiomyopathy – Cardiomyopathy is a deterioration of the myocardium. Several classifications have been used to categorize cardiomyopathies with the most common being primary vs. secondary, and dilated vs. restrictive vs. hypertrophic (presented below).
- Disorders of the pericardium
- Pericarditis – Inflammation of the pericardium that is typically idiopathic or infectious in nature (the membrane covering the heart). This inflammation is accompanied by swelling at the level of this membrane, in particular due to an excess of fluid circulating between the pericardium and the heart. The main symptoms of pericarditis are pain in the chest. These pains can occur suddenly, sharply and severely. The pain is usually worse at night when lying down and less when sitting. Treatment of viral & idiopathic pericarditis is NSAIDs or aspirin.
- Constrictive pericarditis – Pericarditis that constricts the expansion of the heart and inhibits heart function. Causes include infections (tuberculosis, fungus, parasites) and surgery. Definitive surgery is a pericardiectomy.
- Dressler syndrome – A form of pericarditis that develops 2–3 weeks after myocardial infarction and is accompanied by fever, pleuritic chest pain, and symptoms of pericarditis.
- Constrictive pericarditis – Pericarditis that constricts the expansion of the heart and inhibits heart function. Causes include infections (tuberculosis, fungus, parasites) and surgery. Definitive surgery is a pericardiectomy.
- Pericardial effusion – The serous pericardium normally contains fluid that reduces friction, but an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardium is called a pericardial effusion. The list of causes is lengthy but includes pericarditis, rheumatic diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus), trauma, and blood from myocardial rupture. If an effusion worsens then the fluid can inhibit heart function and symptoms of cardiac tamponade appear. Treatment includes pericardiocentesis to drain the fluid, if necessary, and treatment of the underlying cause.
- Pericardial tamponade – Tamponade is a medical emergency resulting from accumulation of fluid in the pericardium that inhibits heart function. Tamponade is a consequence of the fibrous pericardium being too inelastic to permit adequate heart expansion during diastole. The classic finding is pulsus paradoxus as well as Beck’s triad (low arterial blood pressure, distended neck veins, & soft heart sounds). Treatment is supportive until in a hospital where pericardiocentesis or a pericardial window can be performed to drain the fluid.
- Pericarditis – Inflammation of the pericardium that is typically idiopathic or infectious in nature (the membrane covering the heart). This inflammation is accompanied by swelling at the level of this membrane, in particular due to an excess of fluid circulating between the pericardium and the heart. The main symptoms of pericarditis are pain in the chest. These pains can occur suddenly, sharply and severely. The pain is usually worse at night when lying down and less when sitting. Treatment of viral & idiopathic pericarditis is NSAIDs or aspirin.
- Disorders of the heart valves
- Specific valvular problems – Specific problems of each valve.
- Aortic valve – Disorders and treatments of the aortic valve that separates the left ventricle and aorta.
- Aortic regurgitation / aortic insufficiency – Deficiency of the aortic valve that permits regurgitation from the aorta into the left ventricle.
- Aortic stenosis – Narrowing of the aortic valve opening that reduces blood flow through the valve. Stenosis commonly occurs from calcification of the valve, which happens prematurely in those with a bicuspid aortic valve. Stenosis of the aortic valve produces a harsh systolic murmur that classically radiates in the carotid arteries as well as pulsus parvus et tardus.
- Aortic valve replacement – Replacement of the aortic valve due to aortic regurgitation, aortic stenosis, or other reasons. A special kind of replacement called percutaneous aortic valve replacement is done through catheters are does not require open-heart surgery.
- Aortic valve repair – Repair, instead of replacement, of the aortic valve.
- Aortic valvuloplasty – Repair of the valve by using a balloon catheter to force it open.
- Mitral valve – Disorders and treatments of the mitral valve that separates the left atrium and left ventricle.
- Mitral valve prolapse – Prolapse of the mitral valve into the left atrium during ventricular systole.
- Mitral regurgitation / mitral insufficiency – Deficiency of the mitral valve that permits regurgitation from the left ventricle into the left atrium. Regurgitation produces a systolic murmur that radiates into the axilla.
- Mitral stenosis – Narrowing of the mitral valve opening that reduces blood flow through the valve.
- Mitral valve replacement – Replacement of the mitral valve due to mitral regurgitation, mitral stenosis, or other reasons.
- Mitral valve repair – Repair, instead of replacement, of the mitral valve.
- Mitral valvuloplasty – Repair of the valve by using a balloon catheter to force it open.
- Pulmonary valve – Disorders of the pulmonary valve that separates the right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
- Pulmonary regurgitation / pulmonary insufficiency – Deficiency of the pulmonary valve that permits regurgitation from the pulmonary artery into the right ventricle.
- Pulmonic stenosis – Narrowing of the pulmonary valve opening that reduces blood flow through the valve.
- Tricuspid valve – Disorders of the tricuspid valve that separates the right atrium and right ventricle.
- Tricuspid regurgitation / tricuspid insufficiency – Deficiency of the tricuspid valve that permits regurgitation from the right ventricle into the right atrium.
- Tricuspid stenosis – Narrowing of the tricuspid valve opening that reduces blood flow through the valve.
- Ebstein’s anomaly – A congenital heart defect that results in the tricuspid valve leaflets being deeper in the heart (toward the apex) than normal. The annulus of the valve is in the correct position, however, and the portion of the ventricle affected becomes “atrialized” with thinner walls. The right atrium becomes hypertrophied and can result in conduction defects (e.g., Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome).
- Tricuspid atresia – A congenital heart defect that results in the absence of the tricuspid valve
- Aortic valve – Disorders and treatments of the aortic valve that separates the left ventricle and aorta.
- Endocarditis – The thin, inner lining of the heart is the endocardium and inflammation of this layer is called endocarditis. Endocarditis commonly affects the heart valves.
- Infective endocarditis – Commonly affects the valves due to absence of blood supply to the heart valve, which results in a decreased immune response to the valve leaflets. Typically, bacteria cause infective endocarditis of the mitral valve, but intravenous drug users (e.g., heroin, methamphetamine) have an increased risk of infection of the tricuspid valve. Common signs include Janeway lesions (non-tender), Osler’s nodes (tender), and splinter hemorrhage of the nails.
- Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE) – Growths on the valves that are not from an infectious source and are composed of fibrin and platelets, and is associated with a history of rheumatic fever. The aortic valve is the most common valve affected (followed by mitral, tricuspid, & then pulmonary).
- Libman–Sacks endocarditis – A form of nonbacterial endocarditis specific to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and tends to affect the mitral valve (unlike NBTE which affects the aortic valve). It is the second most common heart finding in SLE after pericarditis
- Specific valvular problems – Specific problems of each valve.
- Congenital heart defects – defects in the structure of the heart which are present at birth and are often the result of aberrant embryological development. Defects can be syndromic or non-syndromic, with the later meaning defects that are isolated and not found in patterns (i.e., a syndrome). The top two syndromic causes of congenital heart defects are Noonan syndrome and Down syndrome. Down syndrome is more common than Noonan syndrome, but has a lower incidence of congenital heart defects, which makes Noonan syndrome the most common syndromic cause of congenital heart defects.
- Atrial septal defect (ASD) – Defect in the interatrial septum that permits blood flow between atria, including a patent foramen ovale (PFO).
- Bicuspid aortic valve – Formation of two valve leaflets in the aortic valve instead of three leaflets. This leads to aortic stenosis as the valve prematurely calcifies (as compared to calcification of a trileflet valve).
- Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) – Narrowing of the aorta, typically of the aortic arch and is classically found in Turner syndrome. A “complete” coarction is called an interrupted aortic arch.
- Cor triatriatum – A membrane that divides one of the atria results in “three” atria (hence “triatriatum“). This tends to affect the left atrium more than the right atrium. The membrane may be present without complete division of the atrium. It presents similarly to stenosis of the respective semilunar valve (i.e., tricuspid stenosis for right atrium).
- Dextrocardia – Dextrocardia is a condition in which the apex of the heart is on the right side of the body, instead of the left. This can exist in isolation or as a part of situs inversus in which the entire body is mirrored not just the heart. Situs inversus can be a part of primary ciliary dyskinesia (aka Kartagener syndrome) that has recurrent respiratory infections and male infertility. A simple chest xray is sufficient to diagnose dextrocardia, provided care is taken in marking the correct side of the radiograph.
- Ebstein’s anomaly – Malformation of the tricuspid valve (see above).
- Great artery defects – There are several conditions that affect the great arteries (e.g., double aortic arch, aberrant subclavian artery) that often result in problems with the trachea and breathing.
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome – Defect in the development of the left heart such that it is hypoplastic (under developed).
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) – Failure of the ductus arteriosus to close on birth.
- Patent foramen ovale (PFO) – An atrial septal defect in that the foramen ovale fails to close at birth.
- Persistent truncus arteriosus – Defect in that the truncus arteriosus fails to divide.
- Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) – Narrowing of the pulmonary valve that is the key finding in Noonan syndrome.
- Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) – Set of four anatomical abnormalities: pulmonary stenosis, overriding aorta, ventricular septal defect, and right ventricular hypertrophy.
- Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) – Abnormal spatial arrangement of the great vessels (superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and aorta).
- Uhl anomaly – Partial or total loss of the right ventricular wall.
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD) – Defect in the ventricular septum that permits blood flow between ventricles.
- Diseases of blood vessels – diseases of the blood vessels can be multidisciplinary in nature. For example, medical treatment of atherosclerosis tends to be managed by cardiologists while vascular surgery repairs aneurysms and stenotic arteries.
- Atherosclerosis – Thickening of an arterial wall due to increased cholesterol and macrophages (see above).
- Aneurysm – Balloon-like bulging of arteries (also possible of the heart: see ventricular aneurysm above).
- Aortic aneurysm – Aneurysm of the aorta, typically of the abdominal aorta (abdominal aortic aneurysm or AAA). They are associated with a smoking history and in connective tissue diseases (e.g., Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome). Current USPSTF recommendations are for a single abdominal ultrasound screening for a AAA in anyone 65 or older who has smoked. Surgical repair of a AAA is advised after it is larger than 5.0–5.5 cm because of concern for rupture that leads to death from internal bleeding.
- Cerebral aneurysm – Aneurysms of the arteries in the brain most commonly affect the anterior cerebral artery. Rupture of the aneurysm results in a subarachnoid hemorrhage and a very severe headache.
- Aortic dissection – Dissection along the length of the aorta between the layers of the aortic wall. Dissection of the ascending aorta (type A) is a surgical emergency while dissection of the descending aorta (type B) can possibly be managed medically. Dissection of the ascending aorta is an emergency because dissection may interrupt coronary blood flow and blood flow to the brain, neither of which tolerate ischemia particularly well.
- Aortic rupture – Frank rupture of the aorta is often fatal from internal bleeding. Rupture of the aorta can occur at the sites of aneurysm, but is also due to trauma and results in a traumatic aortic rupture.
- Carotid artery – Diseases of the carotid arteries:
- Carotid artery stenosis / carotid artery disease – Narrowing of the carotid artery, typically due to atherosclerosis.
- Carotid artery dissection – Dissection along the length of the carotid artery between the layers of the carotid wall and filled with blood.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) – Formation of a thrombus in a deep vein, commonly in the legs that may break loose, travel to the lungs, and occlude blood flow (pulmonary embolism) sufficient to interrupt oxygenation to the body.
- Traveller’s thrombosis / economy class syndrome: A DVT due to being sedentary during air travel.
- Microangiopathy – Disease of capillaries in which the walls become thick and weak, and result in bleeding and decreased blood flow. One very common cause is diabetes mellitus in which microangiopathy results in diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic neuropathy.
- Varicose veins – Veins that have become enlarged and tortuous with failed valves, commonly in the legs. Vericose veins have cosmetic concerns, but they may become painful. Surgery and sclerotherapy are two options for treating varicose veins.
- Vasculitis – Inflammation of blood vessels (veins & arteries) with a long list of causes.
- Aortitis – Inflammation of the aorta that can be seen in giant cell arteritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, rheumatoid arthritis, syphilis and Takayasu’s arteritis.
- Behçet’s disease – Affects small-sized vessels that often initially presents with oral aphthous ulcers, genital ulcers and uveitis, and can be fatal from ruptured aneurysms. Pericarditis is commonly seen with Behçet’s.
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA; formerly known as Churg-Strauss syndrome) – Affects small- & medium-sized vessels that often affects lungs, kidneys, & heart in those with a history of airway allergic hypersensitivity and p-ANCA antibodies.
- Giant-cell arteritis (GCA) / Temporal arteritis – Affects medium- & large-sized vessels of the head, typically branches of the external carotid artery and namely the temporal artery. Occlusion of the ophthalmic artery results in blindness. Suspicion of GCA necessitates immediate treatment with glucocorticoids and temporal artery biopsy.
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) – Affects small- & medium-sized vessels that often affects the lung & kidneys (RPGN) with classic saddle nose and c-ANCA antibodies.
- IgA vasculitis (IgAV; formerly known as Henoch-Schönlein purpura) – Affects small-sized vessels and produces palpable purpura and proteinuria from immunocomplex (IgA) deposition.
- Kawasaki disease – Affects medium-sized vessels mostly seen in young children with myocarditis, & pericarditis, and is the most common cause of acquired heart disease in children (results in coronary artery aneurysms). Myocardial infarction from coronary thrombosis is the most common cause of death from Kawasaki disease.
- Thromboangiitis obliterans – Affects small- & medium-sized vessels that is strongly associated with tobacco products. Pain, diminished pulses, gangrene and eventual amputation of affected hands and feet.
List of respiratory diseases
Acute upper respiratory infections
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| acute rhinitis , infectious rhinitis , acute rhinopharyngitis , infectious rhinopharyngitis, rhinitis | Acute rhinopharyngitis [colds] |
| Acute maxillary sinusitis (acute sinusitis ), acute frontal sinusitis acute sinusitis ethmoid , acute sphenoid sinusitis , acute pansinusitis | Acute sinusitis |
| Acute sore throat, streptococcal pharyngitis , acute pharyngitis nnb, acute pharyngitis | Acute pharyngitis |
| Acute tonsillitis , streptococcal tonsillitis , angina follicularis | Acute tonsillitis |
| Acute laryngitis , acute tracheitis , acute laryngotracheitis | Acute laryngitis and tracheitis |
| Acute obstructive laryngitis [ croup ], acute epiglottitis | Acute obstructive laryngitis [croup] and epiglottitis |
| Acute laryngopharyngitis , flu-like infection | Acute infections in multiple or unspecified locations of the upper respiratory tract |
Hypoxia: is a medical term used to refer to a lack of oxygen supply to the tissues of the body. Localized or generalized, hypoxia requires adequate medical management to avoid the onset of complications.
Influenza and Pneumonia (Lung infection)
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Bird flu | Influenza due to avian influenza viruses that have been proven |
| flu | Influenza from other known influenza viruses |
| – | Flu, viruses not detected |
| Viral pneumonia | Viral Pneumonia, not elsewhere classified |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Pneumonia due to Streptococcus pneumoniae |
| Haemophilus influenzae | Haemophilus influenzae pneumonia |
| Bacterial pneumonia | Bacterial pneumonia, not elsewhere classified |
| Pneumonia due to other infectious agents | Pneumonia due to other infectious agents, not elsewhere classified |
| Pneumonia in Diseases Classified Elsewhere | Pneumonia in Diseases Classified Elsewhere |
| Pneumonia, pathogen | Pneumonia, pathogen unspecified |
Other acute lower respiratory infections
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Acute bronchitis , acute tracheobronchitis | Acute bronchitis |
| Acute bronchiolitis | Acute bronchiolitis |
| – | Acute lower respiratory infection, unspecified |
Other diseases of the upper respiratory tract
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Rhinopathia vasomotorica, allergic rhinitis (hay fever, pollen allergy, pollinosis ) | Vasomotor and allergic rhinopathy |
| Chronic rhinitis, Ozaena, chronic nasopharyngitis, chronic pharyngitis, chronic pharyngitis | Chronic rhinitis, rhinopharyngitis, and pharyngitis |
| Chronic maxillary sinusitis, chronic maxillary sinusitis, chronic frontal sinusitis, chronic ethmoidal sinusitis, chronic sphenoidal sinusitis, chronic pansinusitis | Chronic sinusitis |
| Polyp of the nasal cavity, choanal polyp, nasopharyngeal polyp, polyposis nasalis deformans (Woakes syndrome, ethmoiditis) | Nasal polyp |
| Abscess, boils and carbuncles of the nose; Cyst or mucocele of the nose and sinus; Nasal septal deviation; Turbinate hypertrophy, perforation of the nasal septum, rhinolite | Other diseases of the nose and sinuses |
| Chronic tonsillitis, hyperplasia of the tonsils, hyperplasia of the pharynx (adenoid vegetation), almond stone, tonsil ulcer | Chronic diseases of the tonsils and tonsils |
| Peritonsillar abscess, peritonsillar phlegmon, tonsillar abscess, retrotonsillar abscess | Peritonsillar abscess |
| Chronic laryngitis, chronic laryngotracheitis | Chronic laryngitis and laryngotracheitis |
| Glottislähmung, laryngeal paralysis, vocal cord paralysis, polyp, Kehlkopfpolyp, vocal cord nodules (nodular chorditis, fibrinous chorditis, tuberous chorditis, teacher nodules, Singer nodules), Stimmlippengranulom, laryngeal edema, Reinke’s edema, laryngeal spasm, Laryngismus, croup, laryngeal stenosis | Diseases of the vocal folds and larynx, not elsewhere classified |
| Retropharyngeal, Parapharyngealabszess, Nasopharynxabszess, Rachenphlegmone, tornwaldt cyst | Other diseases of the upper respiratory tract |
Chronic lower respiratory diseases
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Bronchitis , tracheobronchitis | Bronchitis, not designated as acute or chronic |
| Chronic bronchitis | Simple and slimy-purulent chronic bronchitis |
| Bronchitis , tracheitis , tracheobronchitis | Unspecified chronic bronchitis |
| Pulmonary emphysema , McLeod syndrome ( unilateral emphysema , unilateral light lung ), panlobular emphysema ( panacinous emphysema ), centrilobular emphysema | Emphysema |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Other chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| Bronchial asthma , allergic bronchial asthma , allergic bronchitis , atopic asthma , exogenous allergic bronchial asthma ( extrinsic asthma ), nonallergic bronchial asthma , endogenous nonallergic bronchial asthma ( intrinsic asthma ), analgesic asthma , asthmatic bronchitis , late-onset asthma | bronchial asthma |
| Status asthmaticus ( acute severe bronchial asthma ) | Status asthmaticus |
| Bronchiectasis , bronchiolectasis | Bronchiectasis |
Lung diseases caused by exogenous substances
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Coal miners pneumoconiosis , anthracosis , anthracosilicosis , coal dust lung | Coal Miners Pneumoconiosis |
| Asbestosis | Pneumoconiosis due to asbestos and other inorganic fibers |
| silicosis | Pneumoconiosis due to fumed silica |
| Aluminosis , bauxite fibrosis , berylliosis , graphite fibrosis , siderosis , stannosis | Pneumoconiosis due to other inorganic dusts |
| – | Unspecified pneumoconiosis |
| Pneumoconiosis associated with tuberculosis | Pneumoconiosis associated with tuberculosis |
| Byssinosis , flat-worker’s disease , Cannabiose | Respiratory disease caused by specific organic dust |
| Allergic alveolitis , farmer’s lung (Drescher-lung, harvester-lung, Moldy hay disease), Bagassose (bagasse disease, bagasse pneumonitis ), bird breeders lung (pigeon fancier’s disease , pigeon fancier lung, budgerigar breeder’s disease , budgie breeders lung ), Suberosis (Cork worker disease, cork worker lung , cork peeler disease , cork peeler lung ),Malt worker lung , mushroom worker lung , maple bark peeler lung , humidifier lung (air conditioning lung), fish meal worker lung , cheese washer lung, coffee worker lung, furrier lung, sequoiosis , exogenous allergic alveolitis ( hypersensitive pneumonitis ) | Allergic alveolitis due to organic dust |
| – | Respiratory diseases caused by inhalation of chemical substances, gases, smoke and vapors |
| Aspiration pneumonia , lipid pneumonia | Pneumonia due to solid and liquid substances |
| Radiation pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis after exposure to radiation | Respiratory diseases caused by other exogenous substances |
Other diseases of the respiratory organs, mainly affecting the interstitium
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Adult respiratory distress syndrome ( Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome , ARDS, Hyaline Membrane Disease ) | Respiratory distress syndrome in adults [ARDS] |
| Acute pulmonary edema , pulmonary congestion | Pulmonary edema |
| Eosinophilic lung infiltrate ( Löffler syndrome (I), tropical eosinophilia , pulmonary eosinophilia ) | Eosinophilic pulmonary infiltrate, not elsewhere classified |
| Alveolar proteinosis , microlithiasis alveolaris pulmonum , acute interstitial pneumonia ( diffuse pulmonary fibrosis , fibrosing alveolitis , Hamman-Rich syndrome , idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis ), interstitial pneumonia | Other interstitial lung diseases |
Purulent and Necrotizing Lower Respiratory Diseases
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Pulmonary gangrene , pulmonary necrosis , lung abscess , mediastinal abscess | Abscess of the lungs and mediastinum |
| Pyothorax , pleural abscess , thoracic abscess , empyema , pyopneumothorax | Pyothorax |
Other diseases of the pleura
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Pleural effusion | Pleural effusion, not elsewhere classified |
| – | Pleural effusion in diseases classified elsewhere |
| Pleural plaques ( pleural thickening ) | Pleural plaques |
| Pneumothorax , spontaneous pneumothorax , tension pneumothorax | Pneumothorax |
| Chylothorax , fibrothorax , hemothorax , hemopneumothorax , hydrothorax | Other conditions of the pleura |
Other diseases of the respiratory system
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Mendelson’s syndrome | Respiratory diseases following medical intervention, not elsewhere classified |
| Respiratory failure | Respiratory failure, not elsewhere classified |
| Broncholithiasis , stenosis of the bronchus , Tracheobronchial dyskinesia , tracheobronchial collapse syndrome , ulcer of the bronchus , lung collapse , atelectasis , interstitial emphysema , mediastinal , Pneumolithiasis , Cystic lung disease (acquired), mediastinal , mediastinitis , displacement of the mediastinum , Relaxatio diaphragmatica , diaphragmatic paralysis , diaphragm inflammation | Other respiratory diseases |
Cancer list
Types of Cancer | List all of Cancers | Adult, Children, Head and neck, Digestive and Types of Blood Cancer
List of eye diseases and disorders
- Blepharospasm: is when your eyelids squeeze shut suddenly.
- Disorders of eyelid, tear apparatus and orbit: problems with the eyelids, tear production system, and the bony socket holding the eye.
- Conjunctival disorders: isorders are issues with the clear layer covering the white part of the eye.
- Disorders of sclera, cornea, iris and ciliary body: problems with the outer protective layer, clear front part, colored part, and muscle controlling the lens of the eye.
- Disorders of lens: problems with the part of the eye that helps focus on objects.
- Choroid and retinal disorders: issues with the back part of the eye where we see things.
- Glaucoma: high eye pressure leading to possible vision loss.
- Disorders of vitreous body and eyeball: problems inside the eye.
- Disorders of optic nerve and optic pathways: trouble with transmitting visual information.
- Disorders of eye muscles and disorders in binocular eye movement, accommodation and refraction: difficulty in moving eyes and focusing.
- Visual disturbances and blindness: problems seeing, potentially leading to blindness.
- Other disorders of the eye and adnexes (Other Eye and Adjacent Issues: Various additional eye-related problems).
List of genetic diseases (identified gene, unidentified gene)
Inherited diseases follow different inheritance patterns and are associated with different inheritance, recurrence and disease probabilities. A distinction is made between autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant inheritance from gonosomal and mitochondrial inheritance.
Autosomal recessive modes of inheritance
The peculiarity only appears if there is a change ( mutation ) in both copies of a certain gene on both chromosomes , i.e. That is, if the person in question has inherited one change from his biological father and one from his biological mother. The parents do not have to be affected, so the phenotype does not occur in every generation. The mutation does not have to be identical. If two mutations that can be distinguished by molecular genetics lead to the same loss of function in a gene, one speaks of compound heterozygosity . Examples of autosomal recessive inheritance are cystic fibrosis and albinismand phenylketonuria (PKU) (a defect in phenylalanine hydroxylase).
Autosomal recessive inherited diseases are mostly loss-of-function mutations . The causes of apparent deviations in autosomal recessive inheritance are pseudo-dominance , heterogeneity , isodisomy and the fact that heterozygotes with sick children are not included in the calculation. Typical examples are:
- Adrenogenital syndrome (AGS)
- Maple syrup disease
- Albinism
- Alkaptonuria
- Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency
- Galactosemia
- Hereditary fructose intolerance
- Hemochromatosis
- Joubert syndrome
- Cretinism
- Short rib polydactyly syndromes (types I, II, III, IV),
- Laurence-Moon-Biedl-Bardet syndrome ( LMBB syndrome )
- Cleft lip and palate
- Wilson disease
- Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS)
- Cystic fibrosis or cystic fibrosis
- Finnish type nephrotic syndrome
- Peters Plus Syndrome
- Phenylketonuria (PKU)
- Ribbing syndrome
- Thalassemia
- Xeroderma pigmentosum
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)
Autosomal dominant patterns of inheritance
Here an altered allele (alleles are the mutually and at the same time oppositely corresponding genes of a diploid chromosome set) on one of the two homologous chromosomes leads to the characteristic expression. The genetic information is available on one of the 44 autosomes and is inherited regardless of gender . So women and men are equally affected. The phenotype occurs in every generation. Examples are:
- Achondroplasia
- Apert syndrome
- Brachydactyly
- Huntington’s Disease (“St. Vitus’s Dance”)
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (types I – IV, VII A / B, VIII)
- Engelmann syndrome
- Erythropoietic protoporphyria
- Factor V Leiden mutation
- Familial hypercholesterolemia
- HMSN type I ( Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease )
- Malignant hyperthermia
- Marfan’s Syndrome
- Darier’s disease
- Multiple cartilaginous exostoses
- Type I myotonic dystrophy
- Neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen’s disease)
- Osteogenesis imperfecta (type I)
- Piebaldism
- Polydactyly
- Retinoblastoma
- Ruvalcaba-Myhre-Smith syndrome and
- Sickle cell anemia
- Tuberous sclerosis
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
Gonosomal modes of inheritance
Hereditary gonosomal diseases, i.e. those in which the change affects the sex chromosomes X or Y, are in most cases on the X chromosome , since the Y chromosome contains fewer genes. The X chromosome has 155 megabases, the Y chromosome 59 megabases. Using the example of X-linked inheritance , the following peculiarities become clear:
X-linked recessive
Girls / women are only affected if both X chromosomes are damaged, otherwise they are only carriers (conductors), d. In other words, they can pass on the changed X chromosome to their children, but do not develop a corresponding phenotype themselves. Girls / women can often compensate for the change on one X chromosome with their second X chromosome if it is not changed. Boys / men are affected if they inherit one of the changed X chromosomes from the phenotypically healthy mother, or one of the two changed X chromosomes from a phenotypically diseased mother, since boys / men definitely have one X chromosome from the Get a mother and have only this one. Boys / men are phenotypically affected more often, since girls / women compensate for the defect with the other X chromosome. Examples are glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G-6-PD deficiency),Hemophilia A and B (hemophilia), Lesch-Nyhan syndrome , Fabry disease , mucopolysaccharidosis type II, muscular dystrophy (Duchenne type, Becker-Kiener type), Norrie syndrome , retinitis pigmentosa , red-green blindness , septic granulomatosis , X- SCID (severe combined immune deficiency) and ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency ( urea cycle defect )
X-linked dominant
Boys / men are 50% affected if their mother is a carrier of a disease-causing allele on an X chromosome. If, on the other hand, both of their X chromosomes contain the disease-causing allele, all children are affected. Overall, girls / women are more frequently affected, as the probability of receiving an altered X chromosome is higher with two X chromosomes (one from the father, one from the mother) than with boys / men (one from the mother). Examples are familial phosphatemic rickets (also called idiopathic Debré-de-Toni-Fanconi syndrome or vitamin D-resistant rickets ), Rett syndrome and orofacio-digital syndrome type 1 .
Mitochondrial or extrachromosomal inheritance
About 0.1 percent of the DNA in a human cell is not in the nucleus, but in the mitochondria . Since egg cells, unlike sperm, have several hundred thousand mitochondria, mutations in the mitochondrial DNA are only inherited on the maternal side. The same applies to the chloroplasts of photosynthetically active organisms.
See also extrachromosomal inheritance
Diagnosis and treatment
If a hereditary disease is suspected, a human genetic test can provide clarity. The chromosomes are checked for numerical and structural changes. If there is an urgent suspicion of a certain genetic defect, a more extensive, complex investigation of individual gene constellations is also possible. The results can then be helpful in assessing the risk of inheritance.
If the genetic make-up is peculiar to itself, it is usually not possible to act on the causes with today’s medical options. Therefore advice is usually given regarding lifestyle, education about risk factors and symptomatic measures. These are then individual decisions, especially since it is not always an illness, but often a disposition.
For a few diseases, such as B. spinal muscular atrophy, there are first attempts at therapy.
History
The term genetic disease , which has only been used since the 20th century to mean genetic disease , was also often misused in the first half of the 20th century , including for alleged “diseases” such as “criminal tendencies” or “antisociality”. This thinking influenced sterilization programs and the euthanasia idea and found its extreme expression in German National Socialism, but was also present in many other countries such as the USA, England and France at the time. Today, only those diseases are called hereditary diseases that can be defined as clearly as possible and are very likely to be due to genetic defects.
Chromosome Related Inheritance Diseases for X and Y (Genetic Disorders)
Benign hereditary diseases
| illness | Inheritance | Chromosome / gene | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albinism | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 11 , locus q14-21, chromosome 15 , locus q11-13, chromosome 9 , locus p23, chromosome 5 , locus p13.3 | Lack of synthesis of melanin leads to light or white hair, eyes and skin color |
| Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 14 , locus q32.1 | An increased risk of liver cirrhosis or pulmonary emphysema due to a congenital lower concentration of this enzyme |
| Chorea huntington | Autosomal dominant | Chromosome 4 , locus p16.3 | Fatal motor and psychological disorder due to the increased incorporation of glutamine in the protein huntingtin |
| Galactosemia | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 9 | If left untreated, intracellular storage of galactose is often fatal due to the lack of the enzyme galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase |
| Hemophilia A. | X-linked | X chromosome | Increased bleeding tendency due to a lack of coagulation factor VIII |
| Hemophilia B. | X-linked | X chromosome | Increased bleeding tendency due to a lack of coagulation factor IX |
| cretinism | Autosomal recessive or dominant | Multiple genes, e.g. B. Chromosome 2 , locus q14.1 and chromosome 14 , locus q31.1 | Short stature, deformity of the limbs, speech disorders and intellectual disorders caused by a congenital deficiency of thyroid hormone ( thyroxine ) |
| Cleft lip and palate | Polygenetic | (multiple genes) | Congenital splitting of the lips, upper jaw, roof of the mouth, or a combination of these |
| Metachromatic Leukodystrophy | Polygenetically autosomal recessive | (multiple genes) | Unsteady gait, speech disorders due to lack of aryl sulfate |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type 1 | Polygenetically autosomal | (multiple genes) | Different symptoms, which only appear in childhood, due to the storage of glycosaminoglycans in cells. |
| Cystic fibrosis | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 7 , locus q31.2 | Dysfunction of the lungs and pancreas due to the formation of thick mucus, leading in the end stage to lung failure or pancreatic insufficiency |
| Neurofibromatosis | Autosomal dominant (spontaneous mutation in 50% of cases) | Chromosome 17 , locus q11.2 | Development of benign tumors on the skin, in the eyes and bones, and in the central nervous system |
| Phenylketonuria | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 12 , locus q22 to q24 | Impaired brain development and skull growth due to a lack of the enzyme phenyl alanine hydroxylase |
| Sickle cell anemia | Autosomal codominant | Chromosome 11 | Deformities of the red blood cells lead to painful crises; symptomatic only in the homozygous form |
| Spinal muscular atrophy | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 5 , locus q13 | Muscle wasting due to the loss of motor nerve cells in the spinal cord |
| Tay-Sachs syndrome | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 15 , locus q23-24 | Severe mental retardation with blindness from birth; the fewest children affected are older than three years |
| Cystic kidneys | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 16 | Development of multiple cysts in the kidneys from adulthood, leading to renal failure in the end-stage |
List of infectious diseases
Mental illness, mood disorders, personality disorders
Organic mental disorders, including symptomatic disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Dementia in Alzheimer’s disease (G30) | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Vascular dementia | Multiinfarct dementia, subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy, infarction |
| Dementia in other classified diseases | Pick disease (G31.0), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (A81.0), Chorea Huntington (G10), Parkinson’s disease (G20), AIDS (B22) |
| Unspecified dementia | – |
| Organic amnestic syndrome, not caused by alcohol or other psychotropic substances | Amnesia, Korsakov Syndrome |
| Delir, not caused by alcohol or other psychotropic substances | delirium |
| Other mental disorders due to brain damage or dysfunction or physical illness | Organic Psychosyndrome, Hallucination |
| Personality and behavioural disorder due to illness, damage or dysfunction of the brain | Frontal brain syndrome, personality disorders |
| Unspecified organic or symptomatic mental disorder | psychosis |
Mental and behavioral disorders related to the use of psychotropic substances
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by alcohol | Alcohol-related illness, Korsakov syndrome |
| Mental and behavioral disorders caused by opioids | opioid |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by cannabinoids | Cannabinoids |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by sedatives or hypnotics | Harmful use of benzodiazepines, sedative, hypnotic, sleep aids |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by cocaine | cocaine |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by other stimulants, including caffeine | Stimulant, Caffeine |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by hallucinogens | Hallucinogen, Horror trip |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by tobacco | tobacco |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by volatile solvents | – |
| Mental and behavioural disorders due to multiple substance use and use of other psychotropic substances | |
| description | Names of Complications (Additional to Encrypt * Code) |
| Acute Intoxication [Acute Intoxication] | intoxication |
| Harmful use | – |
| Dependency syndrome | Dependency syndrome |
| Withdrawal syndrome | – |
| Withdrawal syndrome with Delir | delirium |
| Psychotic disorder | Substance-induced psychosis |
| Amnestic syndrome | Korsakov syndrome |
Schizophrenia, schizotype and delusional disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| schizophrenia | Schizophrenia, catatonia, hebephrene schizophrenia |
| Schizotype Disorder | Schizotypic personality disorder |
| Persistent delusional disturbances | delusion |
| Acute transient psychotic disorders | psychosis |
| Induced delusional disorder | Induced delusional disorder |
| Schizoaffective disorders | Schizoaffective disorder |
Affective Disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Manic episode | Hypomania, Mania |
| Bipolar affective disorder | bipolar disorder |
| Depressive Episode | depression |
| Recurrent depressive disorder | depression |
| Persistent mood disorders | Zyklothymia, Dysthymia |
Neurotic, Stress and Somatoform Disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Phobic disorders | Agoraphobia, Social Phobia, Acrophobia, Specific Phobia, Phobic Disorder, List of Phobic Disorders |
| Other anxiety disorders | Panic disorder, Generalized anxiety disorder, anxiety and depressive disorder (mixed), other anxiety disorders |
| OCD | Obsessive compulsive disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, obsession |
| Reactions to severe loads and adaptation disorders | Post-traumatic stress disorder, Acute stress response, Adaptation disorder, Hospitalism |
| Dissociative Disorders [Conversion Disorders] | Fugue, Poriomania,Dromomania, Conversion Hysteria, Amnesia, Ganser Syndrome, Multiple Personality Disorder, Pseudodebility, Obsession, Conversion (Psychology) |
| Somatoform disorders | Somatoform disorder, somatoform pain disorder, briquet syndrome,psychogens: dysphagia, itching, bruxism, hyperventilation |
| Other neurotic disorders | Neurasthenia, Depersonalization, Derealization, Writing Spasms, Dhat Syndrome, Psychasthenia, Psychogenic Syncope (Medicine) |
Behavioural abnormalities with physical disorders and factors
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| eating disorders | Anorexia nervosa, bulimia, binge eating, pica syndrome, |
| Non-organic sleep disorders | Parasomnia, Primary Insomnia, Somnambulism, Pavor nocturnus |
| Sexual dysfunction not caused by an organic disorder or disease | Sexual Appetenz Disorder, Hypersexuality, Nymphomania, Satyriasis, Psychogens /-er: Vaginismus, Anorgasmia and Hyporgasmia, Impotence, Dyspareunia |
| Mental or behavioural disorders in the weekbed, not classified elsewhere | Postpartum mood crises |
| Psychological or behavioural factors in other classified diseases | z.B. in asthma, ulcerative colitis, dermatitis, stomach ulcers, mucomembranous colitis , urticaria (hives) |
| Harmful use of non-dependency-causing substances | drug or drug abuse, abusus, addiction or dependence; Withdrawal syndrome, withdrawal symptoms |
| Unspecified behavioural abnormalities in physical disorders and factors | – |
Personality and Behavioural Disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Specific personality disorders | paranoids, Schizoide, Borderline, Dissocial, Emotionally unstable, Histrionic, Anankatic (compulsive), Anxious (avoiding), Dependent (asthenic) and Other specific personality disorder (eccentric, baseless, narcissistic, passive-aggressive,psychoneurotic, immature) |
| Combined and other personality disorders | – |
| Persistent personality changes, not consequence of brain damage or disease | Complex post-traumatic stress disorder |
| Abnormal habits and disturbances of impulse control | Pathological play, pyromania, kleptomania, trichotillomania |
| Disorders of gender identity | Transsexualism, transvestitism while retaining both sex roles |
| Disorders of sexual preference | fetishism, fetishistic transvestitism, exhibitionism, voyeurism, paedophilia, sadomasochism,multiple disorders of sexual preference, other disorders of sexual preference(frotteurism, necrophilia) |
| Mental and behavioural disorders associated with sexual development and orientation | Sexual Maturation Crisis, Ichdystone Sexual Orientation,Sexual Relationship Disorder |
| Other personality and behavioural disorders | Development of physical symptoms for psychological reasons(retirement neurosis), artificial disorder |
Intelligence Reduction
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Light intelligence reduction | – |
| Medium-grade intelligence reduction | – |
| Heavy intelligence reduction | – |
| Heaviest intelligence reduction | – |
| Other intelligence reduction | – |
| Unspecified intelligence reduction | – |
Developmental Disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Described developmental disorders of speech and language | Articulation disorder (dyslaly), expressive speech disorder, prescription speech disorder, acquired aphasia with epilepsy (Landau-Kleffner syndrome) |
| Described developmental disorders of school skills | Reading and spelling disorder (dyslexia), Isolated spelling disorder, Numeracy disorder (dyscalculia), Combined disorders of school skills |
| Described developmental disturbance of motor functions | Dyspraxia |
| Combined defined developmental disorders | – |
| Deep developmental disorders | Early Childhood Autism, Atypical Autism, Rett Syndrome,Other Desintegrative Childhood Disorder(Heller’s Dementia),Overactive Disorder with Intelligence Reduction and Movement Stereotypes, Asperger’s Syndrome |
| Other developmental disorders | Developmental Agnosia (Agnosia) |
Behavioural and emotional disorders with the beginning of childhood and adolescence
| Description | Diseases and further articles |
| Hyperkinetic disorders | Simple activity and attention disorder, hyperkinetic disturbance of social behavior |
| Disorders of social behaviour | Disturbance of social behaviour limited to the family context, disturbance of social behaviour in the absence of social ties, disturbance of social behaviour in existing social ties, disturbance of social behaviour with oppositional, rebellious behaviour |
| Combined disturbance of social behaviour and emotions | Disorder of social behaviour with depressive disorder |
| Emotional disorders of childhood | Emotional disorder with fear of separation of childhood (fear ofseparation),phobic disorder of childhood(phobic disorder),disorder with social anxiety of childhood(social phobia),emotional disorder with sibling rivalry (sibling rivalry), |
| Disorders of social functions with the beginning of childhood and adolescence | Elective mutism, reactive bonding disorder of childhood(binding disorder), binding disorder of childhood with inhibition |
| Tic disorders | Temporary Tic Disorder, Chronic Motor or Vocal Tic Disorder, Combined Vocal and Multiple Motor Tics(Tourette Syndrome)) |
| Other behavioural and emotional disorders with the beginning of childhood and adolescence | Non-organic enuresis, non-organic copresis, feeding disorder in early childhood, pica in childhood (Pica syndrome), stereotypemovement disorders (stereotyping (medicine)), stuttering [stems], buzzing,Other more specific behavioral and emotional disorders with onset in childhood and adolescence (nose drilling, onychophagia, thumb sucking) |
List of rare diseases
| List of rare diseases: |
| A |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Below is a list of conditions . A condition is the collective name for symptoms, syndromes, clinical signs, diseases, disabilities and injuries.
A
- Abscess
- Acute Radiation Sickness
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Anthrax
- Appendicitis
- Allergy
- Ankylosing
- Arthritis
- Aseptic meningitis
- Asthma
- Astigmatism
- Atherosclerosis
B
- Bacterial meningitis
- B Virus (herpes B, monkey B virus, herpesvirus simiae, and herpesvirus B)
- Beriberi
- Black Death
- Botulism
- Breast cancer
- Bronchitis
- Brucellosis
- Bubonic plague
- Burnout Parental
- Bunion
- Boil
C
- Capgras delusion syndrome
- Campylobacter infection
- Cancer
- Candidiasis
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Coeliac disease (Celiac Disease)
- Cerebral palsy
- Chagas disease
- Chickenpox
- Chlamydia
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Cholera
- Chordoma
- Chorea
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Circadian rhythm sleep disorder
- Colitis
- Common cold
- Condyloma
- Congestive heart disease
- Coronary heart disease
- COVID-19
- Cowpox
- Crohn’s Disease
- Coronavirus
D
E
F
G
H
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Heart disease
- Hemorrhoids
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis D
- Hepatitis E
- Hepatitis G
- Histiocytosis (childhood cancer)
- HIV
- Human papillomavirus
- Huntington’s disease
- Hypermetropia
- Hyperopia
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroid
- Hypotonia
I
- Impetigo
- Infectious Diseases and Contagious (viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi, protozoa)
- Infertility
- Influenza
- Interstitial cystitis
- Iritis
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Ignious Syndrome
- Intestine ache
- Intestine Gas
- Intestine disease
- Upset Intestine
J
K
L
- Laryngitis
- Lead poisoning
- Legionellosis
- Leishmaniasis
- Leprosy
- Leptospirosis
- Listeriosis
- Leukemia
- Lice
- Loiasis
- Lung cancer
- Lupus erythematosus
- Lyme disease
- Lymphogranuloma venereum
- Lymphoma
- Limbtoosa
M
- Mad cow disease
- Malaria
- Marburg fever
- Measles
- Melanoma
- Metastatic cancer
- Meniere’s disease
- Meningitis
- Migraine
- Monkeypox
- Mononucleosis
- Multiple myeloma
- Multiple sclerosis
- Mumps
- Muscular dystrophy
- Myasthenia gravis
- Myelitis
- Myoclonus
- Myopia
- Myxedema
- Morquio Syndrome
- Mattticular syndrome
- Mononucleosis
N
O
P
- Palindromic rheumatism
- Paratyphoid fever
- Parkinson’s disease
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Peritonitis
- Periodontal disease
- Pertussis
- Phenylketonuria
- Plague
- Poliomyelitis
- Porphyria
- Progeria
- Prostatitis
- Psittacosis
- Psoriasis
- Pubic lice
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pilia
- pneumonia
- Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) | Rare Brain Disorder
Q
R
- Rabies
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome (herpes zoster oticus) affects the facial nerve near one of ears
- Repetitive strain injury
- Rheumatic fever
- Rheumatic heart
- Rheumatism
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rickets
- Rift Valley fever
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Rubella
S
- Salmonellosis
- Scabies
- Scarlet fever
- Sciatica
- Scleroderma
- Scrapie
- Scurvy
- Sepsis
- Septicemia
- SARS
- Shigellosis
- Shin splints
- Shingles
- Sickle-cell anemia
- Siderosis
- SIDS
- Silicosis
- Smallpox
- Stevens–Johnson syndrome
- STD – STI | List of Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Infections
- Stiff Person Syndrome
- Stomach flu
- Stomach ulcers
- Strabismus
- Strep throat
- Streptococcal infection
- Synovitis
- Syphilis
- Swine influenza
- Schizophrenia
- Stomach Gas
- Stomach Ache
- stomach Disease
- Kids Stomach Ache
- Upset Stomach
T
- Taeniasis
- Tay-Sachs disease
- Tennis elbow
- Teratoma
- Tetanus
- Thalassaemia
- Thrush
- Thymoma
- Tinnitus
- Tonsillitis
- Tooth decay
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Trichinosis
- Trichomoniasis
- Trisomy
- Tuberculosis
- Tubular Breast (Tuberous Breasts) Malformation of Breasts
- Tularemia
- Tungiasis
- Typhoid fever
- Typhus
- Tumor
U
V
- Varicella
- Varicose veins
- Vasovagal syncope
- Vitiligo
- Von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Viral fever
- Viral meningitis
W
- Warkany syndrome
- Warts
- Watkins
Y
Sources: PinterPandai, Health On the Net (NGO),
Notice:
Information in CleverlySmart.com is updated on a regular basis. It may happen that new discoveries are made in between updates and do not yet appear in the disease profile. The date of the last update is indicated. Professionals are always encouraged to consult the most recent publications before making any decisions based on the information provided.
Information in CleverlySmart.com is not intended to replace professional health care. CleverlySmart.comcannot be held responsible for harmful, truncated or erroneous use of any information found in the CleverlySmart.com database.
List of Diseases
This list of diseases groups together the main families of diseases. Disease is an alteration in the functions or health of a living organism. We speak as well of disease, referring to all the alterations in health, as of a disease, which then designates a particular entity characterized by causes, symptoms, development and specific therapeutic possibilities. A patient is a person suffering from a disease, whether it is determined or not. When it is the subject of medical care, we speak of a patient. Health and disease are linked to biological processes and to interactions with the social and environmental environment. Generally, disease is defined as an entity opposed to health, the negative effect of which is due to an alteration or disharmonization of a system at any level (molecular, bodily, mental, emotional, etc.) of the state. physiological or morphological considered as normal, balanced or harmonious. We can speak of faulty homeostasis.
This list of diseases groups together the main families of diseases
- List of dermatological diseases
- List of cardiovascular diseases
- List of respiratory diseases
- Cancer list
- List of eye diseases and disorders
- List of genetic or hereditary diseases (identified gene, unidentified gene)
- List of infectious diseases
- Mental illness (mood disorders, personality disorders)
- List of rare diseases
List of dermatological diseases
Signs can include itching, pain, and hyperhidrosis. Physical signs include: vitropression effect, Nikolsky’s sign, Wood’s lamp fluorescence, and Blaschko lines. Dermatological investigations include skin biopsy. Dermatological lesions Atrophies Bubbles Dyschromia Erythema (and exanthema) Keratosis Macules Nodules Papules Purpuras Pustules Dander Sclerosis Tumors Ulcerations Vegetations or condylomas Vesicles Dermatological pathologies Acanthosis nigricans Achromia Acne Alopecia Amyloidosis Angiodermatitis Stellate angioma Staphylococcal anthrax Aphthosis Atrophy Balanitis Behçet (disease of) Bowen’s disease Basal cell Carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Candidiasis Soft chancroid Rosacea Darier’s disease Degos (disease) Chronic actinic dermatitis Dermatitis herpetiformis Atopic dermatitis Dermatophytosis Perioral dermatitis Seborrheic dermatitis Dermographism Dyshidrosis Eczema Epidermolysis bullosa Erysipelas Erythema ab igne Erythema nodosum Fixed pigmented erythema Erythema multiforme Erythroderma Erythrasma Pressure sore Fiessinger-Leroy-Reiter (syndrome) Folliculitis Boil Scabies Gangrene Granuloma annulare Herpes Ichthyosis Impetigo Intertrigo Actinic keratosis Keratosis pilaris Leishmaniasis Meadow Leukokeratosis Lichen planus Scleroatrophic lichen Livedo Lupus erythematosus Lyell syndrome Plantar perforator Occupational disease Mastocytosis Melanoma Miliary Mucinosis Molluscum contagiosum Myases Lipoid necrobiosis Angioedema Panniculitis Papillonite Achromiant parakeratosis Guttate parapsoriasis Body pediculosis Scalp pediculosis Alopecia areata Bullous pemphigoid Pemphigus Perionyxis Perleche Photodermatosis Gibert’s rosé pityriasis Tinea versicolor Poikiloderma Porphyrias Prurigo Psoriasis Purpura rosacea Sarcoidosis Scarlet fever Sycosis Mouth-hand-foot syndrome Stevens-Johnson syndrome Syphilis Ringworm Bullous drug eruption Trombidiosis Tuberculosis Tungose Urticaria Varicella Necrotizing vasculitis Wart Vitiligo Vulvovaginitis Xanthoma Xeroderma pigmentosum Shingles.
This is a long list of skin problems. They can cause things like itching, pain, and sweaty skin. Some signs that doctors look for include changes when they press the skin, certain reactions under special lights, and patterns on the skin. Doctors might also take a small piece of skin to check. These skin problems can show up in different ways, like red spots, small bumps, or changes in skin color. Some problems are caused by things like infections or allergies, and others are more serious. It’s important to see a doctor if you have any skin concerns.
List of respiratory diseases
Acute upper respiratory infections
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| acute rhinitis , infectious rhinitis , acute rhinopharyngitis , infectious rhinopharyngitis, rhinitis | Acute rhinopharyngitis [colds] |
| Acute maxillary sinusitis (acute sinusitis ), acute frontal sinusitis acute sinusitis ethmoid , acute sphenoid sinusitis , acute pansinusitis | Acute sinusitis |
| Acute sore throat , streptococcal pharyngitis , acute pharyngitis nnb, acute pharyngitis | Acute pharyngitis |
| Acute tonsillitis , streptococcal tonsillitis , angina follicularis | Acute tonsillitis |
| Acute laryngitis , acute tracheitis , acute laryngotracheitis | Acute laryngitis and tracheitis |
| Acute obstructive laryngitis [ croup ], acute epiglottitis | Acute obstructive laryngitis [croup] and epiglottitis |
| Acute laryngopharyngitis , flu-like infection | Acute infections in multiple or unspecified locations of the upper respiratory tract |
Influenza and Pneumonia (Lung infection)
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Bird flu | Influenza due to avian influenza viruses that have been proven |
| flu | Influenza from other known influenza viruses |
| – | Flu, viruses not detected |
| Viral pneumonia | Viral Pneumonia, not elsewhere classified |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Pneumonia due to Streptococcus pneumoniae |
| Haemophilus influenzae | Haemophilus influenzae pneumonia |
| Bacterial pneumonia | Bacterial pneumonia, not elsewhere classified |
| Pneumonia due to other infectious agents | Pneumonia due to other infectious agents, not elsewhere classified |
| Pneumonia in Diseases Classified Elsewhere | Pneumonia in Diseases Classified Elsewhere |
| Pneumonia, pathogen | Pneumonia, pathogen unspecified |
Other acute lower respiratory infections
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Acute bronchitis , acute tracheobronchitis | Acute bronchitis |
| Acute bronchiolitis | Acute bronchiolitis |
| – | Acute lower respiratory infection, unspecified |
Other diseases of the upper respiratory tract
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Rhinopathia vasomotorica, allergic rhinitis (hay fever, pollen allergy, pollinosis ) | Vasomotor and allergic rhinopathy |
| Chronic rhinitis, Ozaena, chronic nasopharyngitis, chronic pharyngitis, chronic pharyngitis | Chronic rhinitis, rhinopharyngitis, and pharyngitis |
| Chronic maxillary sinusitis, chronic maxillary sinusitis, chronic frontal sinusitis, chronic ethmoidal sinusitis, chronic sphenoidal sinusitis, chronic pansinusitis | Chronic sinusitis |
| Polyp of the nasal cavity, choanal polyp, nasopharyngeal polyp, polyposis nasalis deformans (Woakes syndrome, ethmoiditis) | Nasal polyp |
| Abscess, boils and carbuncles of the nose; Cyst or mucocele of the nose and sinus; Nasal septal deviation; Turbinate hypertrophy, perforation of the nasal septum, rhinolite | Other diseases of the nose and sinuses |
| Chronic tonsillitis, hyperplasia of the tonsils, hyperplasia of the pharynx (adenoid vegetation), almond stone, tonsil ulcer | Chronic diseases of the tonsils and tonsils |
| Peritonsillar abscess, peritonsillar phlegmon, tonsillar abscess, retrotonsillar abscess | Peritonsillar abscess |
| Chronic laryngitis, chronic laryngotracheitis | Chronic laryngitis and laryngotracheitis |
| Glottislähmung, laryngeal paralysis, vocal cord paralysis, polyp, Kehlkopfpolyp, vocal cord nodules (nodular chorditis, fibrinous chorditis, tuberous chorditis, teacher nodules, Singer nodules), Stimmlippengranulom, laryngeal edema, Reinke’s edema, laryngeal spasm, Laryngismus, croup, laryngeal stenosis | Diseases of the vocal folds and larynx, not elsewhere classified |
| Retropharyngeal, Parapharyngealabszess, Nasopharynxabszess, Rachenphlegmone, tornwaldt cyst | Other diseases of the upper respiratory tract |
Chronic lower respiratory diseases
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Bronchitis, tracheobronchitis | Bronchitis, not designated as acute or chronic |
| Chronic bronchitis | Simple and slimy-purulent chronic bronchitis |
| Bronchitis , tracheitis , tracheobronchitis | Unspecified chronic bronchitis |
| Pulmonary emphysema , McLeod syndrome (unilateral emphysema , unilateral light lung), panlobular emphysema (panacinous emphysema), centrilobular emphysema | Emphysema |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Other chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| Bronchial asthma, allergic bronchial asthma, allergic bronchitis, atopic asthma, exogenous allergic bronchial asthma ( extrinsic asthma ), nonallergic bronchial asthma, endogenous nonallergic bronchial asthma (intrinsic asthma), analgesic asthma, asthmatic bronchitis, late-onset asthma | bronchial asthma |
| Status asthmaticus (acute severe bronchial asthma) | Status asthmaticus |
| Bronchiectasis, bronchiolectasis | Bronchiectasis |
Lung diseases caused by exogenous substances
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Coal miners pneumoconiosis , anthracosis , anthracosilicosis , coal dust lung | Coal Miners Pneumoconiosis |
| Asbestosis | Pneumoconiosis due to asbestos and other inorganic fibers |
| silicosis | Pneumoconiosis due to fumed silica |
| Aluminosis , bauxite fibrosis , berylliosis , graphite fibrosis , siderosis , stannosis | Pneumoconiosis due to other inorganic dusts |
| – | Unspecified pneumoconiosis |
| Pneumoconiosis associated with tuberculosis | Pneumoconiosis associated with tuberculosis |
| Byssinosis , flat-worker’s disease , Cannabiose | Respiratory disease caused by specific organic dust |
| Allergic alveolitis , farmer’s lung ( Drescher-lung , harvester-lung , Moldy hay disease ), Bagassose ( bagasse disease , bagasse pneumonitis ), bird breeders lung ( pigeon fancier’s disease , pigeon fancier lung , budgerigar breeder’s disease , budgie breeders lung ), Suberosis ( Cork worker disease , cork worker lung , cork peeler disease , cork peeler lung ),Malt worker lung , mushroom worker lung , maple bark peeler lung , humidifier lung (air conditioning lung), fish meal worker lung , cheese washer lung , coffee worker lung , furrier lung , sequoiosis , exogenous allergic alveolitis ( hypersensitive pneumonitis ) | Allergic alveolitis due to organic dust |
| – | Respiratory diseases caused by inhalation of chemical substances, gases, smoke and vapors |
| Aspiration pneumonia , lipid pneumonia | Pneumonia due to solid and liquid substances |
| Radiation pneumonitis , pulmonary fibrosis after exposure to radiation | Respiratory diseases caused by other exogenous substances |
Other diseases of the respiratory organs, mainly affecting the interstitium
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Adult respiratory distress syndrome ( Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome , ARDS, Hyaline Membrane Disease ) | Respiratory distress syndrome in adults [ARDS] |
| Acute pulmonary edema , pulmonary congestion | Pulmonary edema |
| Eosinophilic lung infiltrate ( Löffler syndrome (I), tropical eosinophilia , pulmonary eosinophilia ) | Eosinophilic pulmonary infiltrate, not elsewhere classified |
| Alveolar proteinosis , microlithiasis alveolaris pulmonum , acute interstitial pneumonia ( diffuse pulmonary fibrosis , fibrosing alveolitis , Hamman-Rich syndrome , idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis ), interstitial pneumonia | Other interstitial lung diseases |
Purulent and Necrotizing Lower Respiratory Diseases
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Pulmonary gangrene , pulmonary necrosis , lung abscess , mediastinal abscess | Abscess of the lungs and mediastinum |
| Pyothorax , pleural abscess , thoracic abscess , empyema , pyopneumothorax | Pyothorax |
Other diseases of the pleura
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Pleural effusion | Pleural effusion, not elsewhere classified |
| – | Pleural effusion in diseases classified elsewhere |
| Pleural plaques ( pleural thickening ) | Pleural plaques |
| Pneumothorax , spontaneous pneumothorax , tension pneumothorax | Pneumothorax |
| Chylothorax , fibrothorax , hemothorax , hemopneumothorax , hydrothorax | Other conditions of the pleura |
Other diseases of the respiratory system
| Names of diseases (synonyms) | description |
| Mendelson’s syndrome | Respiratory diseases following medical intervention, not elsewhere classified |
| Respiratory failure | Respiratory failure, not elsewhere classified |
| Broncholithiasis , stenosis of the bronchus , Tracheobronchial dyskinesia , tracheobronchial collapse syndrome , ulcer of the bronchus , lung collapse , atelectasis , interstitial emphysema , mediastinal , Pneumolithiasis , Cystic lung disease (acquired), mediastinal , mediastinitis , displacement of the mediastinum , Relaxatio diaphragmatica , diaphragmatic paralysis , diaphragm inflammation | Other respiratory diseases |
Cancer list
List of eye diseases and disorders
Disorders of eyelid, tear apparatus and orbit Conjunctival disorders Disorders of sclera , cornea , iris and ciliary body Disorders of lens Choroid and retinal disorders Glaucoma Disorders of vitreous body and eyeball Disorders of optic nerve and optic pathways Disorders of eye muscles and disorders in binocular eye movement, accommodation and refraction Visual disturbances and blindness Other disorders of the eye and adnexes
List of genetic diseases (identified gene, unidentified gene)
Inherited diseases follow different inheritance patterns and are associated with different inheritance, recurrence and disease probabilities. A distinction is made between autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant inheritance from gonosomal and mitochondrial inheritance.
Autosomal recessive modes of inheritance
The peculiarity only appears if there is a change ( mutation ) in both copies of a certain gene on both chromosomes , i.e. That is, if the person in question has inherited one change from his biological father and one from his biological mother. The parents do not have to be affected, so the phenotype does not occur in every generation. The mutation does not have to be identical. If two mutations that can be distinguished by molecular genetics lead to the same loss of function in a gene, one speaks of compound heterozygosity . Examples of autosomal recessive inheritance are cystic fibrosis and albinismand phenylketonuria (PKU) (a defect in phenylalanine hydroxylase). Autosomal recessive inherited diseases are mostly loss-of-function mutations . The causes of apparent deviations in autosomal recessive inheritance are pseudo-dominance , heterogeneity , isodisomy and the fact that heterozygotes with sick children are not included in the calculation. Typical examples are:
- Adrenogenital syndrome (AGS)
- Maple syrup disease
- Albinism
- Alkaptonuria
- Alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency
- Galactosemia
- Hereditary fructose intolerance
- Hemochromatosis
- Joubert syndrome
- Cretinism
- Short rib polydactyly syndromes (types I, II, III, IV)
- Laurence-Moon-Biedl-Bardet syndrome (LMBB syndrome)
- Cleft lip and palate
- Wilson disease
- Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS)
- Cystic fibrosis or cystic fibrosis
- Finnish type nephrotic syndrome
- Peters Plus Syndrome
- Phenylketonuria (PKU)
- Ribbing syndrome
- Thalassemia
- Xeroderma pigmentosum
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)
Autosomal dominant patterns of inheritance
Here an altered allele (alleles are the mutually and at the same time oppositely corresponding genes of a diploid chromosome set) on one of the two homologous chromosomes leads to the characteristic expression. The genetic information is available on one of the 44 autosomes and is inherited regardless of gender . So women and men are equally affected. The phenotype occurs in every generation. Examples are:
- Achondroplasia
- Apert syndrome
- Brachydactyly
- Huntington’s Disease (“St. Vitus’s Dance”)
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (types I – IV, VII A / B, VIII)
- Engelmann syndrome
- Erythropoietic protoporphyria
- Factor V Leiden mutation
- Familial hypercholesterolemia
- HMSN type I (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease)
- Malignant hyperthermia
- Marfan’s Syndrome
- Darier’s disease
- Multiple cartilaginous exostoses
- Type I myotonic dystrophy
- Neurofibromatosis (Recklinghausen’s disease)
- Osteogenesis imperfecta (type I)
- Piebaldism
- Polydactyly
- Retinoblastoma
- Ruvalcaba-Myhre-Smith syndrome and
- Sickle cell anemia
- Tuberous sclerosis
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
Gonosomal modes of inheritance
Hereditary gonosomal diseases, i.e. those in which the change affects the sex chromosomes X or Y, are in most cases on the X chromosome, since the Y chromosome contains fewer genes. The X chromosome has 155 megabases, the Y chromosome 59 megabases. Using the example of X-linked inheritance , the following peculiarities become clear:
X-linked recessive
Girls / women are only affected if both X chromosomes are damaged, otherwise they are only carriers (conductors), d. In other words, they can pass on the changed X chromosome to their children, but do not develop a corresponding phenotype themselves. Girls / women can often compensate for the change on one X chromosome with their second X chromosome if it is not changed. Boys / men are affected if they inherit one of the changed X chromosomes from the phenotypically healthy mother, or one of the two changed X chromosomes from a phenotypically diseased mother, since boys / men definitely have one X chromosome from the Get a mother and have only this one. Boys / men are phenotypically affected more often, since girls / women compensate for the defect with the other X chromosome. Examples are glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G-6-PD deficiency),Hemophilia A and B (hemophilia), Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, Fabry disease , mucopolysaccharidosis type II, muscular dystrophy (Duchenne type, Becker-Kiener type), Norrie syndrome, retinitis pigmentosa, red-green blindness, septic granulomatosis, X- SCID (severe combined immune deficiency) and ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency (urea cycle defect)
X-linked dominant
Boys / men are 50% affected if their mother is a carrier of a disease-causing allele on an X chromosome . If, on the other hand, both of their X chromosomes contain the disease-causing allele, all children are affected. Overall, girls / women are more frequently affected, as the probability of receiving an altered X chromosome is higher with two X chromosomes (one from the father, one from the mother) than with boys / men (one from the mother). Examples are familial phosphatemic rickets (also called idiopathic Debré-de-Toni-Fanconi syndrome or vitamin D-resistant rickets ), Rett syndrome and orofacio-digital syndrome type 1 .
Mitochondrial or extrachromosomal inheritance
About 0.1 percent of the DNA in a human cell is not in the nucleus, but in the mitochondria . Since egg cells, unlike sperm, have several hundred thousand mitochondria, mutations in the mitochondrial DNA are only inherited on the maternal side. The same applies to the chloroplasts of photosynthetically active organisms. See also extrachromosomal inheritance
Diagnosis and treatment
If a hereditary disease is suspected, a human genetic test can provide clarity. The chromosomes are checked for numerical and structural changes. If there is an urgent suspicion of a certain genetic defect, a more extensive, complex investigation of individual gene constellations is also possible. The results can then be helpful in assessing the risk of inheritance. If the genetic make-up is peculiar to itself, it is usually not possible to act on the causes with today’s medical options. Therefore advice is usually given regarding lifestyle, education about risk factors and symptomatic measures. These are then individual decisions, especially since it is not always an illness, but often a disposition . For a few diseases, such as B. spinal muscular atrophy, there are first attempts at therapy.
History
The term genetic disease , which has only been used since the 20th century to mean genetic disease , was also often misused in the first half of the 20th century , including for alleged “diseases” such as “criminal tendencies” or “antisociality”. This thinking influenced sterilization programs and the euthanasia idea and found its extreme expression in German National Socialism, but was also present in many other countries such as the USA, England and France at the time. Today, only those diseases are called hereditary diseases that can be defined as clearly as possible and are very likely to be due to genetic defects.
Benign hereditary diseases
| illness | Inheritance | Chromosome / gene | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albinism | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 11 , locus q14-21, chromosome 15 , locus q11-13, chromosome 9 , locus p23, chromosome 5 , locus p13.3 | Lack of synthesis of melanin leads to light or white hair, eyes and skin color |
| Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 14 , locus q32.1 | An increased risk of liver cirrhosis or pulmonary emphysema due to a congenital lower concentration of this enzyme |
| Chorea huntington | Autosomal dominant | Chromosome 4 , locus p16.3 | Fatal motor and psychological disorder due to the increased incorporation of glutamine in the protein huntingtin |
| Galactosemia | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 9 | If left untreated, intracellular storage of galactose is often fatal due to the lack of the enzyme galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase |
| Hemophilia A. | X-linked | X chromosome | Increased bleeding tendency due to a lack of coagulation factor VIII |
| Hemophilia B. | X-linked | X chromosome | Increased bleeding tendency due to a lack of coagulation factor IX |
| cretinism | Autosomal recessive or dominant | Multiple genes, e.g. B. Chromosome 2 , locus q14.1 and chromosome 14 , locus q31.1 | Short stature, deformity of the limbs, speech disorders and intellectual disorders caused by a congenital deficiency of thyroid hormone ( thyroxine ) |
| Cleft lip and palate | Polygenetic | (multiple genes) | Congenital splitting of the lips, upper jaw, roof of the mouth, or a combination of these |
| Metachromatic Leukodystrophy | Polygenetically autosomal recessive | (multiple genes) | Unsteady gait, speech disorders due to lack of aryl sulfate |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type 1 | Polygenetically autosomal | (multiple genes) | Different symptoms, which only appear in childhood, due to the storage of glycosaminoglycans in cells. |
| Cystic fibrosis | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 7 , locus q31.2 | Dysfunction of the lungs and pancreas due to the formation of thick mucus, leading in the end stage to lung failure or pancreatic insufficiency |
| Neurofibromatosis | Autosomal dominant (spontaneous mutation in 50% of cases) | Chromosome 17 , locus q11.2 | Development of benign tumors on the skin, in the eyes and bones, and in the central nervous system |
| Phenylketonuria | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 12 , locus q22 to q24 | Impaired brain development and skull growth due to a lack of the enzyme phenyl alanine hydroxylase |
| Sickle cell anemia | Autosomal codominant | Chromosome 11 | Deformities of the red blood cells lead to painful crises; symptomatic only in the homozygous form |
| Spinal muscular atrophy | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 5 , locus q13 | Muscle wasting due to the loss of motor nerve cells in the spinal cord |
| Tay-Sachs syndrome | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 15 , locus q23-24 | Severe mental retardation with blindness from birth; the fewest children affected are older than three years |
| Cystic kidneys | Autosomal recessive | Chromosome 16 | Development of multiple cysts in the kidneys from adulthood, leading to renal failure in the end-stage |
List of infectious diseases
Mental illness, mood disorders, personality disorders
Organic mental disorders, including symptomatic disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Dementia in Alzheimer’s disease (G30) | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Vascular dementia | Multiinfarct dementia, subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy, infarction |
| Dementia in other classified diseases | Pick disease (G31.0), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (A81.0), Chorea Huntington (G10), Parkinson’s disease (G20), AIDS (B22) |
| Unspecified dementia | – |
| Organic amnestic syndrome, not caused by alcohol or other psychotropic substances | Amnesia, Korsakov Syndrome |
| Delir, not caused by alcohol or other psychotropic substances | delirium |
| Other mental disorders due to brain damage or dysfunction or physical illness | Organic Psychosyndrome, Hallucination |
| Personality and behavioural disorder due to illness, damage or dysfunction of the brain | Frontal brain syndrome, personality disorders |
| Unspecified organic or symptomatic mental disorder | psychosis |
Mental and behavioral disorders related to the use of psychotropic substances
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by alcohol | Alcohol-related illness, Korsakov syndrome |
| Mental and behavioral disorders caused by opioids | opioid |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by cannabinoids | Cannabinoids |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by sedatives or hypnotics | Harmful use of benzodiazepines, sedative, hypnotic, sleep aids |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by cocaine | cocaine |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by other stimulants, including caffeine | Stimulant, Caffeine |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by hallucinogens | Hallucinogen, Horror trip |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by tobacco | tobacco |
| Mental and behavioural disorders caused by volatile solvents | – |
| Mental and behavioural disorders due to multiple substance use and use of other psychotropic substances | |
| description | Names of Complications (Additional to Encrypt * Code) |
| Acute Intoxication [Acute Intoxication] | intoxication |
| Harmful use | – |
| Dependency syndrome | Dependency syndrome |
| Withdrawal syndrome | – |
| Withdrawal syndrome with Delir | delirium |
| Psychotic disorder | Substance-induced psychosis |
| Amnestic syndrome | Korsakov syndrome |
Schizophrenia, schizotype and delusional disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Schizophrenia | Schizophrenia, catatonia, hebephrene schizophrenia |
| Schizotype Disorder | Schizotypic personality disorder |
| Persistent delusional disturbances | delusion |
| Acute transient psychotic disorders | psychosis |
| Induced delusional disorder | Induced delusional disorder |
| Schizoaffective disorders | Schizoaffective disorder |
Affective Disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Manic episode | Hypomania, Mania |
| Bipolar affective disorder | bipolar disorder |
| Depressive Episode | depression |
| Recurrent depressive disorder | depression |
| Persistent mood disorders | Zyklothymia, Dysthymia |
Neurotic, Stress and Somatoform Disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Phobic disorders | Agoraphobia, Social Phobia, Acrophobia, Specific Phobia, Phobic Disorder, List of Phobic Disorders |
| Other anxiety disorders | Panic disorder, Generalized anxiety disorder, anxiety and depressive disorder (mixed), other anxiety disorders |
| OCD | Obsessive compulsive disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, obsession |
| Reactions to severe loads and adaptation disorders | Post-traumatic stress disorder, Acute stress response, Adaptation disorder, Hospitalism |
| Dissociative Disorders [Conversion Disorders] | Fugue, Poriomania,Dromomania, Conversion Hysteria, Amnesia, Ganser Syndrome, Multiple Personality Disorder, Pseudodebility, Obsession, Conversion (Psychology) |
| Somatoform disorders | Somatoform disorder, somatoform pain disorder, briquet syndrome,psychogens: dysphagia, itching, bruxism, hyperventilation |
| Other neurotic disorders | Neurasthenia, Depersonalization, Derealization, Writing Spasms, Dhat Syndrome, Psychasthenia, Psychogenic Syncope (Medicine) |
Behavioural abnormalities with physical disorders and factors
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| eating disorders | Anorexia nervosa, bulimia, binge eating, pica syndrome, |
| Non-organic sleep disorders | Parasomnia, Primary Insomnia, Somnambulism, Pavor nocturnus |
| Sexual dysfunction not caused by an organic disorder or disease | Sexual Appetenz Disorder, Hypersexuality, Nymphomania, Satyriasis, Psychogens /-er: Vaginismus, Anorgasmia and Hyporgasmia, Impotence, Dyspareunia |
| Mental or behavioural disorders in the weekbed, not classified elsewhere | Postpartum mood crises |
| Psychological or behavioural factors in other classified diseases | z.B. in asthma, ulcerative colitis, dermatitis, stomach ulcers, mucomembranous colitis , urticaria (hives) |
| Harmful use of non-dependency-causing substances | drug or drug abuse, abusus, addiction or dependence; Withdrawal syndrome, withdrawal symptoms |
| Unspecified behavioural abnormalities in physical disorders and factors | – |
Personality and Behavioural Disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Specific personality disorders | paranoids, Schizoide, Borderline, Dissocial, Emotionally unstable, Histrionic, Anankatic (compulsive), Anxious (avoiding), Dependent (asthenic) and Other specific personality disorder (eccentric, baseless, narcissistic, passive-aggressive,psychoneurotic, immature) |
| Combined and other personality disorders | – |
| Persistent personality changes, not consequence of brain damage or disease | Complex post-traumatic stress disorder |
| Abnormal habits and disturbances of impulse control | Pathological play, pyromania, kleptomania, trichotillomania |
| Disorders of gender identity | Transsexualism, transvestitism while retaining both sex roles |
| Disorders of sexual preference | fetishism, fetishistic transvestitism, exhibitionism, voyeurism, paedophilia, sadomasochism,multiple disorders of sexual preference, other disorders of sexual preference(frotteurism, necrophilia) |
| Mental and behavioural disorders associated with sexual development and orientation | Sexual Maturation Crisis, Ichdystone Sexual Orientation,Sexual Relationship Disorder |
| Other personality and behavioural disorders | Development of physical symptoms for psychological reasons(retirement neurosis), artificial disorder |
Intelligence Reduction
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Light intelligence reduction | – |
| Medium-grade intelligence reduction | – |
| Heavy intelligence reduction | – |
| Heaviest intelligence reduction | – |
| Other intelligence reduction | – |
| Unspecified intelligence reduction | – |
Developmental Disorders
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Described developmental disorders of speech and language | Articulation disorder (dyslaly), expressive speech disorder, prescription speech disorder, acquired aphasia with epilepsy (Landau-Kleffner syndrome) |
| Described developmental disorders of school skills | Reading and spelling disorder (dyslexia), Isolated spelling disorder, Numeracy disorder (dyscalculia), Combined disorders of school skills |
| Described developmental disturbance of motor functions | Dyspraxia |
| Combined defined developmental disorders | – |
| Deep developmental disorders | Early Childhood Autism, Atypical Autism, Rett Syndrome,Other Desintegrative Childhood Disorder(Heller’s Dementia),Overactive Disorder with Intelligence Reduction and Movement Stereotypes, Asperger’s Syndrome |
| Other developmental disorders | Developmental Agnosia (Agnosia) |
Behavioural and emotional disorders with the beginning of childhood and adolescence
| description | Diseases and further articles |
| Hyperkinetic disorders | Simple activity and attention disorder, hyperkinetic disturbance of social behavior |
| Disorders of social behaviour | Disturbance of social behaviour limited to the family context, disturbance of social behaviour in the absence of social ties, disturbance of social behaviour in existing social ties, disturbance of social behaviour with oppositional, rebellious behaviour |
| Combined disturbance of social behaviour and emotions | Disorder of social behaviour with depressive disorder |
| Emotional disorders of childhood | Emotional disorder with fear of separation of childhood (fear ofseparation),phobic disorder of childhood(phobic disorder),disorder with social anxiety of childhood(social phobia),emotional disorder with sibling rivalry (sibling rivalry), |
| Disorders of social functions with the beginning of childhood and adolescence | Elective mutism, reactive bonding disorder of childhood(binding disorder), binding disorder of childhood with inhibition |
| Tic disorders | Temporary Tic Disorder, Chronic Motor or Vocal Tic Disorder, Combined Vocal and Multiple Motor Tics(Tourette Syndrome)) |
| Other behavioural and emotional disorders with the beginning of childhood and adolescence | Non-organic enuresis, non-organic copresis, feeding disorder in early childhood, pica in childhood (Pica syndrome), stereotypemovement disorders (stereotyping (medicine)), stuttering [stems], buzzing,Other more specific behavioral and emotional disorders with onset in childhood and adolescence (nose drilling, onychophagia, thumb sucking) |
List of rare diseases
Below is a list of conditions . A condition is the collective name for symptoms, syndromes, clinical signs, diseases, disabilities and injuries.
A
- Abscess
- Acute Radiation Sickness
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Anthrax
- Appendicitis
- Allergy
- Argyll Robertson Pupil | The pupillary response to light is weak
- Arthritis
- Aseptic meningitis
- Asthma
- Astigmatism
- Atherosclerosis
B
- Bacterial meningitis
- Beriberi
- Black Death
- Botulism
- Breast cancer
- Bronchitis
- Brucellosis
- Bubonic plague
- Bunion
- Burnout | How to recognize the early signs?
- Boil
C
- Campylobacter infection
- Cancer
- Candidiasis
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Coeliac disease
- Cerebral palsy
- Chagas disease
- Chickenpox
- Chlamydia
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Cholera
- Chordoma
- Chorea
- Chromosome Related Inheritance Diseases for X and Y (Genetic Disorders)
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Circadian rhythm sleep disorder
- Colitis
- Common cold
- Condyloma
- Congestive heart disease
- Coronary heart disease
- COVID-19
- Cowpox
- Crohn’s Disease
- Coronavirus
D
E
F
- Fibromyalgia
- Foodborne illness
- Fragile X syndrome (FXS) or Martin Bell Syndrome (MBS) causes intellectual disability, behavioral problems, and physical abnormalities
G
H
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Heart diseases
- Hemianopsia
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis D
- Hepatitis E
- Histiocytosis (childhood cancer)
- HIV
- Human papillomavirus
- Huntington’s disease
- Hypermetropia
- Hyperopia
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroid
- Hypotonia
I
- Iritis
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Ignious Syndrome
- Intestine ache
- Intestine Gas
- Intestine disease
- Upset Intestine
J
K
L
- Laryngitis
- Lead poisoning
- Legionellosis
- Leishmaniasis
- Leprosy
- Leptospirosis
- Listeriosis
- Leukemia
- Lice
- Loiasis
- Lung cancer
- Lupus erythematosus
- Lyme disease
- Lymphogranuloma venereum
- Lymphoma
- Limbtoosa
M
- Mad cow disease
- Malaria
- Marburg fever
- Measles
- Melanoma
- Metastatic cancer
- Meniere’s disease
- Meningitis
- Migraine
- Mononucleosis
- Multiple myeloma
- Multiple sclerosis
- Mumps
- Muscular dystrophy
- Myasthenia gravis
- Myelitis
- Myoclonus
- Myopia
- Myxedema
- Morquio Syndrome
- Mattticular syndrome
- Mononucleosis
N
O
P
- Palindromic rheumatism
- Paratyphoid fever
- Parkinson’s disease
- PEComa (Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor) | Non-cancerous soft tissue tumors and Malignant Pecomas
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Peritonitis
- Periodontal disease
- Pertussis
- Phenylketonuria
- Plague
- Poliomyelitis
- Porphyria
- Presbyopia (old eyes)
- Progeria
- Prostatitis
- Psittacosis
- Psoriasis
- Pubic lice
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pilia
- pneumonia
Q
R
- Rabies
- Red eyes
- Retinal diseases
- Repetitive strain injury
- Rheumatic fever
- Rheumatic heart
- Rheumatism
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rickets
- Rift Valley fever
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Rubella
S
- Salmonellosis
- Scabies
- Scarlet fever
- Sciatica
- Scleroderma
- Scleritis (Sclera is the white part of eyeball) eye diseases
- Scrapie
- Scurvy
- Sepsis
- Septicemia
- SARS
- Shigellosis
- Shin splints
- Shingles
- Sickle-cell anemia
- Siderosis
- SIDS
- Silicosis
- Smallpox
- Stevens–Johnson syndrome
- Stomach flu
- Stomach ulcers
- Strabismus (crossed eyes)
- Strep throat
- Streptococcal infection
- Synovitis
- Syphilis
- Swine influenza
- Schizophrenia
- Stomach Gas
- Stomach Ache
- stomach Disease
- Kids Stomach Ache
- Upset Stomach
T
- Taeniasis
- Tay-Sachs disease
- Tennis elbow
- Teratoma
- Testicle pain
- Tetanus
- Thalassaemia
- Thrush
- Thymoma
- Tinnitus
- Tonsillitis
- Tooth decay
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Trichinosis
- Trichomoniasis
- Trisomy (Down syndrome)
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Tungiasis
- Typhoid fever
- Typhus
- Tumor
U
V
- Varicella
- Varicose veins
- Vasovagal syncope
- Vitiligo
- Von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Viral fever
- Viral meningitis
W
Y
Information: Cleverly Smart is not a substitute for a doctor. Always consult a doctor to treat your health condition.
Sources: PinterPandai, Health On the Net (NGO), Notice: Information in CleverlySmart.com is updated on a regular basis. It may happen that new discoveries are made in between updates and do not yet appear in the disease profile. The date of the last update is indicated. Professionals are always encouraged to consult the most recent publications before making any decisions based on the information provided available in your own country. Information in CleverlySmart.com is not intended to replace professional health care. CleverlySmart.com cannot be held responsible for harmful, truncated or erroneous use of any information found in the CleverlySmart.com database.
Photo credit: Public Domain Pictures