Lipoma
A lipoma is a benign tumor made up of fat that usually doesn’t cause any complications. It is above all embarrassing for the person affected aesthetically when it is located at the level of the skin. The origin of this type of tumor is not well known. This pathology mainly affects adults between 40 and 60 years old. Treatment, when necessary, is surgery.
It comes in the form of a soft ball to the touch, they are generally soft to the touch, stretchy, and painless. The fat inside is exactly the same as normal subcutaneous fat. Variable in size, it can appear on different parts of the body: in particular on the neck, torso, arms or breasts, when it is a skin lipoma. But it can exist almost anywhere inside the body (stomach, lungs, brain, liver, etc.). This is a benign tumor that grows gradually. Unlike malignant tumors, cells in a lipoma do not migrate to other organs and do not metastasize. They are most often small, and 80% of them are less than 5 cm, the others do not exceed 10 cm.
Is it painful?
In the vast majority of cases, the lipoma is asymptomatic: there are no symptoms and it is not painful. However, experts estimate that this benign fatty tumor is painful in 25% of cases: it may in particular be a question of a lipoma located near a nerve, causing nerve pain.
Warning: more rarely, we can observe the development of a neural fibrolipoma (also called fibrolipomatous hamartoma) which corresponds to the development of a lipoma in a nerve, causing pain and paresthesias – tingling … Even more rarely (in less in 1% of cases), the lipoma develops in a joint (especially in the knee) and the pain is then mechanical: it occurs during movement.
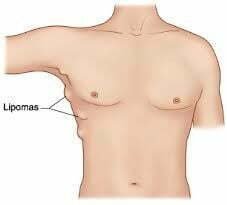
Is it cancer?
The lipoma is defined as a “non-cancerous tumor of the soft tissues”: there is therefore no question of alarming!
On the other hand, a consultation with a dermatologist is necessary if the lipoma becomes painful, if it changes in appearance (if it grows, if it changes color or if it is deformed, for example), if it becomes hard in the touch, or if it becomes mobile (if it “rolls” under the fingers) or immobile (if it gives the impression of “sticking” to the tissues). The lipoma only becomes cancerous in very rare cases!
Types of lipoma and their variants
- Subcutaneous: tumors that look like soft balls of fat under the skin. This is the most common form.
- Other benign lipomas are much less common. It can be:
- Fibrolipomas.
- Benign mesenchymoma.
- Lipoblastoma: occurring in infants or children under 3 years old.
- Pleomorphic lipoma: especially in men over 45 years old.
- Heterotopic: these are lipomas containing fat cells associated with other types of cells, from other tissues. They can be intramuscular lipomas, arborescent lipomas, neural fibrolipomas, parosteal lipomas…
- Hibernomas: These are made up of a particular fat, brown fat.
- Malignant tumors of the lipoma family.
- They are much rarer than benign lipomas:
- Liposarcoma which can be well differentiated, or dedifferentiated.
- Myxoid liposarcoma.
- Pleomorphic liposarcoma.
Read also: Are Rheumatism and Gout the Same Disease? | Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis, Stages
Cause
The cause is not completely clear. They tend to run in families, so genetic factors probably play a role in their development.
When it occurs, it is because fat cells or adipocytes have multiplied there. The origin of this proliferation of fat-storing cells remains unexplained. The genetic factor (heredity) seems to play a role in their occurrence, but the triggering mechanism and other factors involved are not known. Their evolution towards spontaneous healing is also a mystery.
Some people can be suffering from lipomatosis: in this case they have several lipomas on the body.
What are the symptoms of lipoma?
It can vary depending on the type of lipoma and its location. On examination, a lipoma is a ball of soft or elastic consistency, well defined, and of varying size. Sometimes the tumor is accompanied by pain. The pains are quite rare, they result from the compression of other tissues located nearby.
What is the diagnosis?
Observation and palpation of a soft lump in an area of the body may direct the doctor or dermatologist to a lipoma. A lipoma is a mass of soft or elastic consistency and mobile with respect to surrounding structures, non-inflammatory and well demarcated. When it is superficial, an ultrasound can make a diagnosis and know if there is a risk of it turning out to be cancerous. In the case of deep lipomas, an MRI may be necessary.
A biopsy confirms the diagnosis: a tumor fragment is taken and then analyzed.
What are the treatments?
The choice of treatment depends on the nature of the lipoma and its location. While the lipoma does not cause any discomfort, it does not require any special treatment.
It is, however, advisable to watch for a lipoma that is not being operated on to see if it does not get bigger, or if it becomes bothersome.
Treatment of a troublesome lipoma involves surgery, liposuction, or removal of the lipoma (lipectomy). When a lipoma is operated on, it is then routinely sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Liposuction causes less scarring, but it leaves the envelope of the lipoma in place and puts you at risk of recurrence.
In the case of numerous subcutaneous lipomas, or in the case of a person who cannot undergo surgery, an alternative consists in injecting corticosteroids into the lipoma so as to reduce its volume.
What are the complementary approaches to lipoma?
Homeopathy.
In homeopathy, it is proposed to treat lipomas mainly with the help of two substances: Thuya occidentalis and / or Baryta carbonica (which also acts on warts or acne), especially in the case of lipomas located in the neck and back.
Information: Cleverly Smart is not a substitute for a doctor. Always consult a doctor to treat your health condition.
Sources: PinterPandai, NHS UK, Mayo Clinic,
Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons
Photo explanations (main photo): Lipoma on the forearm.




It is essential to distinguish common lipomas from liposarcoma especially the well-differentiated one.
Currently, it is differentiated by testing for MDM2 (murine double minute-2) gene amplification which essentially requires a biopsy.[5] They share similar characteristics, although the latter poses a greater risk to the patient. As mentioned earlier, while treatment is not always necessary, if it is decided that a patient should seek treatment, then the options are typically steroid injections or excision of the tumor.