Tubular Breast (Tuberous Breasts)
Tubular breast or tuberous breasts are a growth disorder of the female or male breast caused by the presence of abnormal breast tissue that prevents proper growth.
This growth disorder results in an asymmetrical breast, often of small size, and several typical peculiarities.
This disorder of the shape of the breast causes significant psychological, social and intimate repercussions. To date, researchers have not been able to confirm a clear cause for the development of the disease.
Certain clinical features indicate the diagnosis of tuberous breasts:
1 ° Anomaly in shape: A cylindrical shape of one or both breasts: the breast or breasts are said to be tube-shaped.
2 ° Anomaly of segment 3: The lower part of the breast or segment 3 does not develop due to the presence of abnormal tissue called a striation ring or fibrous ring. The growth of segment 3 is prevented and the mammary gland enlarges in the shape of a tube or tubercle.
3 ° Anomaly in the height of the submammary folds: The submammary fold of the tuberous breast spreads less and is often found higher than that of the contralateral breast.
4 ° Areola anomaly: The areola of a tuberous breast is often very large and protruding. The ring of striation present in segment 3 prevents the expansion of the mammary gland in the lower part of the breast, which consequently develops into herniation through the skin of the areola which is allowed to stretch.
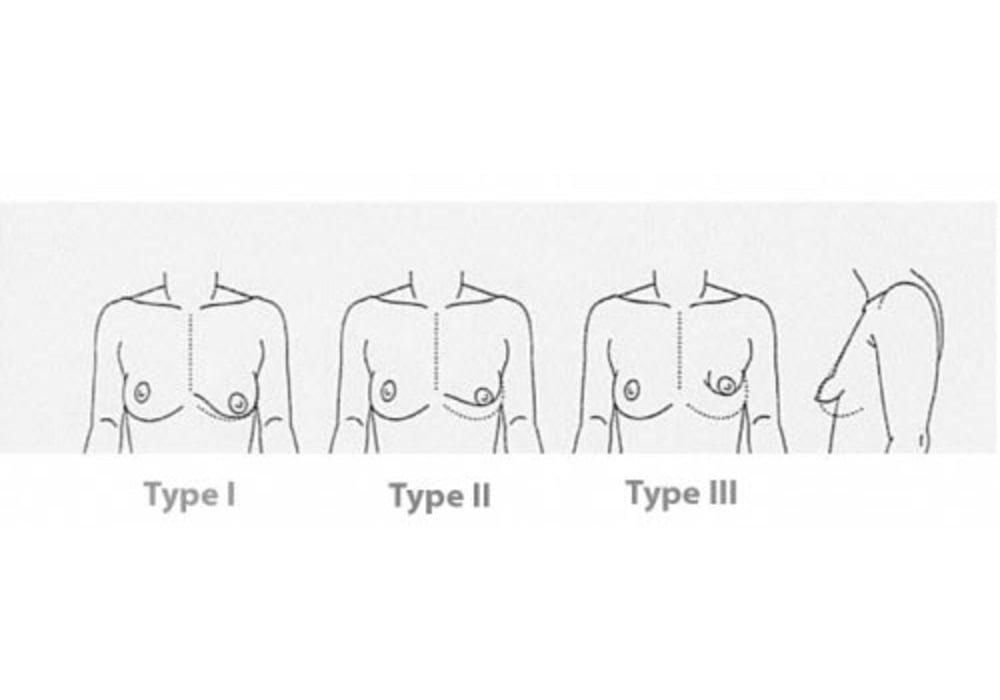
What are the different stages of a tuberous breast?
There are several classifications of tuberous breasts, the most commonly used is Professor Grolleau’s classification published in 1999.
Stage 1: Absence of the infero-internal part of the breast (internal segment 3) with anomaly of the areola.
Stage 2: Absence of the entire lower part of the breast (segment 3) with ascension of the inframammary fold and anomaly of the areola.
Stage 3: Absence of the 4 quadrants of the breast, aspect of the breast in the form of a tube, too large and protruding areola, ascended inframammary fold, reduction in breast width.
Goals
Repair the growth disorders of tuberous breasts by creating a pretty, natural breast and harmonious volume.
Restore well-being and self-confidence: The patients regain a pretty breast and feel much better from the first intervention.
What are the good candidates for tuberous breast surgery?
All women with tuberous breasts who are complexed by their breasts.
WHAT ARE THE PREOPERATIVE STEPS?
Progress of the preoperative consultation
Doctor will assesses the psychological impact and wishes of each patient.
Doctor will examines the breast and draws up a list of abnormalities in each breast.
At the end of the consultation:
- A first treatment plan is proposed with the number and order of necessary interventions including:
- One or more breast lipofilling sessions.
- Placement of breast implants.
- The repair and repositioning of the areolas.
- Doctor will draft a request for prior agreement with health insurance.
What are the management criteria for tuberous breasts?
The non-development of the lower part of the breasts.
Tube-shaped breasts.
The asymmetry of volume greater than a bra cup.
What are the preoperative examinations?
A mammogram is mandatory for all patients over 25 years old. Before 25 years, a breast ultrasound is sufficient.
A blood test: blood cells, hemostasis, kidney, liver, serologies and blood group.
A consultation with the anesthesiologist.
PROCEDURE OF THE INTERVENTION
The treatment of tuberous breasts at a glance
The duration of the intervention depends on the surgical procedure (s) to be performed.
Arrival at the clinic is 2 hours before the start of the procedure.
A betadine shower is not necessary.
Doctor will take the photos and makes the preoperative drawings.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
What are the possible treatments for a tuberous breast?
The surgical treatment of tuberous breasts has changed completely in recent years: since the advent of breast lipofilling, the treatment of tuberous breasts is much more effective and more reliable.
The complete treatment of tuberous breasts is a combination of different possibilities depending on each patient.
Every flaw in a breast can be corrected:
Failure to develop the lower part of the breast (segment 3).
The height asymmetry of the inframammary folds.
Areolas that are too large, looking down and not at the same height.
Too small and uneven breast volumes.
Breast lipofilling associated with fasciotomies: almost systematic due to the absence of scars, the absence of an implant and its “preparatory” function for the placement of breast implants in a second step.
Breast lipofilling associated with “fasciotomies” is the first-line treatment for tuberous breasts.
Fasciotomies involve “cutting” the fibrous ring without opening the skin with a needle. Part of the breast lipofilling is placed inside the fibrous ring which has been previously broken by “needles” to prevent its recurrence.
The rest of the breast lipofilling is deposited in all the remaining breast tissue, and in particular at the level of segment 3.
Lipofilling relaxes the skin of segment 3, the breast tissue of segment 3 and the fibrous ring to prevent the appearance of a “double groove” after placement of a breast implant.
Glandular plasty: necessary for stage 3 tuberous breasts, but the advent of lipofilling associated with “fasciotomies” significantly reduces the need for glandular plasty.
The glandular plasty which is the open technique to break the fibrous ring. This is streaked or removed directly with an electronic scalpel.
Areolar plastic surgery: Necessary if the width, positioning or areolar asymmetry is inconvenient.
Areolar reconstruction involves repositioning the areolas at the same height and on the axis of the breasts, and decreasing the areolar diameter to form areolas of about 38 millimeters in diameter.
Breast augmentation with breast implants: necessary for shaping, rounding and enlarging tuberous breasts.
The placement of low projection breast implants to preserve the natural side of the end result and avoid the appearance of a double fold.
What are the different scars possible for the treatment of tuberous breasts?
Treatment of tuberous breasts usually requires inconspicuous scarring:
- Or a peri-areolar scar to insert breast implants.
- Or a round block scar, that is to say complete peri-areolar to reduce or raise the areolas.
- Or an “inverted T” scar, for tuberous breasts which are strongly sagging.
What are the risks of tubular breast surgery?
Fortunately, complications from tuberous breast surgery are very rare. The vast majority of patients are very satisfied with the results obtained. However, complications are unpredictable, and can occur even when the surgeon has the skill set required to perform plastic, reconstructive and cosmetic surgery.
Complications depending on the surgical technique
These are the complications of mammary plasties, breast prostheses and lipofilling. For more information, refer to the corresponding chapters.
Complications specific to tuberous breast surgery
Most often, it is a lack of results. Even if the appearance is greatly improved, defects may persist or appear:
- appearance of double contour at the lower pole of the breast (GRADE 2, 3): this insufficiency is due to the memory of the skin which has been detached to recreate a lower submammary fold. The skin cannot be distended by the prosthesis or by the glandular plasty. The double contour can be corrected secondarily either by new glandular plasties or by injection of fat (lipofilling).
- protrusion of the areola: it may reappear after the procedure, and touch-up may correct it.
Areolas still too large: distension of periareolar scars is possible, resulting in an enlarged appearance of the entire areola. A scar recovery corrects the problem.
Information: Cleverly Smart is not a substitute for a doctor. Always consult a doctor to treat your health condition.
Sources: PinterPandai, Medical News Today, National Library of Medicine, Medical Solutions Barcelona, The American Society of Plastic Surgeons Wolters Kluwer Health, HealthLine, Oxford University Press
Photo credit: Centre Médical Esthetique La Valentine 3