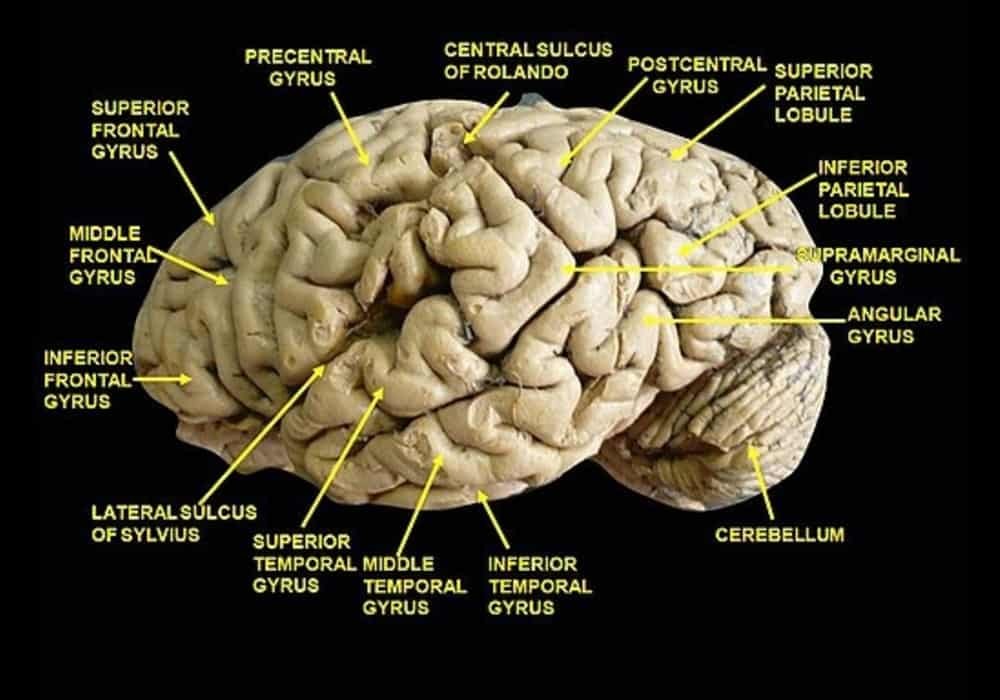
Brain Gyrus and Sulcus
Gyri and sulci are the folds and indentations of the brain that give it its wrinkled appearance.
Gyri (singular: brain gyrus) are the folds or bumps in the brain and the sulci (singular: sulcus) are the indentations or grooves or pleated.
The folding of the cerebral cortex creates gyri and grooves that separate regions of the brain and increase the surface area and cognitive capacity of the brain.
An example of a gyrus is Broca’s gyrus, an area of the brain that orchestrates the production of speech.
Gyri and sulci form boundaries within and between the lobes of the brain and divide it into two hemispheres.
The medial longitudinal fissure is the sulcus that separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The corpus callosum is located in this fissure. The 2 most important central nervous system (CNS) controls most functions of the body and mind. It consists of two parts: the brain and the spinal cord.
What is a gyrus?
The brain has an overall wrinkled appearance, consisting of many ridges and indentations. A gyrus (plural: gyri) is the name given to the bumps ridges on the cerebral cortex (the outermost layer of the brain).
Gyri are found on the surface of the cerebral cortex and are made up of grey matter, consisting of nerve cell bodies and dendrites.
They are unique structures that are important as they increase the surface area of the brain. A larger surface area means that more neurons can be packed into the cortex so that it can process more information. Ultimately, cognitive functions will be better with gyri without having to increase the actual brain size, which would not fit into a skull.
The layout and the size of gyri vary from person to person, although there are certain types of gyri which are found in everyone. Although, these types of gyri can vary in size and location between individuals.
There are specific types of gyri which are necessary to the brain’s function. For instance, the precentral gyrus is important as being the primary motor center of the brain.
Another important area is the superior temporal gyrus which holds Wernicke’s area an area vital for language development and the comprehension of speech.
As gyri are important to the structure of the brain, they have clinical significance. For example, some abnormalities with gyri can result in disorders such as epilepsy.
What is a sulcus?
A sulcus (plural: sulci) is another name for a groove in the cerebral cortex. Each gyrus is surrounded by sulci and together, the gyri and sulci help to increase the surface area of the cerebral cortex and form brain divisions.
They form brain divisions by creating boundaries between the lobes, so these are easily identifiable, as well as serving to divide the brain into two hemispheres.
A sulcus is a shallow groove that surrounds a gyrus, whereas sulci that are larger or deeper are given the term fissures.
The longitudinal fissure is the large furrow which divides the two hemispheres into left and right. A smooth-surfaced cortex would only be able to increase to a certain extent, therefore sulci in the surface area allows for continued growth, overall increasing brain function.
There are two types of sulci which are formed at different times. The primary sulci (e.g. the central sulcus) are formed independently before birth. Secondary sulci, however, are those formed by other factors other than the growth in adjoining areas of the cortex (e.g. the parieto-occipital sulci).
Sulci can also be defined in terms of their depth. A complete sulcus is a sulcus where the groove is very deep (e.g. the collateral sulcus), whereas an incomplete sulcus are not very deep (e.g. the paracentral sulcus).

Functions of Brain gyrus and sulcus
The cerebral gyri and sulci perform two very important functions: they increase the area of the cerebral cortex and they form brain divisions.
The increased surface area of the brain allows more neurons to be packed into the cortex so that it can process more information. Gyri and sulci form brain divisions by creating boundaries between the lobes of the brain and dividing the brain into two hemispheres.
Lobes of the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is divided into the following four lobes, each of which performs several important functions.
- Frontal lobes: The frontal lobes are located in the foremost region of the cerebral cortex. They are vital for motor control, thinking and reasoning.
- Parietal lobes: The parietal lobes are positioned above the temporal lobes near the center of the brain and they process sensory information.
- Temporal lobes: The temporal lobes are placed behind the frontal lobes. They are important for the production of language and speech as well as for the processing of memory and emotions.
- Occipital Lobes: The occipital lobes are found in the posterior region of the cerebral cortex and are the primary centers of visual processing.
- Gyri and sulci are very important features of the central nervous system. Folding the cerebral cortex creates these ridges and grooves that serve to separate brain regions and increase cognitive ability.
Read also: Brain Lobes | The Main Parts of the brain that control various activities and Their Functions
Sulci brain or fissure
Sulci brain or fissure cracks (In anatomy, a fissure is a deep, elongated groove or tear in various parts of the body).
Below is a list of several key furrows / fissures in the brain and the divisions they create:
- Interhemispheric (Medial longitudinal fissure): This is a deep groove located in the center of the brain that separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The corpus callosum, a large ribbon of nerves, is located in this fissure.
- Sylvius fissure (lateral sulcus): This deep grove separates the parietal and temporal lobes.
- Central sulcus (Rolando’s fissure): This sulcus separates the parietal and frontal lobes.
- Collateral sulcus: This sulcus separates the fusiform gyrus and the hippocampal gyrus on the underside of the temporal lobes.
- Parieto-occipital sulcus: This deep crevice separates the parietal and occipital lobes.
- Calcarine Sulcus: This groove is located in the occipital lobes and divides the visual cortex.

Brain Gyrus
Below are a number of important brain gyri.
- Angular gyrus: This fold in the parietal lobe is the area of the brain that helps in processing auditory and visual stimuli. He is also involved in the understanding of language.
- Broca’s Gyrus (Broca’s Area): This area of the brain, located in the left frontal lobe in most individuals, controls motor functions involved with speech production.
- Cingulate Gyrus: This arch-shaped fold in the brain is located above the corpus callosum. It is a component of the limbic system that processes sensory input concerning emotions and regulates aggressive behavior.
- Fusiform Gyrus: This bulge, located in the temporal and occipital lobes, consists of lateral and medial parts. It is thought to play a role in facial and word recognition.
- Hippocampal Gyrus (Parahippocampal Gyrus): This fold on the inner surface of the temporal lobe borders the hippocampus. The hippocampal gyrus surrounds the hippocampus and plays an important role in memory.
- Lingual gyrus: This coil of the occipital lobe is involved in visual processing. The lingual gyrus is bordered by the calcarine sulcus and the collateral sulcus. Anteriorly, the lingual gyrus is continuous with the parahippocampal gyrus and together they form the medial part of the fusiform gyrus.
Sources: PinterPandai, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Frontiers Media, Oxford University Press
Human Brain: How It Works and Ways to Improve Your Cognitive Function