Lean Startup | Definition, Principles, and Implementation Guide
The Lean Startup is a business development method designed to shorten product development cycles, reduce waste, and increase the chances of building products that truly meet customer needs. Whether you’re launching a tech startup, a physical product, or even a new service inside a large company, this methodology provides a flexible, repeatable approach to innovation.
What Is Lean Startup?
The Lean Startup approach is a validated learning process that focuses on building a minimum viable product (MVP), measuring user response, and learning whether to pivot or persevere. The goal is to avoid building something nobody wants by testing assumptions early with real customers.
Originally introduced by Eric Ries in his best-selling book The Lean Startup, this method allows entrepreneurs and organizations to iterate quickly and cost-effectively. Instead of investing months or years developing a product, you bring a version to market early, collect feedback, and improve it rapidly.

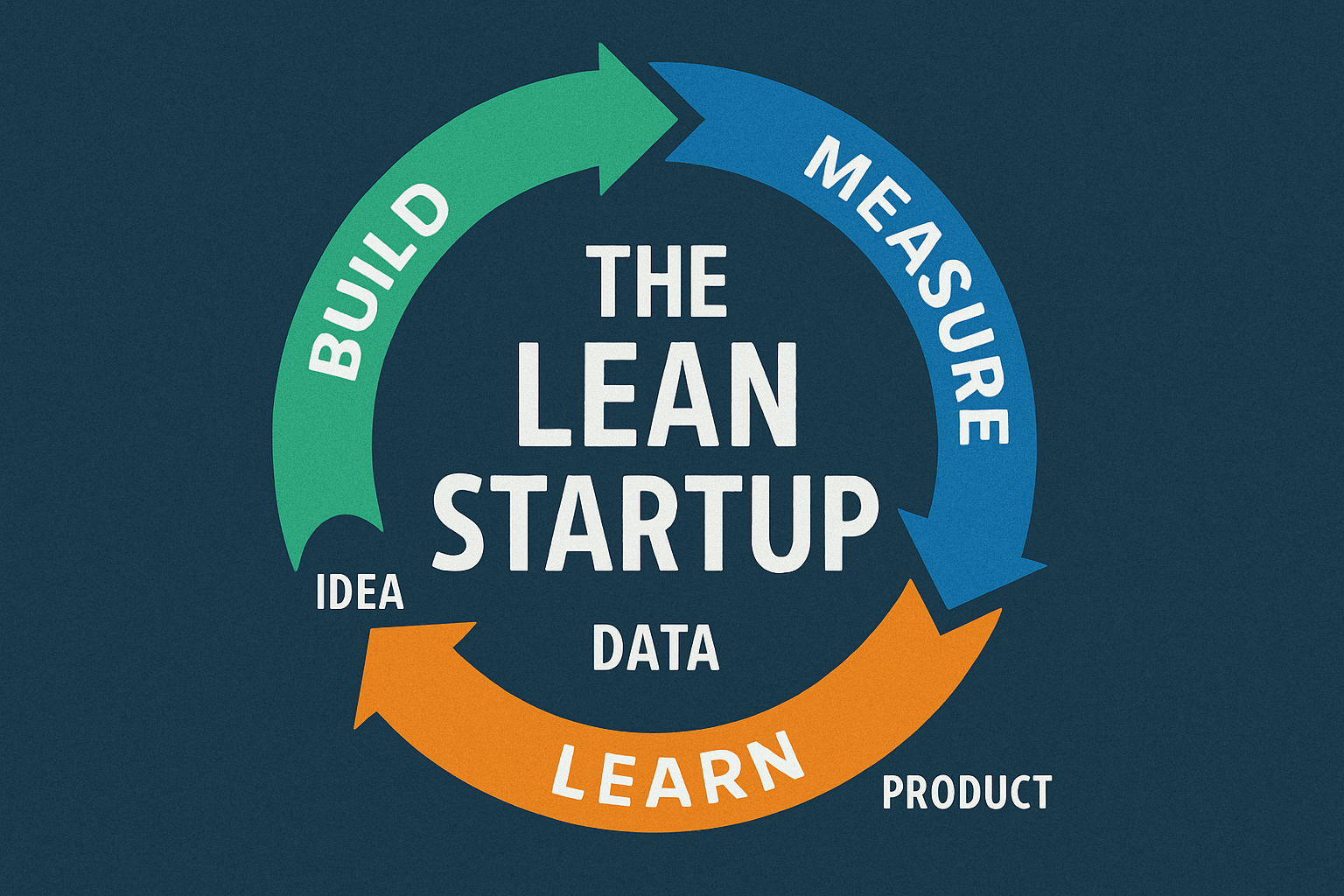
The Lean Startup Process in 3 Key Steps
1. BUILD – Create Your Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Don’t wait until everything is perfect to launch. Start with an MVP — the simplest version of your product that solves the core problem for users.
🎯 The MVP should be functional, not flawless. Focus on validating your assumptions.
Ways to build an MVP include:
A landing page
A clickable prototype
A simple video demo
A mock-up or wireframe
A live webinar or feedback session
Use this phase to test your initial hypotheses about the market, the problem, and your solution.
2. MEASURE – Collect Feedback and Learn
Once your MVP is in the hands of potential users, collect as much feedback as possible.
Ask:
Do users understand your value proposition?
What frustrates them?
What do they love about it?
Would they pay for it or recommend it?
💬 Every form of feedback, especially critical comments, is valuable. It means someone is interested enough to care.
Experiment with:
A/B testing
Crowdfunding campaigns
Free trials
Surveys and interviews
Chatbots, forms, and landing pages
Social media engagement metrics
At this stage, focus on customer behavior, not opinions. What they do is more important than what they say.
3. LEARN – Adapt and Iterate
Analyze what you’ve learned from your users. Does your product or service solve the problem effectively? If not, it might be time to pivot — adjust your offer, your audience, or even your entire business model.
Key questions to ask:
Does my audience understand what I’m offering?
Are they willing to pay for it?
Would they recommend it to others?
🔁 Repeat the Build-Measure-Learn cycle until you find your product-market fit — when customer demand matches what you’re offering.
Once you’ve validated the product, you can scale your operations confidently and invest in growth with less risk.

Origins of the Lean Startup Method
The Lean Startup draws inspiration from Lean Manufacturing, a method pioneered by Toyota post-World War II. The goal was to eliminate all forms of waste in production — including time, materials, and effort.
Eric Ries adapted these principles to the startup world, emphasizing speed, learning, and market responsiveness. He observed that many startups failed because they built products based on assumptions, not actual customer needs.
Common Challenges in Starting a Business
Startups typically face three key issues:
Lack of time to fully develop an idea before running out of resources.
Unvalidated assumptions, leading to products no one wants.
Lack of customers, due to poor problem-solution fit or unclear messaging.
The Lean Startup method addresses these problems by encouraging founders to test and adapt continuously — minimizing cost and risk.
Before You Start: Define Your Hypotheses
Before you build anything, define:
The problem you’re solving
The solution you propose
What makes your solution unique or valuable
Your ideal customer segment
How success will be measured (KPIs)
This clarity allows you to focus on what really matters, instead of spending time and money building unnecessary features.
Tips for Implementing Lean Startup
✅ Be ready to discard ideas that don’t work
✅ Test with real customers, not just friends or internal teams
✅ Be transparent and open to critique
✅ Stay agile — adjust your product and business model as needed
✅ Use low-cost tools to validate early ideas
Final Thoughts
The Lean Startup is more than just a methodology; it’s a mindset. It empowers entrepreneurs, innovators, and product teams to build customer-centric solutions by minimizing waste, testing ideas early, and learning fast. By focusing on validated learning, you avoid building something nobody wants — and increase your chances of real-world success.
Whether you’re just starting or already running a business, applying the Lean Startup approach could be the key to smarter innovation and sustainable growth.
Quality Management and its System QMS – Total quality and compliance control
Sources: PinterPandai, University Lab Partners, Investopedia
Photo powered by chatGPT