Hypoxia
Hypoxia is a medical term used to refer to a lack of oxygen supply to the tissues of the body. Localized or generalized, hypoxia requires adequate medical management to avoid the onset of complications.
What are the different types of hypoxia?
It can be classified according to various parameters including their origin. We distinguish in particular:
- cerebral, which is an insufficient supply of oxygen to the brain.
- fetal, which is oxygen deficiency in the fetus.
- hypoxemic, which is a drop in the partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2).
- hypoxia of anemia, which results from a decrease in the level of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood.
- circulatory, which is associated with a problem with blood flow;
- cytotoxic, which is caused by changes in respiratory enzymes that cause tissues to fail to use oxygen.
What are the causes of hypoxia?
- anemia, including for example iron deficiency anemia and vitamin deficiency anemia.
- certain respiratory diseases such as chronic bronchopneumopathy, pulmonary embolism or
- pulmonary infarction.
- certain congenital heart disease.
- hemorrhage or shock.
- heart failure.
- hypoventilation.
- carbon monoxide poisoning.
- certain poisons such as cyanide.
- stays at altitude.
- decompression sickness.
Read also? Oximeter | How does it work? What is Normal Range of Blood Oxygen Level?
Who is concerned ?
It is a phenomenon that can occur in many people. Nevertheless, some risk factors have been identified. The risk of hypoxia is particularly greater in:
- people with asthma;
- people at risk of anemia, such as the elderly, pregnant women and nursing mothers;
- people with cardiovascular risk;
- divers;
- smokers.
What is the risk of complications?
Because of the importance of oxygen for the proper functioning of the body, hypoxia can cause complications such as:
cyanosis, which is characterized by the appearance of a bluish coloration in the skin and mucous membranes;
neurological lesions, which may in particular be responsible for memory disorders.
In the most severe cases, hypoxia can lead to anoxia, which is the absence of oxygen in the tissues. Anoxia is a medical emergency because it exposes the body to serious complications such as:
- heart failure;
- a cerebrovascular accident (stroke);
- irreversible brain damage;
- a coma.
Oximeter | How does it work? What is Normal Range of Blood Oxygen Level?
What are the symptoms of hypoxia?
- nausea
- headache or headache
- hyperventilation
- tachycardia
- behavioral problems.
What are the treatments for hypoxia?
Treatment for hypoxia depends on its origin, course, and severity. It usually relies on the administration of oxygen, which can be done in different ways depending on the abnormality identified.
Supplemental oxygen supply can be done by using:
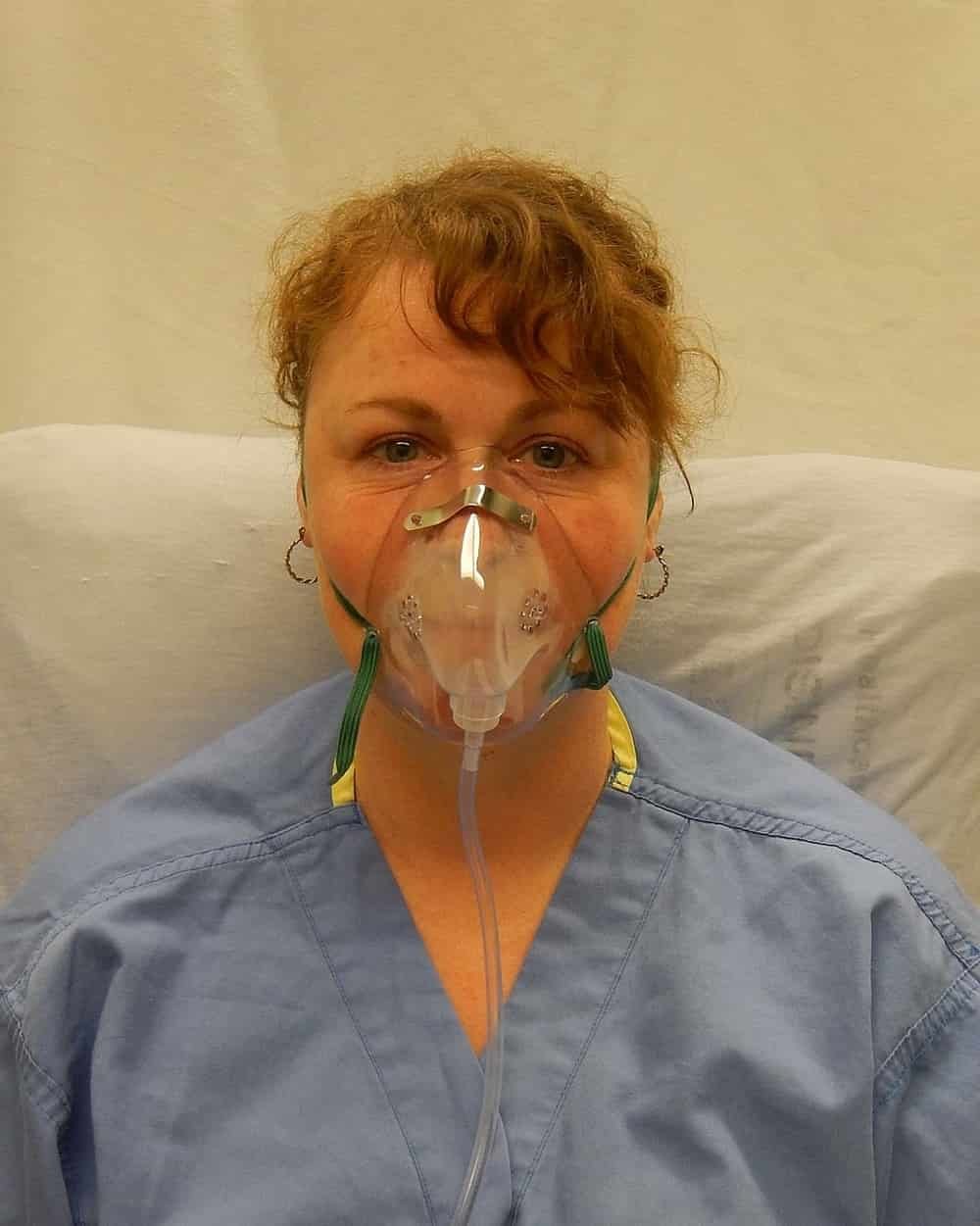
- an oxygen mask, covering the nose and mouth, to supply oxygen to the lungs;
- an endotracheal intubation tube, inserted through the mouth or through the nose, to maintain mechanical ventilation;
- a tracheostomy cannula, which is a tube placed at the level of the trachea by surgery to ensure breathing;
- a hyperbaric oxygen chamber, which is used in particular to provide oxygen in the event of carbon monoxide poisoning
Sources: Michigan Medicine, WHO
Source of photo: Wikimedia Commons