Genetic Diseases
While almost all genetic diseases are rare diseases, not all rare diseases are genetic. About 80% of rare diseases have a genetic origin and 90% of genetic diseases are rare.
What is a genetic disease?
Genetic diseases are pathologies due to abnormalities of genes or chromosomes. Some genetic abnormalities can be passed on to offspring; these genetic diseases are then family diseases. These are rare diseases that can appear at birth (or even in utero), or sometimes later in life. It is estimated that there are 8,000 to 10,000 genetic diseases.
In humans, it is estimated that there are between 20,000 and 30,000 genes. When, by chance, a genetic abnormality appears in one of these genes, its protein will be modified or will not be manufactured. However, it is essential for the functioning of our body.
What is the difference between DNA, genes and chromosomes?
The human body consists of 70,000 billion cells. Cells are the basic unit of living things. They have different functions and shapes. There are also gametes (sperm in men and eggs in women) which are the cells responsible for sexual reproduction.
The control center of the cell is the nucleus. Each nucleus of our cells contains the genetic heritage of each human being formed by 23 pairs of chromosomes (i.e. 46 chromosomes per person). Twenty-two of these pairs, the autosomes, are common to both sexes. The two remaining chromosomes are the sex chromosomes (XX for females and XY for males).
At the time of fertilization, the future child receives half of the genetic heritage of the father (23 chromosomes) and half of the genetic heritage of the mother (23 chromosomes). It is chance that determines this mixture of chromosomes.
The 46 chromosomes are formed by a filament: DNA (deoxyribunocleic acid). This filament looks like a spiral staircase called the double helix. This scale is made up of a sequence of interlocking elements called nucleotides. There are four types of nucleotides: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). The combination of these four letters out of 3 billion characters constitutes the genome, the encyclopedia where all the information necessary for the functioning of an individual is archived.
A gene is a piece of DNA with a specific function. It is the recipe allowing the production of a particular protein which will be responsible for a function of our body. Humans have around 20,000 genes.
None of us have exactly the same DNA. Each individual therefore has variations in their DNA. These variations make us different. However, when one of these genetic variations leads to a change in a protein that alters its function and can result in a disease, we speak of a pathogenic mutation.
Read also: Medical Genetics | The Key to Understand Chromosomes, DNA, Genes
How do you get a genetic diseases?
When a genetic disease results from an anomaly of a single gene, it is said to be monofactorial, or monogenic. In the same family, the mode of transmission of a monofactorial or monogenic genetic disease follows Mendel’s laws, which explains the use of the term “Mendelian disease”. 4 modes of transmission are defined for Mendelian diseases: autosomal or X-linked, depending on whether the gene involved is located on an autosomal chromosome or on the X chromosome; dominant or recessive, depending on whether the disease is dominant (a mutation in one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disease) or recessive (a mutation in each of the two copies of the gene is required to cause the disease).
1. What is autosomal dominant inheritance?
Some diseases are transmitted in a family according to the autosomal dominant mode. This means that a person inherits a normal copy of a gene and an abnormal copy of the same gene. However, the abnormal gene is dominant compared to the normal gene, in other words it is he who expresses himself. This explains that this person will be affected by a genetic disease. The particular characteristics of this genetic disease depend on the instructions that the abnormal gene will give to the organism.
Some dominant diseases occur from birth. Others appear only in adulthood. They are called “late”. Examples of dominant diseases are polycystic kidney disease and Huntington’s disease.
2. What is autosomal recessive inheritance?
Some diseases are transmitted in a family according to the autosomal recessive mode. This means that a person must inherit two defective copies of the same gene (one copy from each parent) to develop the genetic disease. If the person inherits only one defective copy and the other is normal, then in most cases that individual will be a healthy carrier of the gene change (mutation) because the normal copy of the gene compensates for the defective the abnormal copy. Being a healthy carrier means that you do not develop the disease, but carry an abnormal copy of the gene in the corresponding gene pair.
Examples of autosomal recessive diseases are cystic fibrosis or sickle cell disease.
3. What is X-linked inheritance?
The X chromosome contains several genes important for growth and development. The Y chromosome is much smaller and contains few genes. Women have two X chromosomes (XX) and if one of the genes on one of the X chromosomes is changed (mutated), the normal gene in the other X chromosome can compensate for its defect. In this case, the woman is a healthy carrier of the X-linked disease. Being a carrier means that you do not develop the disease, but that you carry a defective copy of the gene. Rarely, in some of these X-linked diseases, women may also show signs of the disease.
In men, if one gene on their single X chromosome is abnormal, the disease is expressed.
Examples of X-linked diseases are hemophilia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and fragile X syndrome. These diseases therefore often affect male subjects.
Am I suffering from a genetic disease?
Thanks to progress in genetics, it is possible to detect a genetic anomaly for a large number of these diseases, to know the mode of transmission of a genetic disease and to evaluate the risk of occurrence of this disease among the members of a family. These steps are carried out during a genetic counseling consultation in a genetics centre.
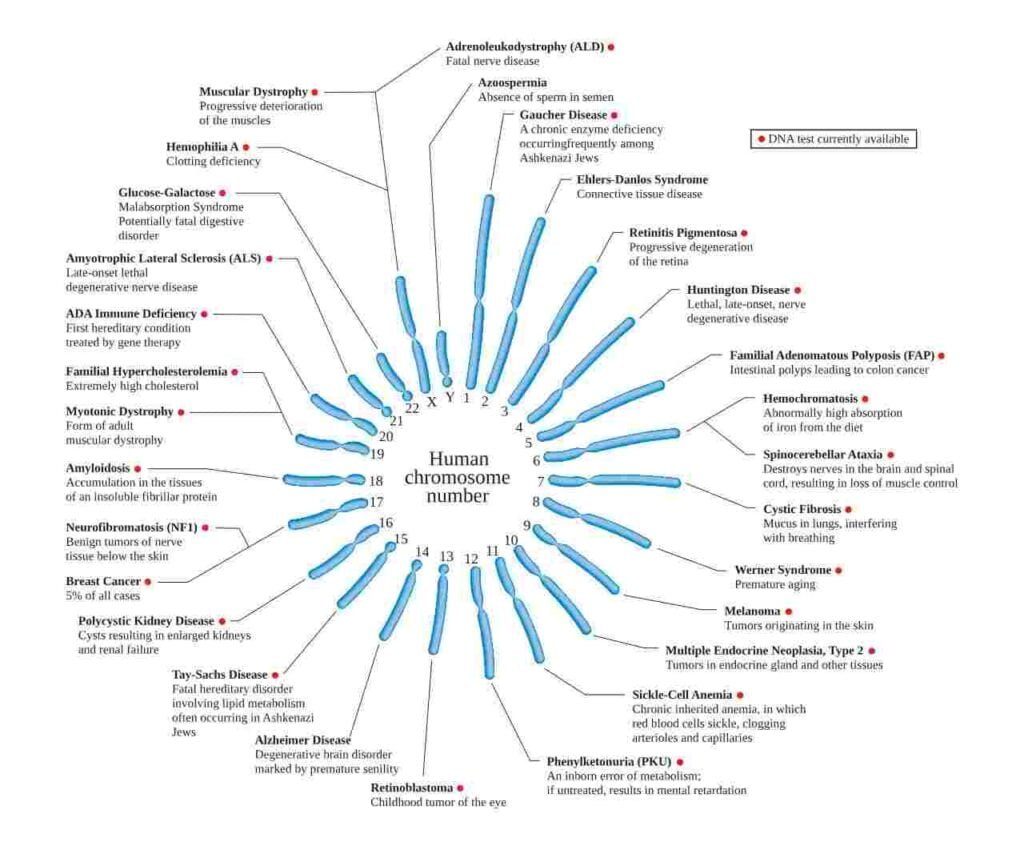
Zoom on examples of a disease located on each chromosome
Diagram of the human chromosome set, showing the location of some genes whose mutant forms cause hereditary diseases. Conditions that can be diagnosed using DNA analysis are indicated by a red dot. Ігор Пєтков, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Examples of genetic diseases and their origins
There are approximately 6,000 genetic diseases in the world. Their causes are as diverse as the resulting symptoms. This article provides an overview of how six genetic diseases work. It shows that there is no genetic disease BUT a genetic disease with each its own particularities.
MUCOVISCIDOSE (Cystic fibrosis): AN AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE DISEASE
Description
It is the most frequent genetic disease in Western populations (1 newborn in approximately 4000). Cystic fibrosis (mucoviscidose) is an inherited genetic disease. It affects the cellular functioning of almost all organs such as the lungs, the ENT system, the digestive system, the pancreas, the liver and the bile ducts, as well as the reproductive organs.
Symptoms
Cystic fibrosis is a disease that affects the respiratory tract and the digestive system. The main symptoms are bronchial congestion, respiratory infections, digestive problems and male sterility. A deregulation of the transport of chlorine in the cells leads to an increase in the viscosity of the mucus: this accumulates in the respiratory and digestive tracts, which causes the symptoms.
Genetic origin
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disease, therefore transmitted by both parents at the same time. It is caused by a mutation in both copies of the CFTR gene, located on chromosome 7. The parents of an affected child are carriers of a single mutation, with no consequences for their own health. But each of their children has a 1 in 4 chance of inheriting the two parental mutations and therefore of being affected by the disease.
Cystic fibrosis manifestations. Maen K Abu Househ, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
NEUROFIBROMATOSIS TYPE 1: A DOMINANT DISEASE
Description
There are different types of neurofibromatosis. Type 1 is the most common and affects around 1 in 4,000 people. Neurofibromas are soft, flesh-like lumps that originate from nerve tissue.
Symptoms
The clinical manifestations vary greatly from one person to another, even within the same family. Skin manifestations of the “café-au-lait” type (dark spots on the skin) are the most frequent. Other possible symptoms include benign tumors of varying sizes (called neurofibromas), more or less disabling, located along the nerves or on the skin.
A small proportion of patients are affected by serious complications, mainly malignant tumours.
Genetic origin
Neurofibromatosis is an autosomal dominant disease, which means that even if only one of the two alleles of the gene is mutated, the person is sick. The risk for a person of transmitting the disease to their child is 1 in 2.
There is a high rate of spontaneous mutations (de novo mutation): thus, in half of the cases, neurofibromatosis type 1 appears without any family history (neither the father nor the mother are ill).
The causative gene is the NF1 gene located on chromosome 17.
Back of an elderly woman with neurofibromatosis type 1. Almazi, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
TRISOMY 21: A CHROMOSOME DISEASE
Description
Also called Down syndrome, trisomy 21 results from a chromosomal abnormality.
Symptoms
The usual consequences of trisomy 21 are a variable intellectual deficiency, a characteristic facial appearance (which does not prevent the child from having features resembling his parents); a decrease in muscle tone, malformations of variable importance, most often of the heart or the digestive system.
Genetic origin
Trisomy 21 results from a chromosomal abnormality caused by the presence of a third copy (complete or partial) of chromosome 21. It occurs without any family history in the vast majority of cases, often in connection with a high maternal age.
HEMOPHILIA: A DISEASE LINKED TO CHROMOSOME X
Description
Hemophilia mainly affects boys (about 1/5000). It is a hereditary hemorrhagic disease due to the absence or deficiency of a blood coagulation factor.
Symptoms
Hemophilia is the cause of spontaneous bleeding or bleeding following trauma, even minor ones. Joint bleeding (haemarthrosis) is responsible for pain and can lead to joint destruction.
Genetic origin
The hemophilia gene is located on the X chromosome, which explains the mode of transmission: only boys are affected because they have only one X chromosome, women carrying the mutation being only carriers. A female carrier can transmit her genetic anomaly with a probability of 1 in 2 to each of her children: one boy in two will be affected, one girl in two will be a carrier.
MYOPATHIES: MUSCLE DISEASES
Description
Myopathies are a group of neuromuscular diseases, the best known of which is Duchenne muscular dystrophy (1 in 3300 male newborns). But there are many others, of variable expression and transmission. Myopathy is a general term that designates diseases whose point is generally associated with impaired muscle function.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary in their manifestations and intensity depending on the type of myopathy. Generally, these diseases result in generalized muscle weakness. This often causes heart and respiratory problems.
Genetic origin
Each type of myopathy corresponds to a different deficient protein, playing a role in the production and functioning of muscles or in the junction between muscles and nerves. There are about a hundred different genes involved in myopathies: some are linked to the X chromosome, others are autosomal recessive or dominant.
Nervous and mental diseases. Method of rising from the ground in myopathy. Internet Archive Book Images, No restrictions, via Wikimedia Commons
SICKLE CELL DISEASE – GENETIK BLOOD DISORDERS
Description
Sickle cell disease is a genetic blood disease that particularly affects populations of African origin, approximately 50 million people worldwide.
It is characterized by an anomaly of the hemoglobin, contained by the red blood cells, which ensures the transport of oxygen to the tissues. The abnormal hemoglobin will cause deformation and abnormal rigidity of these blood cells.
Symptoms
Abnormal red blood cells are destroyed in excess, which is a source of chronic anemia. In addition, they tend to aggregate and clog blood vessels. These “vaso-occlusive crises” are painful and sources of infection.
Genetic origin
Sickle cell disease is an autosomal recessive disease: the person is sick only if they carry both mutated copies of the HBB (Hemoglobin Subunit Beta) gene. It is located on chromosome pair 11 and is responsible for coding one of the constituents of hemoglobin. If the parents of an affected child are carriers of a single mutation, each of their children has a probability of 1 in 4 of inheriting both parental mutations and therefore of being affected by the disease.
Figure (A) shows normal red blood cells flowing freely through a blood vessel. The inset shows a cross-section of a normal red blood cell with normal haemoglobin. Figure (B) shows abnormal, sickled red blood cells sticking at the branching point in a blood vessel. The inset image shows a cross-section of a sickle cell with long polymerized sickle haemoglobin (HbS) strands stretching and distorting the cell shape to look like a crescent moon. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Other genetic diseases
Genetic diseases are disorders caused by mutations or changes in an individual’s DNA. These mutations can affect various aspects of health and development. Here are some examples of genetic diseases along with brief explanations:
Certainly, let’s delve deeper into a few of the genetic diseases mentioned, including their causes, prevention strategies, and available treatments:
- Cystic Fibrosis:
- Cause: Cystic fibrosis is caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, which affects the production of a protein responsible for regulating the movement of salt and water in and out of cells. As a result, mucus becomes thick and sticky, clogging airways and leading to respiratory and digestive issues.
- Prevention: Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder, so prevention involves genetic counseling and testing for carriers before pregnancy. Prenatal testing can also help identify the condition in the fetus.
- Treatment: There is no cure for cystic fibrosis, but treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. This includes medications to thin mucus, respiratory therapies, and lung transplantation in severe cases.
- Huntington’s Disease:
- Cause: Huntington’s disease is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene, leading to the accumulation of a toxic protein in brain cells. This results in progressive damage to nerve cells.
- Prevention: Genetic testing can identify the presence of the mutation before symptoms appear. This information can help individuals make informed family planning decisions.
- Treatment: Currently, there is no cure for Huntington’s disease. Treatment aims to manage symptoms, such as movement disorders and psychiatric symptoms, with medications and therapies.
- Sickle Cell Anemia:
- Cause: Sickle cell anemia is caused by a mutation in the HBB gene, leading to the production of abnormal hemoglobin. This causes red blood cells to become misshapen, leading to blockages in blood vessels.
- Prevention: Carrier screening before pregnancy can help identify couples at risk of having a child with sickle cell anemia. Prenatal testing and genetic counseling are essential for at-risk couples.
- Treatment: Treatment includes managing pain, preventing infections, and maintaining healthy blood flow. Blood transfusions and bone marrow transplants can also be considered in severe cases.
- Down Syndrome:
- Cause: Down syndrome is caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. This leads to developmental and intellectual differences.
- Prevention: Down syndrome is not preventable since it is caused by a random genetic event during conception.
- Treatment: Early intervention programs, such as speech and physical therapy, can help individuals with Down syndrome reach their developmental milestones. Medical management focuses on addressing associated health issues.
- Phenylketonuria (PKU):
- Cause: PKU is caused by a mutation in the PAH gene, leading to an inability to break down the amino acid phenylalanine. High levels of phenylalanine can cause brain damage.
- Prevention: Early diagnosis through newborn screening allows for dietary management. A low-phenylalanine diet can prevent intellectual disability.
- Treatment: PKU can be managed by strictly adhering to a low-phenylalanine diet. Nutritional supplements and medical foods are often prescribed.
Preventing and treating genetic diseases often involve a combination of genetic counseling, prenatal testing, early diagnosis, and medical interventions tailored to each condition. It’s important to note that research into these conditions continues, and new treatments may become available in the future. Early detection and intervention play a crucial role in improving outcomes for individuals with genetic diseases.
- Muscular Dystrophy:
- Cause: Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic disorders characterized by the progressive weakening and wasting of muscles. Different types of muscular dystrophy are caused by mutations in various genes involved in muscle structure and function.
- Prevention: In many cases, muscular dystrophy is inherited, and carriers can undergo genetic testing before planning a pregnancy. Prenatal testing can also help identify affected fetuses.
- Treatment: While there is no cure, management focuses on maintaining mobility and quality of life. Physical therapy, mobility aids, and medications can help manage symptoms. Research into gene therapies and other treatments is ongoing.
- Fragile X Syndrome:
- Cause: Fragile X syndrome is caused by a mutation in the FMR1 gene, leading to a lack of a protein needed for normal brain development. It is the most common inherited cause of intellectual disability in males.
- Prevention: Genetic testing and counseling can help individuals understand their risk of passing on the condition to their children.
- Treatment: Treatment involves therapies to address developmental and behavioral challenges, including speech therapy, occupational therapy, and behavioral interventions. Medications can help manage specific symptoms.
- Tay-Sachs Disease:
- Cause: Tay-Sachs disease is caused by mutations in the HEXA gene, leading to the accumulation of a fatty substance in the brain and nerve cells. This causes progressive neurological deterioration.
- Prevention: Carrier testing and genetic counseling are important for couples with a family history of Tay-Sachs disease. Prenatal testing can help identify affected pregnancies.
- Treatment: There is no cure for Tay-Sachs disease. Treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life through supportive care and symptom-specific interventions.
- Hemophilia:
- Cause: Hemophilia is caused by mutations in genes that produce blood clotting factors. Without these factors, blood clotting is impaired, leading to prolonged bleeding and easy bruising.
- Prevention: Genetic testing can determine carrier status and guide family planning decisions.
- Treatment: Hemophilia is managed with clotting factor replacement therapy. This can involve regular infusions of clotting factors to prevent and treat bleeding episodes.
- Neurofibromatosis:
- Cause: Neurofibromatosis is caused by mutations in genes that regulate cell growth and division. This leads to the development of tumors on nerve tissue.
- Prevention: Genetic testing and counseling can help individuals understand their risk of passing on the condition. Regular medical monitoring is important for early detection of complications.
- Treatment: Treatment varies based on the type and severity of neurofibromatosis. It may involve surgery to remove tumors, medication to manage symptoms, or other interventions.
- Color Blindness:
- Cause: Color blindness is caused by mutations in genes that encode photopigments in the eye’s cone cells. These mutations affect the perception of certain colors.
- Prevention: Color blindness is typically inherited. Genetic testing can provide information about an individual’s color vision status.
- Treatment: Currently, there is no cure for color blindness. However, special glasses and apps have been developed to help individuals with color vision deficiencies distinguish between colors.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD):
- Cause: PKD is caused by mutations in genes that regulate kidney cell growth. It leads to the development of fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys.
- Prevention: Genetic testing and counseling can help assess the risk of passing on PKD to children. Regular medical check-ups and monitoring are essential for early detection.
- Treatment: Treatment involves managing symptoms and complications such as high blood pressure and kidney infections. In severe cases, kidney transplantation may be necessary.
- Marfan Syndrome:
- Cause: Marfan syndrome is caused by mutations in the FBN1 gene, which affects the connective tissues. This can lead to a variety of skeletal, cardiovascular, and ocular issues.
- Prevention: Genetic testing and counseling can help identify individuals at risk of Marfan syndrome. Early diagnosis and management are crucial.
- Treatment: Treatment involves managing specific symptoms and complications. Medications to control blood pressure and surgical interventions to repair aortic aneurysms are often used.
- Turner Syndrome:
- Cause: Turner syndrome is caused by the absence or partial deletion of one X chromosome in females. It leads to developmental and physical differences.
- Prevention: Turner syndrome is not preventable since it is caused by a random genetic event during conception.
- Treatment: Treatment includes growth hormone therapy to improve height, hormone replacement therapy to induce puberty, and addressing associated medical issues.
- Progeria (Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome):
- Cause: Progeria is caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene, leading to rapid aging and various health problems in children.
- Prevention: Progeria is extremely rare and not usually inherited. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis.
- Treatment: Management focuses on addressing symptoms and complications, such as cardiovascular issues. Research into potential treatments is ongoing.
-
Albinism:
- Cause: Albinism is caused by mutations in genes that affect the production of melanin, resulting in little to no skin, hair, or eye color.
- Prevention: Albinism is typically inherited. Genetic counseling can help families understand the inheritance pattern and risks.
- Treatment: Treatment involves managing visual impairments, protecting the skin from sun exposure, and addressing any associated health concerns.
Advancements in genetic science continue to shed light on the underlying causes of these genetic diseases. While many genetic conditions currently lack definitive cures, ongoing research offers hope for improved treatments and interventions in the future. Early detection, proactive management, and a multidisciplinary approach involving medical professionals, genetic counselors, and support networks can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with genetic diseases.
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS):
- Cause: ALS is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Mutations in genes such as SOD1 can contribute to the development of the disease.
- Prevention: While the exact cause is complex and not fully understood, avoiding known risk factors and maintaining a healthy lifestyle may help reduce the risk.
- Treatment: There is no cure for ALS, but treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Supportive care, physical therapy, and assistive devices are often used.
- Gaucher Disease:
- Cause: Gaucher disease is caused by mutations in the GBA gene, leading to the buildup of a fatty substance in cells. This can result in various symptoms affecting the liver, spleen, bones, and nervous system.
- Prevention: Genetic testing and counseling can help identify carriers and guide family planning decisions.
- Treatment: Enzyme replacement therapy is available to help break down the accumulated fatty substance. Other therapies focus on managing specific symptoms and complications.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD):
- Cause: DMD is caused by mutations in the DMD gene, leading to the absence of a protein called dystrophin. This results in progressive muscle weakness and loss.
- Prevention: Genetic testing can identify carrier status and help with family planning decisions.
- Treatment: While there is no cure, interventions such as physical therapy, orthopedic devices, and medications can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Research into gene therapies is ongoing.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA):
- Cause: SMA is caused by mutations in the SMN1 gene, which affects motor neurons in the spinal cord. This leads to muscle weakness and atrophy.
- Prevention: Carrier testing and genetic counseling are important for couples with a family history of SMA.
- Treatment: A breakthrough treatment called gene therapy has been developed for SMA. This therapy aims to replace the missing or defective SMN1 gene and has shown significant improvements in motor function in affected individuals.
- Prader-Willi Syndrome:
- Cause: Prader-Willi syndrome is caused by a genetic abnormality involving chromosome 15. It leads to developmental and behavioral challenges, as well as an insatiable appetite and obesity.
- Prevention: Prader-Willi syndrome is not preventable, as it typically arises from a random genetic event during conception.
- Treatment: Management involves addressing the physical, developmental, and behavioral aspects of the syndrome. A multidisciplinary approach, including nutritional and behavioral interventions, is essential.
- Rett Syndrome:
- Cause: Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in the MECP2 gene, affecting brain development and leading to severe cognitive and motor impairments.
- Prevention: Rett syndrome is typically not inherited, as it often occurs sporadically.
- Treatment: There is no cure for Rett syndrome, but supportive care, therapies (such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy), and medications can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
These examples showcase the diversity of genetic diseases, their underlying causes, and the different approaches to prevention and treatment. As our understanding of genetics continues to evolve, so too do the possibilities for improved therapies and interventions for individuals affected by these conditions.
- Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia (SED):
- Cause: SED refers to a group of genetic disorders that affect bone and cartilage growth, leading to skeletal abnormalities and short stature.
- Prevention: Genetic counseling can help families understand the inheritance pattern and assess the risk of passing on the condition.
- Treatment: Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and complications, which may include orthopedic interventions, physical therapy, and pain management.
- Hemochromatosis:
- Cause: Hemochromatosis is caused by mutations in genes that regulate iron absorption. It leads to excessive iron accumulation in the body’s organs.
- Prevention: Genetic testing and counseling can help identify individuals at risk. Regular monitoring of iron levels and therapeutic phlebotomy (removing excess blood) are often used.
- Treatment: Treatment involves reducing iron levels through phlebotomy or chelation therapy. Dietary adjustments and management of complications are also important.
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia:
- Cause: Familial hypercholesterolemia is caused by mutations in genes involved in regulating cholesterol levels. It leads to high levels of LDL (“bad”) cholesterol in the blood.
- Prevention: Genetic testing can help identify individuals with the condition and guide management strategies.
- Treatment: Treatment includes lifestyle changes (diet, exercise) and medications to lower cholesterol levels. Statins and other cholesterol-lowering drugs are commonly used.
- Friedreich’s Ataxia:
- Cause: Friedreich’s ataxia is caused by mutations in the FXN gene, leading to impaired mitochondrial function and neurodegeneration. It results in progressive loss of coordination and muscle strength.
- Prevention: Genetic testing and counseling can provide insight into carrier status and potential risks.
- Treatment: Currently, there is no cure for Friedreich’s ataxia. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and complications, such as physical therapy, mobility aids, and medications.
- Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP):
- Cause: XP is caused by mutations in genes involved in DNA repair mechanisms. It leads to extreme sensitivity to UV radiation and a high risk of skin cancer.
- Prevention: Protection from sun exposure is crucial for individuals with XP.
- Treatment: Treatment involves strict sun protection measures, including protective clothing, sunscreen, and avoiding sunlight. Regular skin cancer screenings are important.
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency:
- Cause: Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is caused by mutations in the SERPINA1 gene, leading to insufficient production of a protein that protects the lungs and liver.
- Prevention: Genetic testing can help identify carriers and those at risk. Avoiding smoking and environmental lung irritants is recommended.
- Treatment: Management includes lifestyle modifications, lung and liver disease management, and augmentation therapy to provide additional alpha-1 antitrypsin protein.
Each of these genetic diseases presents unique challenges, and ongoing research and medical advancements are continuously improving our understanding and ability to manage these conditions. Genetic counseling, early diagnosis, and a comprehensive care plan involving healthcare professionals are crucial components of addressing the needs of individuals with genetic diseases.
- Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD):
- Cause: MSUD is caused by mutations in genes that affect the breakdown of certain amino acids. Without proper breakdown, these amino acids accumulate and can cause neurological problems.
- Prevention: Early diagnosis through newborn screening is essential. A special diet low in the problematic amino acids can prevent symptoms.
- Treatment: Treatment involves strict adherence to a special diet and close monitoring of blood amino acid levels. If managed properly, individuals with MSUD can lead relatively normal lives.
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI):
- Cause: OI is caused by mutations in genes that affect collagen production, leading to brittle bones that break easily.
- Prevention: Genetic testing can provide information about the risk of passing on OI. Prenatal testing can help diagnose the condition in the fetus.
- Treatment: Management includes fracture prevention, physical therapy, and medications to strengthen bones. Supportive care and surgeries may be necessary for severe cases.
- Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD):
- Cause: BMD is caused by mutations in the DMD gene, similar to Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). However, BMD is typically milder in its progression.
- Prevention: Similar to DMD, genetic testing and counseling are important for families with a history of the disorder.
- Treatment: Management focuses on maintaining mobility and quality of life. Physical therapy, medication, and assistive devices can help manage symptoms.
- Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS):
- Cause: FXTAS is caused by a mutation in the FMR1 gene, similar to Fragile X syndrome. However, FXTAS affects older individuals and is characterized by tremors and problems with movement and balance.
- Prevention: Genetic counseling and testing can provide information about the risk of developing FXTAS.
- Treatment: Management involves addressing symptoms such as tremors and ataxia through medications and therapies.
- Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS):
- Cause: MPS refers to a group of genetic disorders characterized by the buildup of complex carbohydrates (mucopolysaccharides) in cells. Various gene mutations can cause different types of MPS.
- Prevention: Genetic testing can identify carriers and help with family planning decisions.
- Treatment: Treatment varies depending on the specific type of MPS and may include enzyme replacement therapy, bone marrow transplantation, and supportive care.
- Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome:
- Cause: Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is caused by mutations in the HPRT1 gene, leading to the absence of an enzyme necessary for purine metabolism. This results in neurological and behavioral symptoms.
- Prevention: Genetic testing and counseling can help identify carriers and assess the risk of having an affected child.
- Treatment: Management focuses on addressing symptoms, including behavioral interventions and medications. Quality of life improvements can be achieved with a multidisciplinary approach.
Medical Genetics | The Key to Understand Chromosomes, DNA, Genes
Sources: PinterPandai, MedlinePlus, eMedicineHealth.com (Owned and Operated by WebMD), National Human Genome Research Institute, Johns Hopkins Health System
Photo credit (main picture): Ігор Пєтков, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Photo description: diagram featuring examples of a disease located on each chromosome.