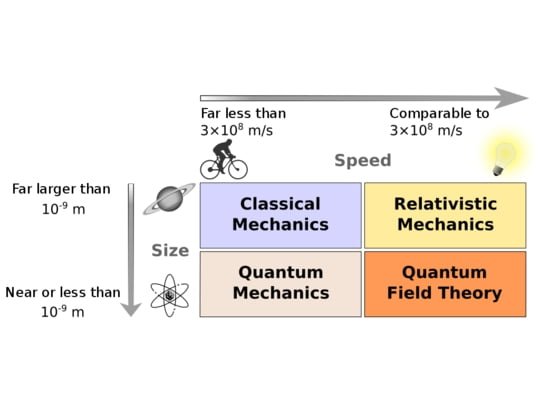
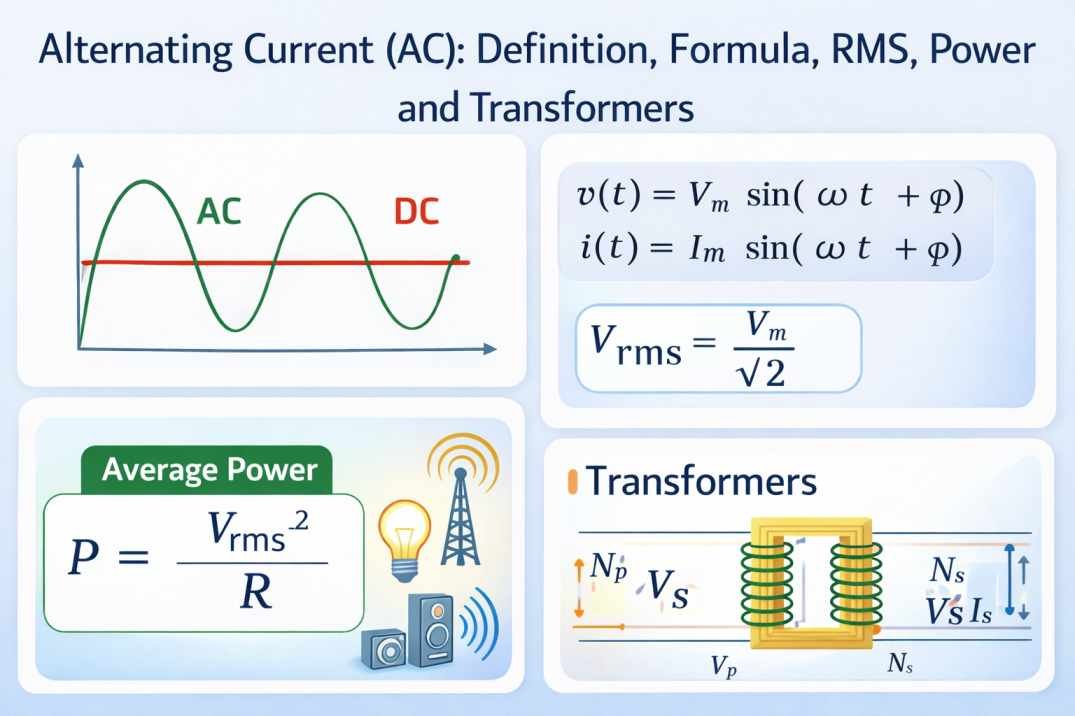
Physics Research Fields
Contemporary physics research fields are divided into various disciplines that study different aspects of the physical world.
They can be broadly divided into nuclear and particle physics; condensed matter physics; atomic, molecular, and optical physics; astrophysics; and applied physics. Some physics departments also support physics education research and physics outreach.
You can fing major fields of physics, along with their subfields and the theories and concepts they employ, are shown below.
| Field / Physics Research fields | Subfields | Major theories | Concepts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nuclear and particle physics | Nuclear physics, Nuclear astrophysics, Particle physics, Astroparticle physics, Particle physics phenomenology | Standard Model, Quantum field theory, Quantum electrodynamics, Quantum chromodynamics, Electroweak theory, Effective field theory, Lattice field theory, Lattice gauge theory, Gauge theory, Supersymmetry, Grand Unified Theory, Superstring theory, M-theory | Fundamental force (gravitational, electromagnetic, weak, strong), Elementary particle, Spin, Antimatter, Spontaneous symmetry breaking, Neutrino oscillation, Seesaw mechanism, Brane, String, Quantum gravity, Theory of everything, Vacuum energy |
| Atomic, molecular, and optical physics | Atomic physics, Molecular physics, Atomic and molecular astrophysics, Chemical physics, Optics, Photonics | Quantum optics, Quantum chemistry, Quantum information science | Photon, Atom, Molecule, Diffraction, Electromagnetic radiation, Laser, Polarization (waves), Spectral line, Casimir effect |
| Condensed matter physics | Solid-state physics, High-pressure physics, Low-temperature physics, Surface physics, Nanoscale and mesoscopic physics, Polymer physics | BCS theory, Bloch’s theorem, Density functional theory, Fermi gas, Fermi liquid theory, Many-body theory, Statistical mechanics | Phases (gas, liquid, solid), Bose–Einstein condensate, Electrical conduction, Phonon, Magnetism, Self-organization, Semiconductor, superconductor, superfluidity, Spin, |
| Astrophysics | Astronomy, Astrometry, Cosmology, Gravitation physics, High-energy astrophysics, Planetary astrophysics, Plasma physics, Solar physics, Space physics, Stellar astrophysics | Big Bang, Cosmic inflation, General relativity, Newton’s law of universal gravitation, Lambda-CDM model, Magnetohydrodynamics | Black hole, Cosmic background radiation, Cosmic string, Cosmos, Dark energy, Dark matter, Galaxy, Gravity, Gravitational radiation, Gravitational singularity, Planet, Solar System, Star, Supernova, Universe |
| Applied physics | Accelerator physics, Acoustics, Agrophysics, Atmospheric physics, Biophysics, Chemical physics, Communication physics, Econophysics, Engineering physics, Fluid dynamics, Geophysics, Laser physics, Materials physics, Medical physics, Nanotechnology, Optics, Optoelectronics, Photonics, Photovoltaics, Physical chemistry, Physical oceanography, Physics of computation, Plasma physics, Solid-state devices, Quantum chemistry, Quantum electronics, Quantum information science, Vehicle dynamics | ||
Source: Stanford University
Photo credit: Wikimedia Commons